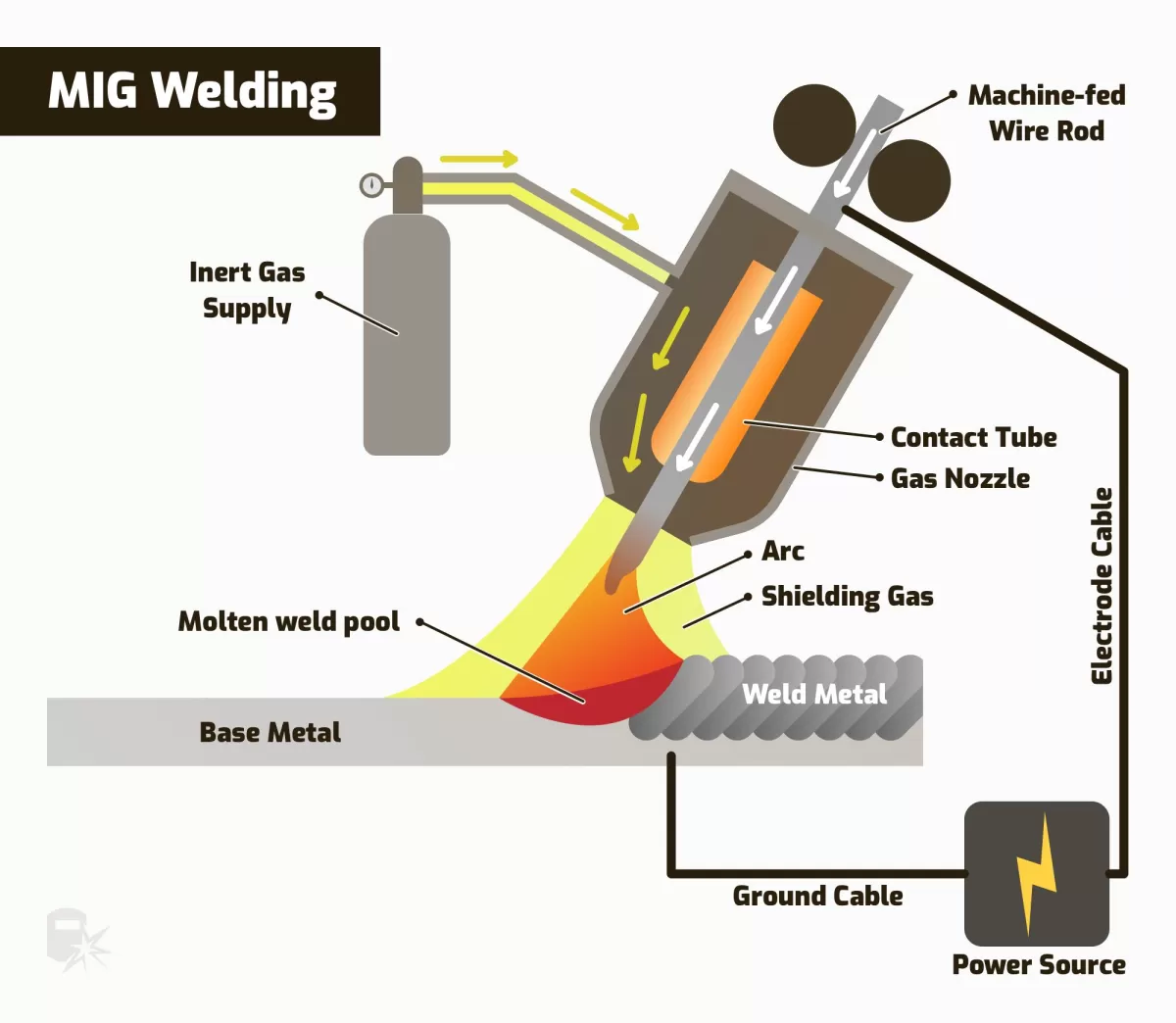
What is MIG Welding
MIG welding, or Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), is a widely used welding process that joins metals by feeding a continuous solid wire electrode through a welding gun. The wire melts and fuses with the base metals, while a shielding gas protects the weld area from contamination.
Key features of MIG welding include:
- Continuous wire feed for fast and consistent welding
- Shielding gas, typically argon or a mix of argon and CO2, to prevent oxidation
- Ease of use, making it suitable for beginners and high-volume projects
- Versatility to weld a variety of metals, including steel, aluminum, and stainless steel
MIG welding is commonly used in automotive repair, manufacturing, construction, and metal fabrication. Its speed and efficiency make it ideal for welding thicker materials and large projects that require strong, durable welds. Whether you’re working on structural steel or aluminum frames, MIG welding delivers reliable results with less cleanup needed.
What is TIG Welding
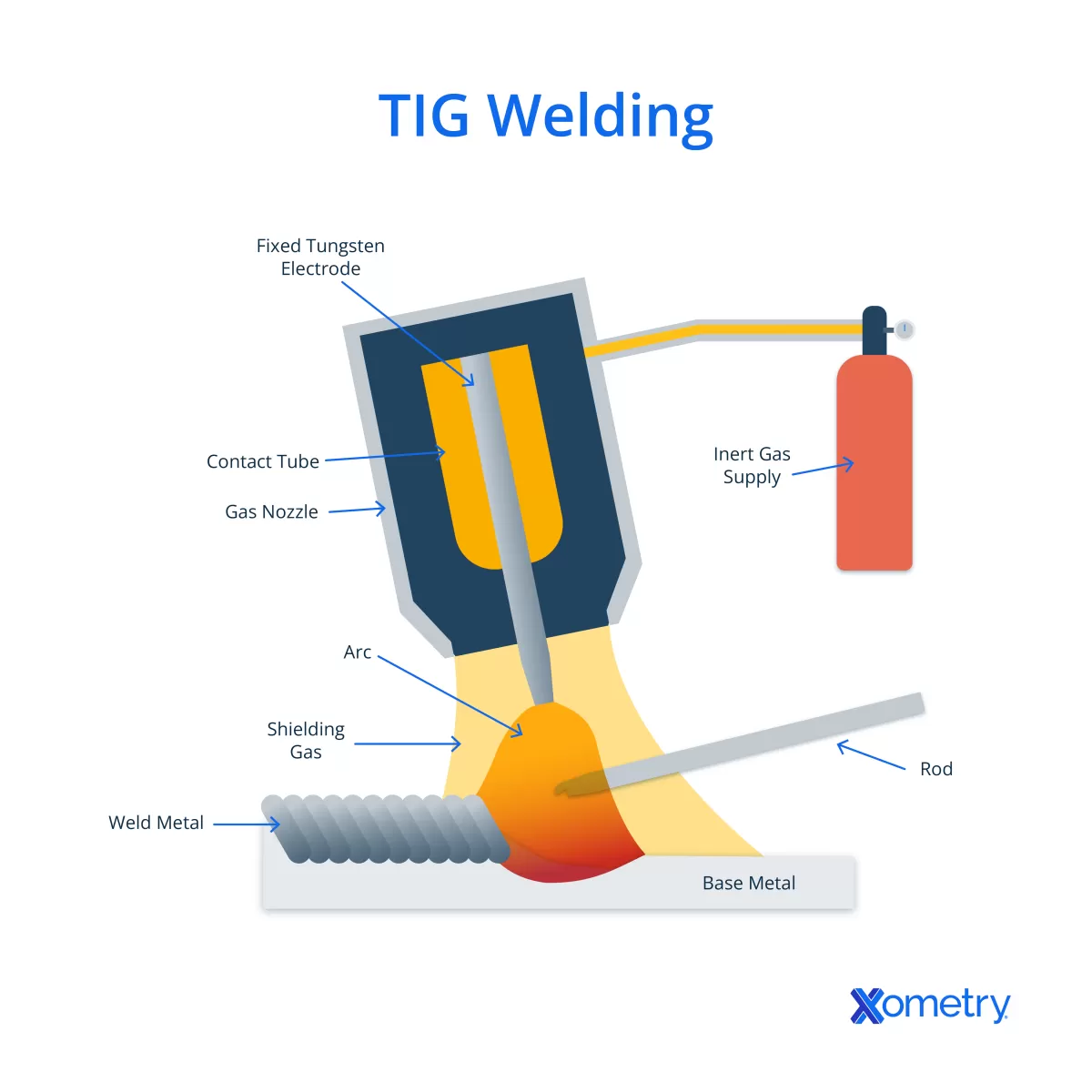
TIG welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), is a process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. It relies on a shielding gas, typically argon, to protect the weld area from contamination. Unlike MIG welding, TIG welding doesn’t use a wire feed; instead, welders often add filler metal manually.
Key Features of TIG Welding
- Precise control over the heat and the weld puddle
- Produces clean, high-quality welds with excellent aesthetics
- Works well on thin materials and delicate metals
- Requires more skill and steady hand coordination
- Can be used with or without filler material
Applications of TIG Welding
TIG welding is a go-to method for projects that demand precision and a clean finish. It’s widely used in industries like aerospace, automotive, and art fabrication. You’ll often see TIG welding on stainless steel, aluminum, and other non-ferrous metals needing strong, neat welds. It’s ideal for welding thin sections and where strength and appearance matter most.
Key Differences Between MIG and TIG Welding
Electrode Type Differences
MIG welding uses a continuously fed wire electrode that melts to form the weld. TIG welding, on the other hand, uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode, which means the electrode doesn’t melt but creates the arc needed to join metals.
Speed and Efficiency Comparison
MIG welding is generally faster and more efficient for bigger jobs because the wire feeds automatically. TIG welding is slower since it requires more control and often involves feeding filler material manually, making it better suited for precision work.
Skill Level Requirements
MIG welding is easier to learn and use, making it popular for beginners and quicker jobs. TIG welding demands a higher skill level due to its precise control over the torch, filler rod, and heat.
Shielding Gas Differences
Both use shielding gas to protect the weld from contamination. MIG typically uses argon mixed with CO2 or pure CO2, ideal for welding thicker materials. TIG mainly uses pure argon or argon mixes, providing cleaner, high-quality welds, especially on aluminum and stainless steel.
Weld Quality and Aesthetics
TIG welds generally offer a smoother, more refined finish with better control over the weld pool. MIG welds can be slightly rougher but are strong and consistent, great for structural work where appearance isn’t the top priority.
Cost Comparison
MIG welding equipment tends to be more affordable and requires less setup time, making it cost-effective for most projects. TIG welding gear is usually pricier and maintenance-heavy but worth it for specialties needing fine detail and quality.
Pros and Cons of MIG Welding
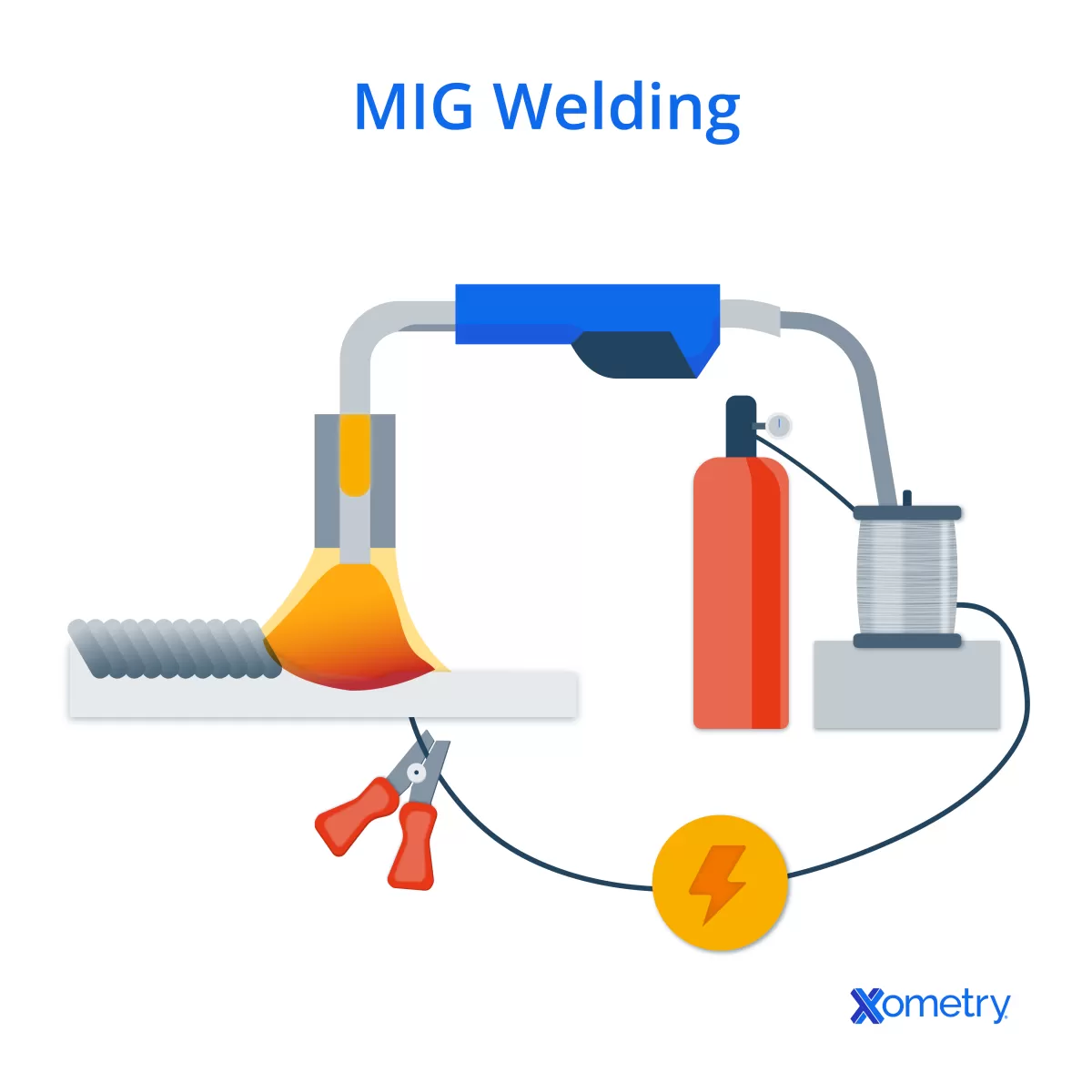
Advantages of MIG Welding
- Fast and efficient: MIG welding is known for its speed, making it great for high-volume projects.
- Easy to learn: It has a straightforward process, so beginners can get the hang of it quickly.
- Versatile on material thickness: Works well on both thin and thick metals, especially steel and aluminum.
- Clean welding process: Produces minimal spatter and requires less post-weld cleanup compared to other methods.
- Continuous wire feed: Allows for longer welds without frequent stops, boosting productivity.
Disadvantages of MIG Welding
- Less control on precision: Not ideal for highly detailed or delicate welds where a cleaner finish is required.
- Susceptible to wind: Shielding gas can be blown away outdoors, causing poor weld quality.
- Equipment cost: Setup and consumables can add up, especially for smaller shops or hobbyists.
- Limited on some metals: Not the best choice for exotic or non-ferrous metals like titanium.
- Requires shielding gas: This adds extra cost and complexity, particularly for outdoor or field work.
Understanding these pros and cons helps you decide if MIG welding fits your project needs, especially when balancing speed and quality. For tips on avoiding common welding issues, check out our guide on welding defects.
Pros and Cons of TIG Welding

Advantages of TIG Welding
- Precision and control: TIG welding gives you smooth, clean welds, perfect for detailed work and thin materials like aluminum and stainless steel.
- High-quality welds: It produces strong, durable joints with excellent weld quality and aesthetics.
- Versatility: Great for welding a wide range of metals, especially where appearance matters.
- Less spatter: TIG welding uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode, so there’s minimal spatter, meaning cleaner work.
- Better for thin materials: Ideal for delicate jobs and precision welding methods that require fine control.
Disadvantages of TIG Welding
- Slower process: TIG welding is more time-consuming compared to MIG welding, making it less efficient for large projects.
- Requires skill: It needs more training and practice to master, meaning beginners might struggle initially.
- Higher cost: TIG welding equipment and argon shielding gas can be pricier, which adds up for long-term use.
- Less suited for thick materials: It’s not the best choice for welding very thick metals where speed is key.
Overall, TIG welding is your go-to for precision, quality, and clean jobs, but expect a longer process and a steeper learning curve.
Material Compatibility
Best Materials for MIG Welding
MIG welding works great with a variety of metals, especially thicker materials. It’s commonly used for welding steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. This method shines when you need quick, strong welds on thicker steel parts or automotive frames. MIG is also ideal for projects where speed and volume are important, like fabrication and construction.
Best Materials for TIG Welding
TIG welding is known for precision and clean welds, making it perfect for thinner metals and delicate jobs. It’s commonly used for welding aluminum, stainless steel, copper, and other non-ferrous metals. TIG is your go-to when appearance matters or when working with thinner gauge metals, such as in aerospace or custom bike frames.
HYCNC Expertise in Different Materials
At HYCNC, we know materials inside and out. Our certified welders have extensive experience working with both MIG and TIG welding techniques across a wide range of metals. Whether it’s heavy steel parts or precision aluminum assemblies, we tailor our welding approach to ensure the best quality and strength for your project. Our CNC capabilities complement our welding services, delivering accurate, reliable results you can trust.
For tips on avoiding common welding defects and ensuring the best weld quality, check out our guide on welding defects.
Choosing the Right Welding Method for Your Project
Picking the right welding method can make a big difference in how your project turns out. Here’s what to keep in mind when deciding between MIG and TIG welding.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Welding Method
- Material type: Some metals work better with one method over the other, like aluminum favoring TIG welding.
- Weld quality needed: If you want clean, precise welds, TIG is usually the choice. For faster, thicker welds, MIG often fits better.
- Project size and speed: Larger jobs that need quick turnaround often benefit from MIG welding.
- Skill level: MIG welding is easier for beginners, while TIG requires more practice and expertise.
- Budget and equipment: TIG setups generally cost more due to equipment and skill required.
When to Choose MIG Welding
- You’re working on thicker materials.
- Speed and efficiency are top priorities.
- The project involves steel or other common metals.
- You want a more straightforward process with less training needed.
- You need consistent production for larger volume jobs.
When to Choose TIG Welding
- You need precise, high-quality welds with great looks.
- The project involves aluminum, stainless steel, or thin materials.
- Welding requires fine control for complex or delicate parts.
- The job demands cleaner welds without much post-processing.
- You have skilled welders on hand or need custom, detailed work.
HYCNC Recommendation for Welding Method Selection
At HYCNC, we work closely with you to evaluate your project needs, materials, and timeline. Our team recommends:
- Use MIG welding for faster, cost-effective results on thicker or structural components.
- Go with TIG welding when weld quality and appearance are crucial, especially with complex designs or metals like aluminum.
- Rely on our CNC service expertise to optimize whichever welding method suits your custom requirements.
We help ensure your welding process matches your project’s goals without unnecessary hassle or expense. Reach out for a consultation to find the best fit for your welding needs.
How HYCNC Enhances Your Welding Projects
At HYCNC, our certified welders bring top-level expertise in both MIG and TIG welding techniques. We understand what it takes to deliver strong, clean welds that meet your project specs every time.
We use advanced equipment and cutting-edge technology to ensure precision welding and consistent quality across all jobs. This means less rework and faster turnaround, saving you time and money.
Our team also offers custom welding solutions tailored to a wide range of industries — from automotive to heavy machinery. Whether you need spot-on gas metal arc welding or delicate gas tungsten arc welding, we have the skills and tools to get it done right.
Ready to improve your welding projects? Contact HYCNC today for a consultation and quote. Let us help you choose the best welding method for your needs and deliver quality results you can count on.