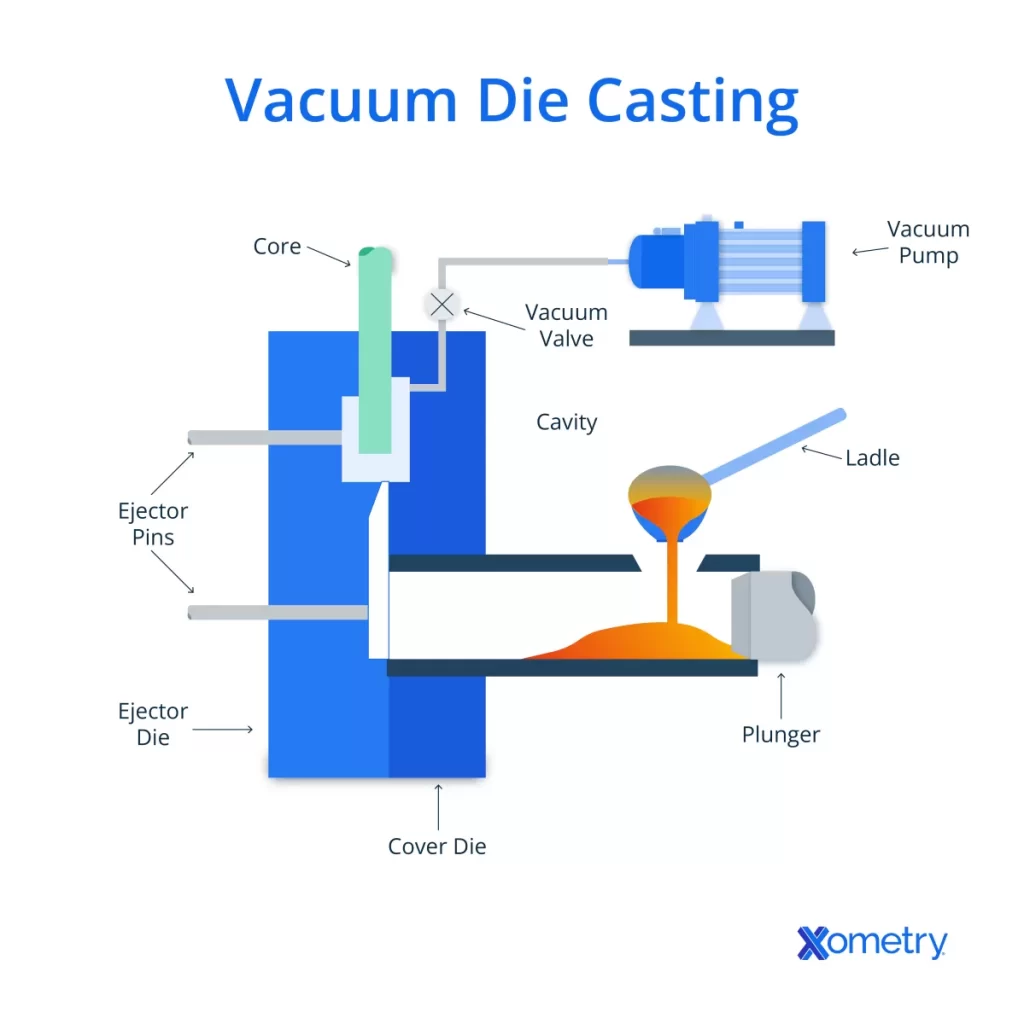
Are you wondering what is vacuum casting and how it can transform your prototyping process? Choosing the right manufacturing method can make or break your product development timeline and budget.
As a leader in CNC machining and prototyping, HYCNC knows that vacuum casting is a game-changer for creating high-quality, cost-effective parts. In this guide, we’ll break down the vacuum casting process, explore its benefits, and show you why it’s the go-to choice for industries like automotive, medical, and consumer goods.
Ready to discover how vacuum casting can bring your ideas to life? Let’s dive in!
Understanding Vacuum Casting Definition and Basics
Vacuum casting is a manufacturing process used to create high-quality plastic parts by pouring liquid polyurethane resin into a silicone mold under vacuum conditions. This method is popular for producing precise prototypes and low-volume production parts with excellent surface finishes.
Key components of vacuum casting
- Master model: A high-detail original part, usually made by CNC machining or 3D printing, which serves as the basis for the silicone mold.
- Silicone mold: Made by encasing the master model in silicone rubber, it captures fine details and can be reused multiple times.
- Polyurethane resin: The liquid material poured into the mold to form the final part.
- Vacuum chamber: Used to remove air bubbles and ensure the resin fills all mold cavities accurately.
How vacuum casting differs from other methods
Unlike injection molding, which requires expensive steel molds and large production volumes, vacuum casting uses flexible silicone molds that are much cheaper and ideal for small runs. The vacuum environment reduces trapped air, resulting in parts with fewer defects and smoother surfaces compared to traditional casting methods. It also offers faster turnaround than processes like metal casting or 3D printing for similar applications.
Brief history of vacuum casting evolution
Vacuum casting developed alongside advances in silicone materials and polyurethane resins during the 20th century. Originally used primarily for prototype manufacturing, it has grown into a versatile technology due to improved vacuum systems and mold materials. Today, it supports rapid prototyping and retooling needs across many industries, bridging the gap between quick 3D printed models and more expensive injection-molded production parts.
Visual suggestion: Include a simple diagram showing the master model, silicone mold setup inside the vacuum chamber, and pouring of resin to illustrate the vacuum casting basics.
Ready to create precise prototypes or low-volume parts? Check out how vacuum casting fits your manufacturing needs. For detailed insights into CNC machining, visit our page on what is CNC machining.
The Vacuum Casting Process Step-by-Step
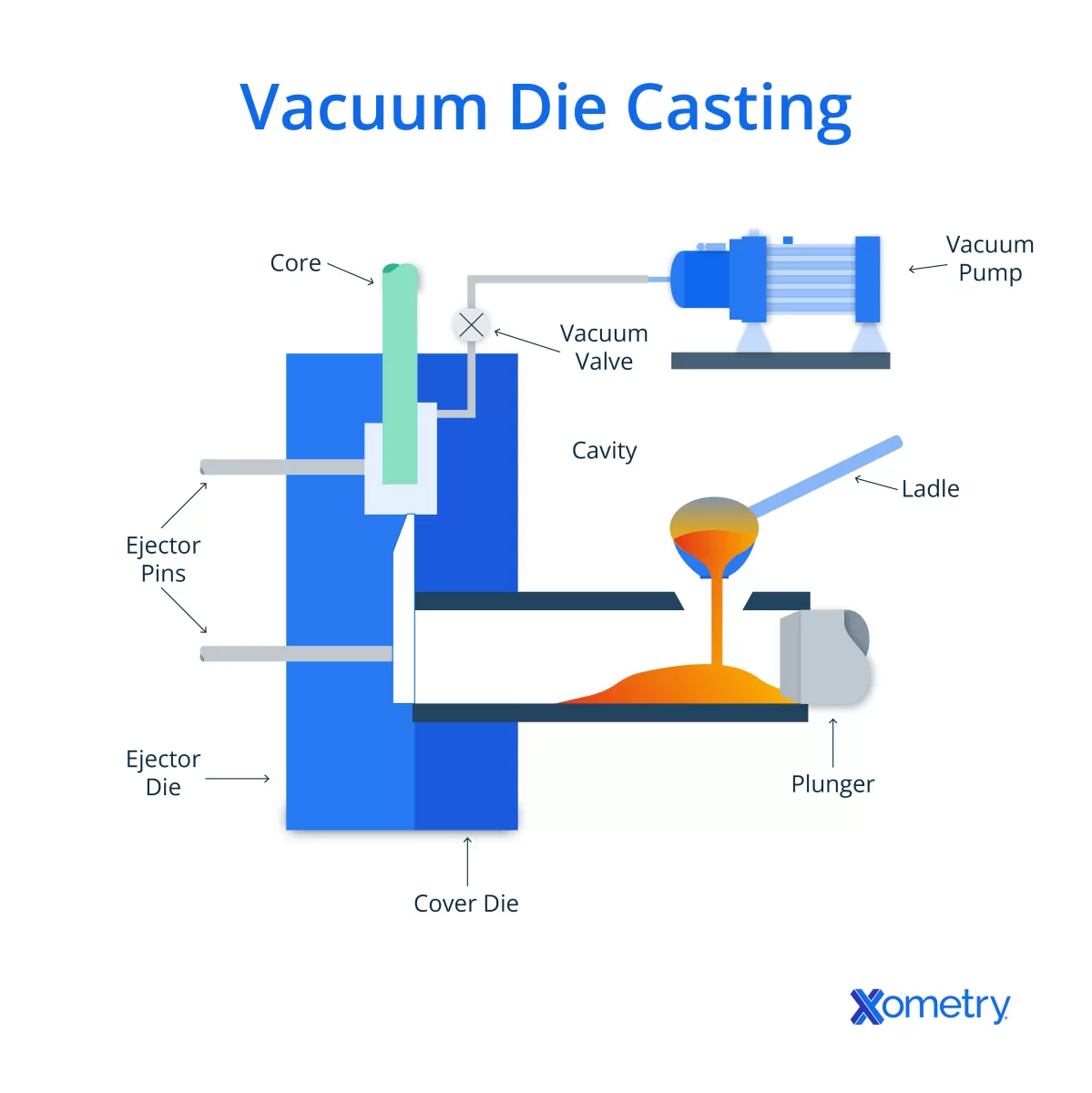
Vacuum casting starts with creating a high-quality master model. This model acts as the original shape for your parts and is usually made using CNC machining or 3D printing. Precision here is key because any small flaw will transfer to the final product.
Next, we build a silicone mold around the master model. Silicone is flexible, allowing easy removal without damaging the mold or the model. Once the silicone cures, the master model is carefully removed, leaving a perfect cavity for casting.
Then comes the pouring phase. Polyurethane resin is poured into the silicone mold under vacuum conditions. The vacuum sucks out all the air bubbles, resulting in parts with excellent surface finish and no internal voids. This step ensures high precision and durability.
After pouring, the resin is left to cure. The curing time varies based on the material but typically lasts a few hours. Once hardened, the part is demolded by peeling back the silicone mold carefully.
Finally, post-processing adds the finishing touches. This can include trimming excess material, sanding, or painting to enhance the part’s appearance and functionality.
This step-by-step vacuum casting process allows for rapid prototyping and low-volume production with great detail and finish.
Materials Used in Vacuum Casting

Vacuum casting mainly uses polyurethane resins, which are popular because they mimic the look and feel of real plastic parts. These resins come in various formulas depending on your needs, from flexible to rigid, clear to colored, and even impact-resistant options. This makes polyurethane casting great for producing parts that need to perform like the final product.
Besides common polyurethane, there are specialty materials available that offer unique properties like increased heat resistance, UV stability, or enhanced toughness. These options help when your prototype or low-volume part needs to handle specific conditions.
One big plus is material customization. You can tweak resin blends to match your part’s weight, color, texture, or mechanical properties. Plus, some resins can be filled with additives like glass fibers for extra strength.
This range of materials and customization means vacuum casting can serve a variety of industries, from automotive prototypes to medical device parts, delivering parts that look and function almost like those made with injection molding.
Benefits of Vacuum Casting
Vacuum casting offers several advantages, especially for businesses and individuals looking for efficient prototype manufacturing or low-volume production. Here are some of the main benefits:
Cost-effectiveness for Low-Volume Production
Vacuum casting is a smart choice when you don’t need thousands of parts. Making silicone molds is much cheaper than investing in metal tooling for injection molding, saving you a lot upfront. This keeps your overall costs down while still delivering quality parts.
High Precision and Surface Finish
This method captures fine details from your master model because the vacuum helps remove air bubbles during the resin pour. The result? Parts with smooth surfaces and crisp edges, ideal for functional prototypes or presentation models.
Fast Turnaround Times
Compared to traditional methods, vacuum casting is quicker. You can move from design to a physical prototype in just a few days. This speed is perfect for projects with tight deadlines where you need feedback fast.
Material Versatility
Vacuum casting works mainly with polyurethane resins, but these come in many varieties. You can choose from flexible, rigid, or high-strength materials, customizing parts to fit specific needs like durability or appearance.
Reusability of Silicone Molds
Silicone molds used in vacuum casting can be reused multiple times—usually 20 to 30 times—before they wear out. This reusability makes it easier and more affordable to produce small batches without remaking molds constantly.
Overall, vacuum casting strikes a great balance between quality, speed, and cost, making it a go-to option for many industries needing high-precision parts without the expense of large-scale manufacturing.
Limitations of Vacuum Casting
While vacuum casting is great for many applications, it does have some limits you should know about.
Mold lifespan and part quantity limits
Silicone molds used in vacuum casting typically last between 20 to 30 casting cycles. This makes vacuum casting ideal for low-volume production, but not for large-scale runs. Once the mold wears out, you need to remake it, which adds cost and time.
Unsuitability for high temperature or pressure materials
Vacuum casting works best with polyurethane resins and similar materials that cure at low temperatures and pressures. It’s not suited for casting metals or plastics that require high heat or pressure, unlike processes such as die casting or injection molding.
Defect risks from flawed master models
The quality of the final parts depends heavily on the master model. If the master has defects or inaccuracies, those flaws show up in every cast. That means you need a high-quality master, often made through CNC machining or high-res 3D printing.
Comparison to injection molding for large scale production
Injection molding is typically more cost-effective and efficient for large-scale manufacturing. Its metal molds last much longer, supporting thousands of parts with consistent quality. Vacuum casting can’t compete here, but it’s an excellent bridge between prototyping and mass production.
For more on manufacturing methods and when to pick each, you can check our posts on what is investment casting and zinc die casting vs aluminum die casting.
Applications of Vacuum Casting Across Industries
Vacuum casting is widely used across various industries thanks to its ability to produce high-precision parts quickly and cost-effectively. Here are some key applications:
Automotive prototypes and components
Vacuum casting is perfect for making prototype parts like dashboards, interior panels, and small mechanical components. It helps car makers test designs before committing to expensive tooling for large-scale production.
Medical device manufacturing
The medical field benefits from vacuum casting for custom parts and prototypes used in devices. The process allows for detailed, biocompatible plastic parts that meet tight standards without costly upfront investments.
Consumer goods examples
From appliances to electronics, vacuum casting helps create smooth, detailed prototypes and limited runs of plastic parts. It’s great for design validation and small-batch production in the consumer market.
Aerospace precision parts
Vacuum casting supports aerospace by producing lightweight, precision plastic components that require fine surface finishes. It’s used for parts that need to match strict specs without the need for metal casting.
Industry-specific tailored solutions
Many other industries—from agriculture to sports equipment—lean on vacuum casting to quickly and affordably produce parts that fit their unique needs. The process is flexible enough for custom materials and complex designs.
Vacuum casting’s mix of speed, cost-effectiveness, and precision makes it a go-to solution for prototypes and low-volume production across the U.S. manufacturing landscape.
Vacuum Casting vs Other Manufacturing Methods
When deciding on a manufacturing method, it helps to compare vacuum casting with popular alternatives like injection molding, 3D printing, and die casting. Here’s a quick breakdown:
Vacuum Casting vs Injection Molding
- Cost: Vacuum casting has lower upfront costs since it uses silicone molds, making it ideal for small to medium batches. Injection molding requires expensive steel molds, best for large-scale runs.
- Scalability: Injection molding is better for high-volume production, offering faster cycle times and consistent output. Vacuum casting suits low-volume projects, especially prototypes and limited runs.
- Lead time: Vacuum casting molds take less time to make, speeding up project delivery compared to injection molding.
Vacuum Casting vs 3D Printing
- Detail and finish: Vacuum casting produces parts with smoother surfaces and higher quality finishes than most 3D prints.
- Material options: It uses real polyurethane resins that mimic final-use plastics, while 3D printing materials are often limited and less durable.
- Speed and cost: 3D printing is great for quick prototypes but can get pricey for larger batches. Vacuum casting balances speed with the ability to produce several identical parts economically.
Vacuum Casting vs Die Casting
- Materials: Vacuum casting is designed for plastics and polymers, while die casting involves metals like aluminum or zinc.
- Part complexity: Both methods handle complex shapes well, but die casting suits metal parts requiring strength and heat resistance.
- Cost and volume: Die casting has high setup costs, favorable only for mass production. Vacuum casting remains cost-effective at low volumes.
Table of Key Differences
| Feature | Vacuum Casting | Injection Molding | 3D Printing | Die Casting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best Volume Range | Low to medium | High | Very low to low | High |
| Mold Cost | Low (Silicone molds) | High (Steel molds) | None | Very High (Metal dies) |
| Material Types | Polyurethane resins | Thermoplastics | Various polymers | Metals |
| Surface Finish | High | High | Moderate | High |
| Lead Time | Short | Long | Very short | Long |
| Ideal Use | Prototyping, small runs | Mass production | Rapid prototyping | Metal parts production |
Understanding these differences can help you pick the right manufacturing technique based on your budget, volume needs, and final part specifications. Vacuum casting shines when you want high-quality, small-batch parts fast and affordably.
Design Tips for Successful Vacuum Casting
To get the best results from vacuum casting, keeping a few design basics in mind is key. Here’s what helps:
-
Account for material shrinkage
Most polyurethane resins shrink a little as they cure. To avoid parts coming out too small or misshapen, adjust your design dimensions slightly bigger upfront.
-
Maintain minimum wall thickness
Thin walls can cause weak spots or incomplete fills. Aim for at least 1.5 to 2 millimeters thickness to ensure strength and smooth casting.
-
Incorporate draft angles for easy mold release
Adding slight tapers (typically 1-3 degrees) on vertical surfaces helps the part pop out of the silicone mold without damage.
-
Use ribs and bosses for strength
Adding ribs reinforces flat areas prone to bending. Bosses provide sturdy points for screws or fasteners without risking cracking.
-
Get professional design support when needed
Working with experienced vacuum casting experts can help fine-tune your model for better mold life, less defect risk, and easier post-processing.
These tips help reduce defects and improve part quality, making vacuum casting a smooth and cost-effective process. For more on designing parts for manufacturing, check out our what is CNC machining guide.
Why Choose HYCNC for Vacuum Casting Services
When it comes to vacuum casting, HYCNC stands out because of our strong expertise in CNC machining and rapid prototyping. We know how critical precision is, and our team handles every detail to deliver parts that match your exact needs.
We offer fast lead times without compromising quality, helping you get your prototypes or small-batch parts quickly. Our pricing is competitive, making vacuum casting an affordable option for low-volume production runs in the U.S. market.
From the initial design stage to post-processing, HYCNC provides comprehensive support. Whether you need help with mold design, choosing the right polyurethane casting materials, or finishing your parts for the best surface finish, we’ve got you covered.
Ready to get started or need a consultation? Contact us today to discuss how HYCNC can help with your vacuum casting projects efficiently and reliably.