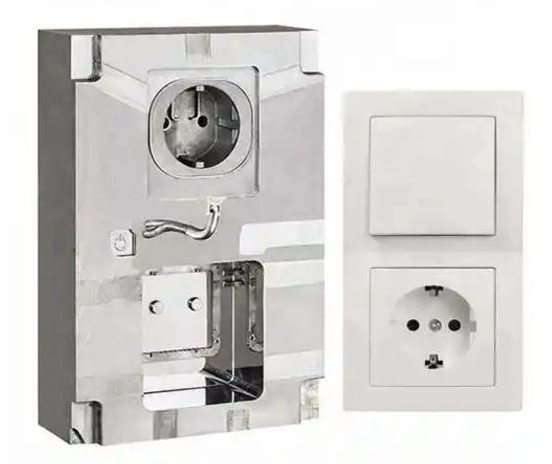
Understanding Zinc and Aluminum Die Casting
When deciding between zinc die casting and aluminum die casting, it helps to start with the basics—what each process involves, the materials used, and their defining characteristics. Both methods fall under precision die casting, a manufacturing process where molten metal is injected into a steel mold under high pressure. But the choice of alloy significantly affects the final product’s properties and suitability for specific applications.
What is Zinc Die Casting
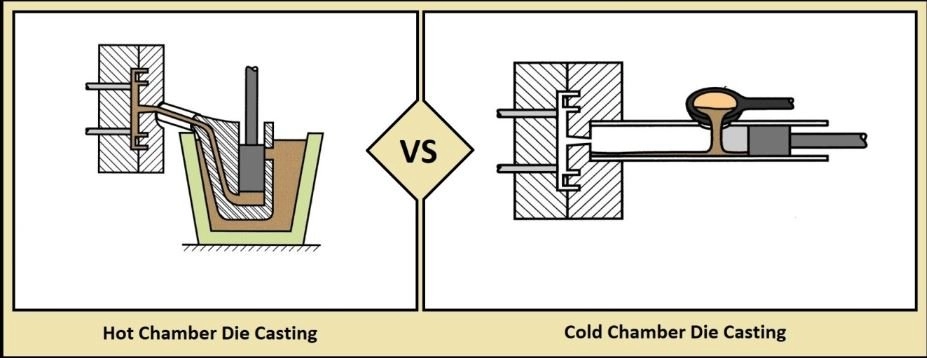
Zinc die casting uses zinc alloys, primarily Zamak 3, Zamak 5, and Zamak 7. These alloys are prized for their excellent flow characteristics, making them ideal for intricate designs and thin walls. Zinc’s ability to fill molds quickly is why hot chamber die casting is often the preferred method for zinc, offering faster cycle times and high productivity.
Key characteristics of zinc die casting include:
- High dimensional stability and excellent surface finish
- Good mechanical strength and impact resistance
- Superior corrosion resistance without extra coatings
- Excellent thermal and electrical conductivity
- Ability to produce complex shapes with tight tolerances
What is Aluminum Die Casting
Aluminum die casting involves alloys such as A380, A360, and ADC12. These aluminum alloys are popular for their lightweight nature combined with good structural strength. Aluminum typically requires cold chamber die casting due to its higher melting point, which involves a more controlled and slower process compared to zinc.
Key characteristics of aluminum die casting include:
- Lightweight with a high strength-to-weight ratio
- Good corrosion resistance, especially with protective coatings
- Better heat dissipation than zinc alloys
- Ability to handle moderate complexity and thin-walled parts
- Good surface finish and suitability for secondary machining
Why Compare Zinc and Aluminum Die Casting
Choosing between zinc and aluminum die casting comes down to matching material properties with product demands. Both are versatile and reliable but excel in different areas such as cost, strength, corrosion resistance, and casting complexity.
Understanding their unique advantages helps manufacturers and designers choose the right material and process for their project. Whether it’s electronics housings, automotive parts, or precision components, knowing when zinc or aluminum makes the most sense can save time, reduce costs, and improve product performance.
For a deeper dive into the die casting process, check out our detailed guide on what is die casting.
Key Differences Between Zinc and Aluminum Die Casting

When deciding between zinc die casting vs aluminum die casting, it helps to know their core differences. Here’s a quick rundown of how they compare on several important factors:
Mechanical Properties
- Zinc offers higher ductility and is great for parts that need strength and toughness with some flexibility.
- Aluminum is lighter and stiffer, making it a better fit for components where weight savings matter but strength is still needed.
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
- Aluminum outperforms zinc in both heat and electrical conductivity, which makes it ideal for parts like heat sinks and electrical housings.
- Zinc has lower thermal conductivity, so it’s less common for thermal management applications.
Corrosion Resistance
- Aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer, giving it good corrosion resistance, especially when anodized.
- Zinc corrodes easily in some environments but performs well with proper plating or coatings.
Melting Point and Casting Process
- Zinc melts at a lower temperature (around 787°F or 419°C), enabling faster production cycles, especially with hot chamber die casting.
- Aluminum melts higher (about 1220°F or 660°C) and often uses cold chamber die casting, which can be slower but handles bigger parts better.
Surface Finishing Options
- Both metals can take a variety of finishes such as powder coating, painting, and plating.
- Zinc generally offers smoother surfaces and finer detail for precision die casting parts.
- Aluminum’s finishes tend to be more durable in outdoor or high-wear environments.
Understanding these differences helps you pick the right die casting material based on your project’s needs for strength, weight, conductivity, and finishing.
Cost and Production Efficiency

When choosing between zinc die casting vs aluminum die casting, cost and production efficiency are big factors to consider.
Material Costs
Zinc is generally cheaper upfront compared to aluminum. Because zinc alloys have a lower melting temperature, they require less energy to melt, which can also reduce material-related costs. Aluminum alloys tend to cost more but offer benefits that can justify the premium, depending on the project.
Production Costs
Zinc uses hot chamber die casting, which is faster and more efficient for high-volume runs, lowering production costs. Aluminum requires cold chamber die casting, a slower process that can increase cycle times and add to labor and machine expenses. This makes zinc more attractive for large production runs where speed matters.
Tooling Life and Maintenance
Aluminum’s higher melting point means the tooling undergoes more wear and tear. This can lead to shorter tool life and more frequent maintenance, increasing costs over time. Zinc casting tools typically last longer because of the lower processing temperatures, meaning less downtime and fewer replacements.
Suitability for Production Volumes
- Zinc die casting is ideal for high-volume, precision parts thanks to fast cycles and durable tooling.
- Aluminum die casting works better for medium to large runs that require lightweight or corrosion-resistant parts but may have higher tooling costs.
Choosing the right process based on your production volume can help balance quality and budget efficiently.
Applications of Zinc and Aluminum Die Casting
Zinc Die Casting Applications
Zinc die casting is popular for parts that need excellent strength and precision without adding much weight. You’ll often find zinc components in:
- Automotive parts like door handles and steering wheels
- Electrical housings and connectors
- Hardware tools and fasteners
- Consumer electronics cases
Its ability to produce sharp, detailed designs makes it ideal where fine features matter. Plus, zinc’s natural corrosion resistance helps in outdoor and marine gear.
Aluminum Die Casting Applications
Aluminum die casting is a go-to for parts requiring lightweight strength and heat dissipation. Common uses include:
- Automotive engine blocks, brackets, and transmission cases
- Aerospace parts where weight cuts fuel costs
- Consumer electronics requiring thermal management like laptop frames
- Industrial machinery components
- Lighting fixtures and heat sinks
Its good thermal and electrical conductivity makes it perfect for electronics and heat-sensitive gear.
Industry Specific Case Studies
- Automotive: Zinc handles and brackets offer toughness and finish, but aluminum blocks and housings help shed pounds for better fuel economy.
- Electronics: Zinc shells protect devices with detailed, sturdy casings, while aluminum cases cool components effectively.
- Tools and Hardware: Zinc die casting lends strength to tools, while aluminum versions keep equipment light and easier to handle.
By matching zinc or aluminum to the job, manufacturers get the best of both worlds—performance and cost-efficiency tailored to specific needs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Zinc and Aluminum Die Casting
Advantages of Zinc Die Casting
- High precision and excellent surface finish making it ideal for detailed parts.
- Good strength and impact resistance for its weight.
- Low melting point means faster production and less wear on tools.
- Great for complex shapes thanks to its fluidity when molten.
- Good corrosion resistance without heavy coatings.
- Cost-effective for small to medium runs due to shorter cycle times.
Disadvantages of Zinc Die Casting
- Heavier than aluminum, which might not suit weight-sensitive applications.
- Lower thermal resistance, not great for high-temperature environments.
- Limited high-temperature strength compared to aluminum.
- Not ideal for very large parts due to material density and cost.
Advantages of Aluminum Die Casting
- Lightweight, making it excellent for automotive and aerospace parts.
- High strength-to-weight ratio for durable yet light components.
- Better corrosion resistance in harsh environments with proper alloys.
- Higher melting point means parts can handle more heat.
- Good electrical and thermal conductivity for certain applications.
- Suitable for larger parts and higher volume production.
Disadvantages of Aluminum Die Casting
- Higher melting temperature leads to longer cycle times and more tool wear.
- More expensive raw material compared to zinc.
- Surface finish may require more work to achieve the same smoothness as zinc.
- Lower fluidity than zinc can limit fine detail in complex molds.
Both zinc and aluminum die casting have clear strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these helps you pick the right metal for your project, balancing cost, performance, and production needs.
How to Choose Between Zinc and Aluminum Die Casting
Choosing between zinc die casting and aluminum die casting depends on several factors based on your project needs. Here’s what to consider:
Factors to Consider
-
Mechanical Requirements
Think about strength, hardness, and weight. Zinc offers higher density and great strength for smaller, more detailed parts. Aluminum is lighter and better suited for larger components that need to stay lightweight.
-
Thermal and Electrical Needs
Aluminum has better thermal and electrical conductivity, ideal for heat sinks or electrical parts. Zinc is less conductive but offers good stability.
-
Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum naturally resists corrosion better than zinc, especially outdoors or in harsh environments.
-
Production Volume and Cost
Zinc often costs less in large runs because of its lower melting point and faster cycle times. Aluminum tooling may last longer but can be pricier upfront.
-
Surface Finish and Details
Zinc can capture finer details and has excellent surface finish options. Aluminum may require more finishing but is easier to machine afterward.
Decision-Making Checklist
- What’s your part’s weight and strength requirement?
- Will the part be exposed to heat or electricity?
- Is the part used in a corrosive environment?
- What’s your budget for material and production?
- Are you producing a large volume or smaller batches?
- Do you need intricate details or smooth surface finishes?
Answering these questions will narrow down your best choice.
How HYCNC Can Help
At HYCNC, we guide you through selecting the right die casting material for your project. Whether it’s zinc die casting benefits you want to leverage or aluminum die casting advantages, we ensure the choices fit your design, cost goals, and timelines.
With deep experience in both hot chamber die casting for zinc and cold chamber methods for aluminum, we offer tailored solutions along with precision CNC machining to finish parts just right. Visit our die casting services page to learn how we make your project easier and more efficient.
We keep your needs front and center, balancing quality, cost, and speed to deliver parts that work for your U.S. market demands.
Why Choose HYCNC for Your Die Casting Needs
When it comes to zinc die casting vs aluminum die casting, having the right partner matters. At HYCNC, we offer comprehensive die casting services that cover everything from material selection to precision finishing. Whether you need zinc or aluminum casting, we handle your project with care and expertise.
Industry Experience and Certifications
We bring years of experience working with various die casting materials and processes, including hot chamber die casting and cold chamber die casting. Our team is fully certified and follows industry standards, ensuring consistent, high-quality results every time. This means your parts meet or exceed the requirements for performance and durability.
Customer-Centric Approach
At HYCNC, we put you first. Our goal is to make your production smooth and cost-effective. We work closely with you on design, prototyping, and production volumes to find the best balance between cost and quality. Plus, our local US-based support means faster communication and quicker turnaround, so your projects stay on schedule.
Learn more about our die casting services and how we can help you make the right material choice for your next project.