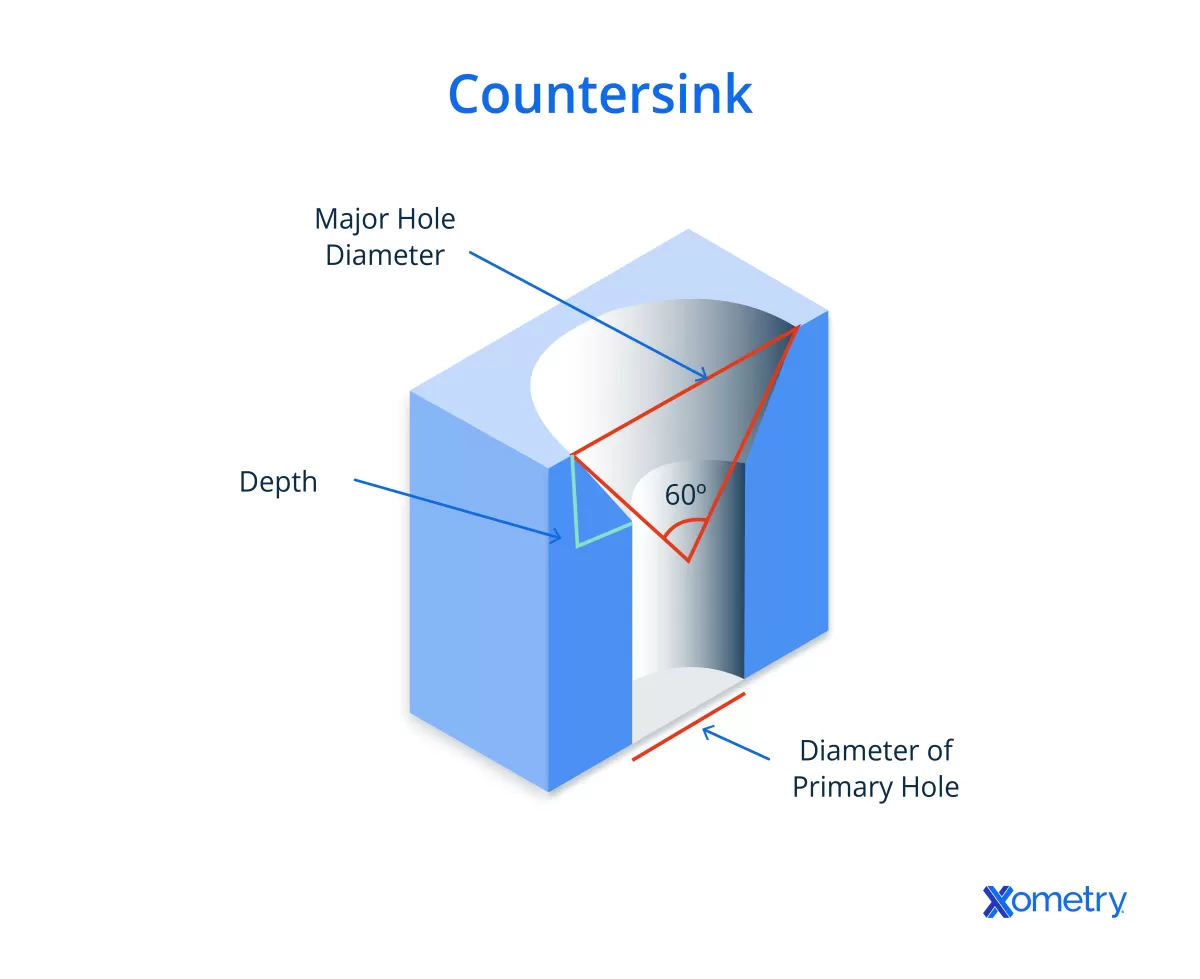
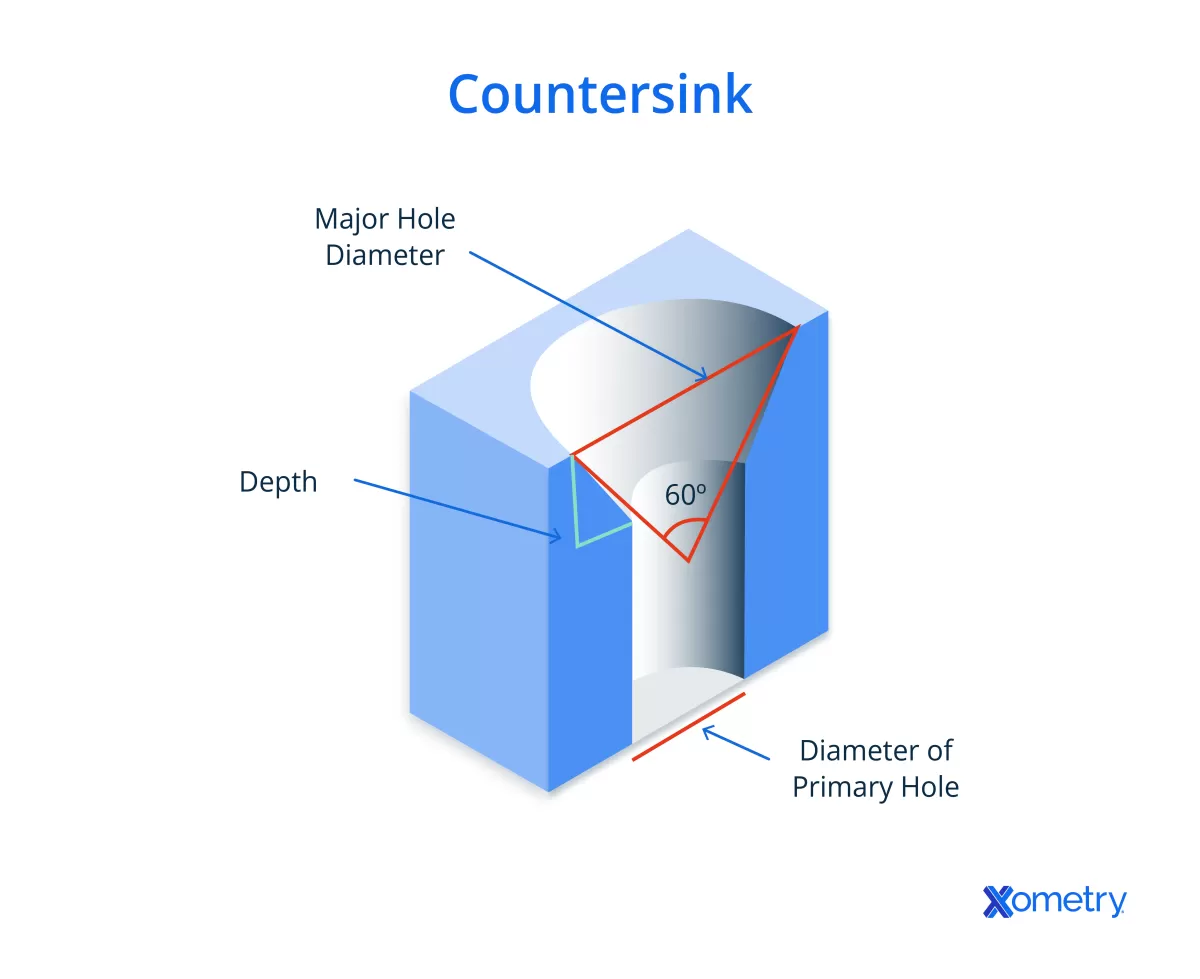
What Are Countersink Holes
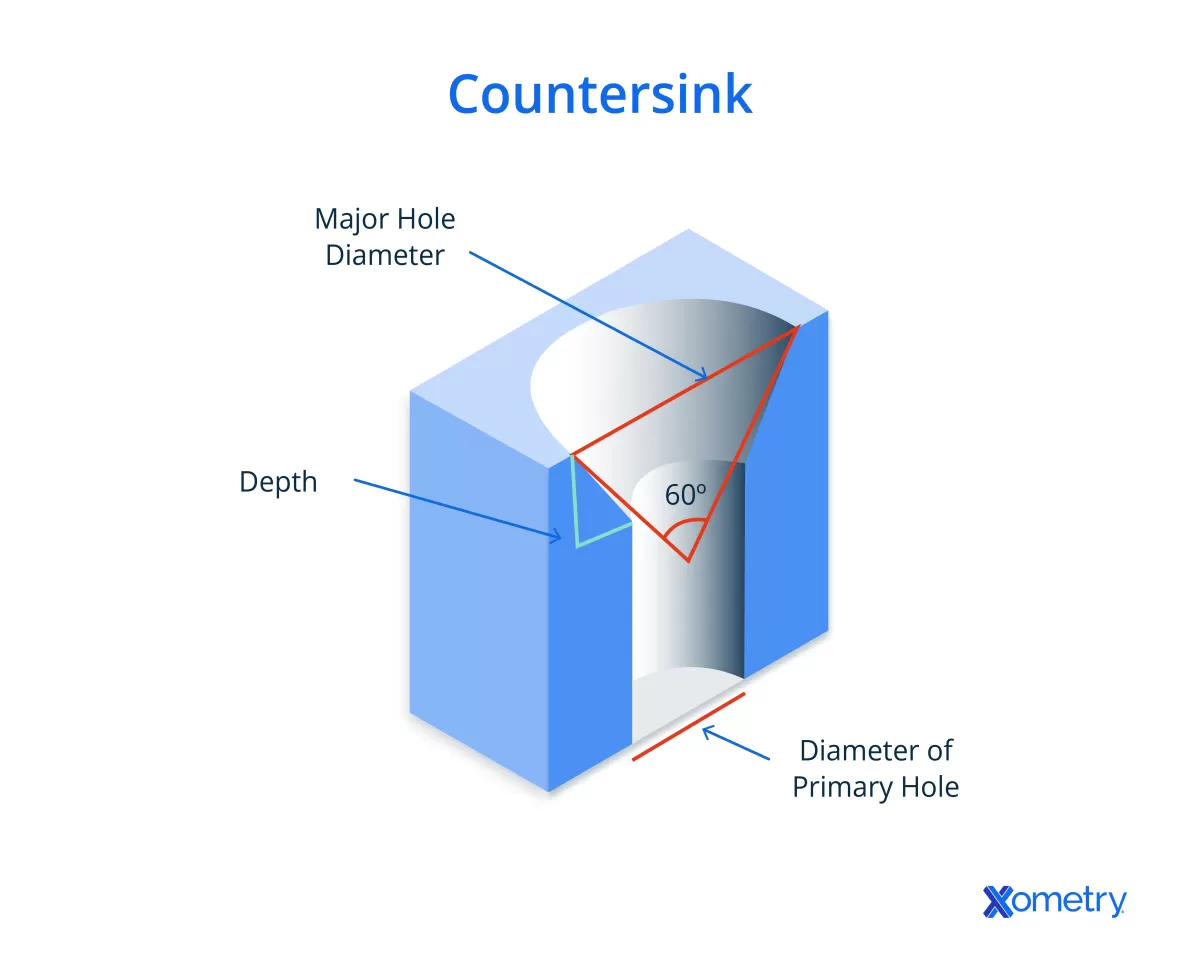
Countersink holes are specially designed conical openings that allow screws to sit flush with or below the surface of a material. This angled shape ensures that flat-head screws or fasteners fit snugly, creating a smooth, finished appearance without any protrusions.
Key Characteristics
- Conical shape typically set at standard angles like 82° or 90°
- Controlled depth to accommodate screw head height precisely
- Ensures a flush or recessed finish for streamlined surfaces
Common Applications
You’ll often find countersink holes used in industries where aesthetics and precision matter, including:
- Aerospace components requiring smooth aerodynamic surfaces
- Automotive parts where flush fasteners improve safety and appearance
- Furniture assembly for clean, professional finishes
Tools Used
Machining countersink holes calls for specific tools such as:
- Countersink drill bits specially shaped for conical cuts
- Traditional drill presses for manual operations
- Advanced CNC machines for high precision and repeatability
Benefits of Countersink Holes
Using countersink holes offers several advantages:
- Provides a sleek and aesthetic finish by hiding fastener heads
- Reduces protrusion, lowering the risk of snagging or interference
- Enhances structural integrity by distributing screw load evenly
For a deeper look into CNC machining processes for these holes, explore our guide on what is CNC machining.
What Are Counterbore Holes
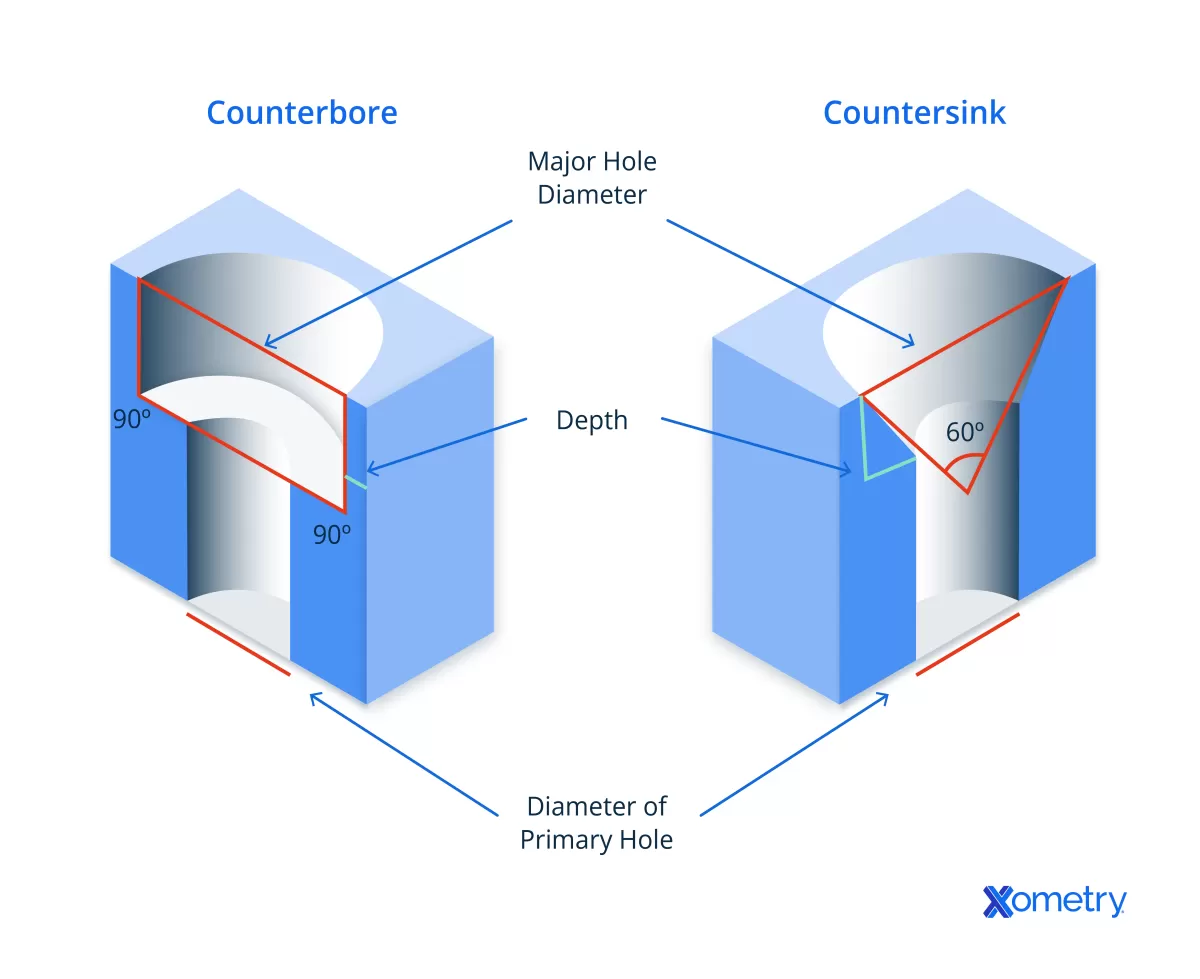
Counterbore holes are cylindrical holes with a flat bottom designed to seat bolts or fasteners securely. Unlike countersink holes, they don’t have a tapered shape but instead have a uniform diameter with a flat shoulder. This flat bottom allows the bolt head or fastener to sit flush or below the surface, providing a clean, stable fit.
Key Characteristics
- Cylindrical shape with consistent diameter
- Flat bottom or shoulder for bolt head seating
- Precise depth control to ensure proper fit
Common Applications
Counterbore holes are widely used in machinery, heavy equipment, and structural components where strong, reliable fastener seating is essential. These holes help distribute load and prevent fastener damage in high-stress applications.
Tools Used
Machining counterbore holes involves counterbore tools, end mills, or CNC machining centers equipped to maintain accuracy and surface finish.
Benefits
- Provides stronger and more secure fastener seating
- Ideal for applications requiring high load capacity
- Helps maintain the overall strength and integrity of the assembly
Countersink vs Counterbore Key Differences
When comparing countersink vs counterbore holes, the main difference lies in their shape. Countersink holes have a conical shape designed to allow screws to sit flush with or below the surface. In contrast, counterbore holes are cylindrical with a flat bottom, meant to house bolt heads or fasteners securely.
Fastener Compatibility
- Countersink holes are perfect for flush screws like flat-head screws that need to blend smoothly with the surface.
- Counterbore holes fit bolts or socket-head fasteners, providing a flat bearing surface for stronger seating.
Aesthetic vs Functional Focus
- Countersinks are mostly about appearance and smooth finishes, reducing protrusion and creating sleek designs.
- Counterbores focus more on strength and load-bearing, ideal for high-stress, heavy-duty applications where fastener integrity is key.
Machining Process and Tooling
- Machining countersink holes requires countersink drill bits or specialized CNC tools set for precise angles and depths.
- Counterbore holes use counterbore tools or end mills designed to maintain uniform diameter and flat bottoms, often in more complex CNC setups.
Here’s a quick comparison table to sum it up:
| Feature | Countersink | Counterbore |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Conical | Cylindrical flat-bottomed |
| Fastener Type | Flush screws (flat-head) | Bolts, socket-head screws |
| Focus | Aesthetic, flush finish | Functional, strong fastening |
| Typical Tools | Countersink drill bits, CNC | Counterbore tools, end mills |
| Common Uses | Aerospace, furniture, automotive | Machinery, heavy equipment |
Understanding these core differences helps you choose the right hole type for your CNC machining applications, whether you prioritize appearance or strength. For more details on precision hole machining and tooling setups, check out our precision machining services or explore CNC machining basics.
When to Use Countersink vs Counterbore Holes
Choosing between countersink and counterbore holes depends a lot on your project’s needs.
Use countersink holes when:
- You want a smooth, clean look with screws sitting flush or slightly below the surface.
- Working with lightweight or thin materials like aluminum or wood.
- The focus is on aesthetics, like in furniture, automotive interiors, or aerospace panels where sleekness matters.
Use counterbore holes when:
- You’re dealing with heavy-duty assemblies where strength is key.
- Working on thick materials like steel or structural components that will face high stress.
- Bolts or socket-head fasteners need to sit firmly with a flat bearing surface, common in machinery and construction equipment.
In industries like aerospace or construction, the choice between these hole types is critical. Precise countersinking ensures aerodynamic surfaces and neat finishes, while counterboring guarantees durability in load-bearing parts.
At HYCNC, we understand these demands and help you pick and tailor the perfect hole type for your project. Our CNC machining services deliver clean, accurate countersink and counterbore holes that meet your exact specs, ensuring your parts perform perfectly in the field.
Machining Considerations for Countersink and Counterbore
When working with countersink and counterbore holes, the material you’re machining matters a lot. Metals, plastics, and composites each react differently to cutting tools. For example, harder metals require more durable countersink drill bits or counterbore tools, while plastics might need slower speeds to avoid melting or chipping.
Precision is also key. Countersink and counterbore holes need tight tolerances and a clean surface finish to ensure screws or bolts seat properly. That means your CNC programming must be spot-on, controlling depth and angle with high accuracy.
Some common challenges include:
- Tool wear, which can affect hole quality and size
- Maintaining depth control for consistent hole dimensions
- Aligning the tool correctly to avoid angled or off-center holes
To get the best results, here are a few tips for machining these holes:
- Choose the right tool based on material and hole requirements
- Adjust feed rates and spindle speeds to balance surface finish and efficiency
- Monitor tools regularly to catch wear early
- Use precise CNC setups to maintain alignment and depth control
Paying attention to these factors will help you get perfect countersink and counterbore holes every time, whether for aerospace parts or heavy machinery components. For more on precise hole machining, check out our precision machining services.
How HYCNC Enhances Countersink and Counterbore Machining
At HYCNC, we specialize in CNC machining holes with precision you can trust. Our advanced technology and skilled team ensure countersink and counterbore holes are made to exact tolerances every time. Whether you need conical holes for flush screw machining or cylindrical holes for strong bolt seating, we deliver consistent, high-quality results.
We use the latest countersink drill bits, counterbore tools, and 5-axis CNC machining centers to handle even the most complex parts. Our expertise in aerospace CNC services and automotive manufacturing means we understand the unique demands of each project and tailor solutions accordingly.
If you’re looking for custom countersink or counterbore hole machining, contact HYCNC. Our precision machining capabilities make us a reliable partner for your next project. Explore our CNC machining services and see how we can help you achieve perfect results.