Are you torn between Alodine and anodizing for your aluminum CNC parts? Choosing the right surface finish can transform your project’s durability, aesthetics, and performance. As a CNC machining expert, I’ve seen how the right coating decision drives success in industries like aerospace and electronics. In this guide, we’ll break down the key differences between Alodine and anodizing, highlight their pros and cons, and share actionable insights to help you pick the perfect finish. Let’s dive in and simplify your choice!
What is Alodine Chromate Conversion Coating
Alodine chromate conversion coating is a chemical treatment applied to aluminum surfaces to enhance corrosion resistance and improve paint adhesion. Also known as a chromate conversion coating, Alodine creates a thin, transparent layer on the metal by reacting with its surface, forming a protective film without adding significant thickness.
The process involves immersing the aluminum part in a chromate-based solution. This causes a controlled chemical reaction that converts the metal surface into a protective layer made primarily of aluminum oxide and chromium compounds. The coating is typically yellow, green, or iridescent, depending on the specific process used.
Key characteristics of Alodine coating include:
- Thin and lightweight protective layer
- Excellent corrosion resistance for indoor and mild outdoor environments
- Improved paint and adhesive bonding on aluminum surfaces
- Maintains electrical conductivity, making it suitable for electronic parts
Common applications for Alodine chromate conversion coatings include aerospace components, automotive parts, electronics housings, and CNC machining finishes where corrosion protection and paint adhesion are critical without compromising electrical properties. It’s favored for parts that require precision and a thin, even coating without added thickness that could affect tight tolerances.
What is Anodizing

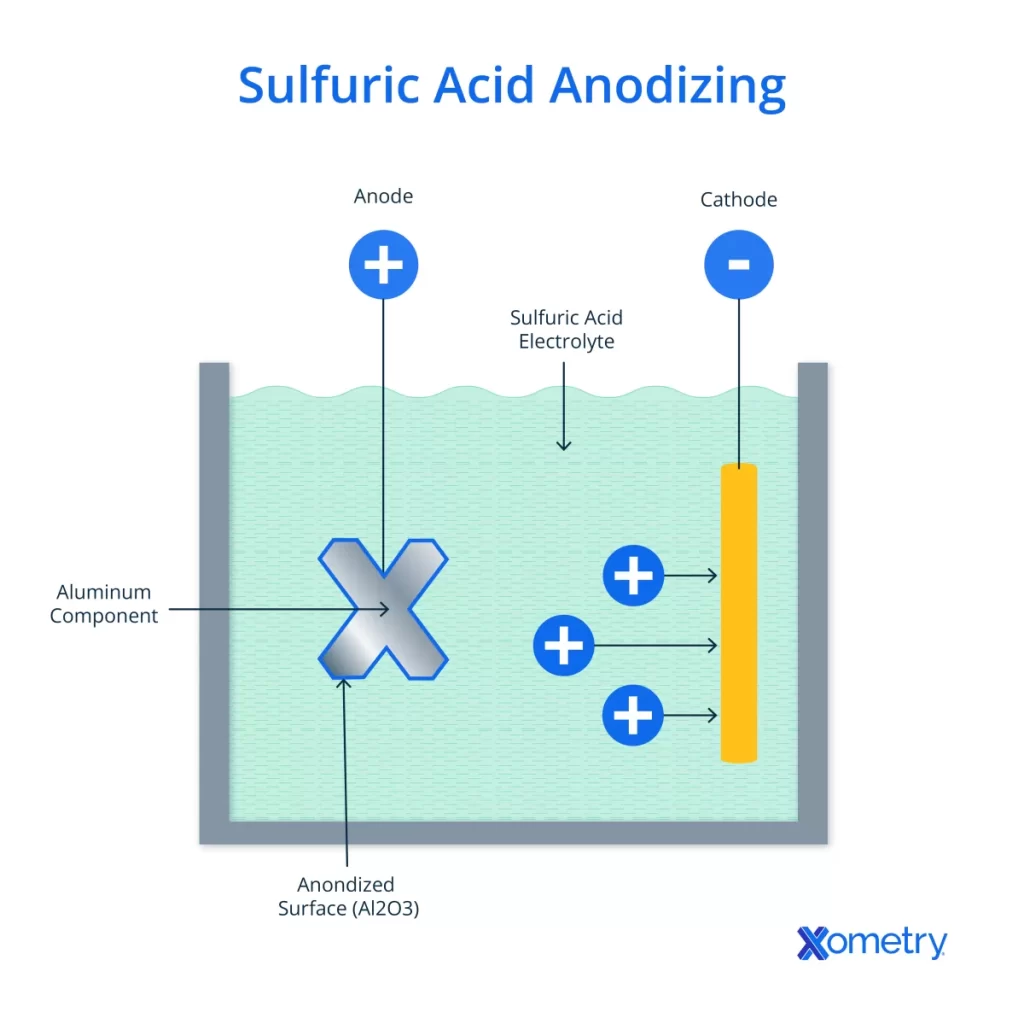
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that enhances the surface of aluminum and other metals by creating a durable oxide layer. This aluminum oxide layer is much thicker and harder than the natural oxide film that forms on aluminum, improving both corrosion resistance and surface hardness.
Process Overview
During anodizing, the metal part is submerged in an acid electrolyte bath and connected to an electrical current. This causes oxygen to form on the metal surface, building up the protective aluminum oxide coating. The thickness and properties of this coating can be controlled by adjusting factors like voltage, temperature, and time.
Key Characteristics
- Increased corrosion resistance to elements like moisture and chemicals
- Enhanced surface hardness for better wear resistance
- Improved paint adhesion due to the porous surface of the oxide layer
- Can be dyed in various colors for aesthetic purposes
- Non-conductive surface which can be a factor depending on the application
Common Applications
- Aerospace components needing lightweight, durable finishes
- Architectural elements like window frames and panels
- Consumer products such as smartphones, cookware, and sporting goods
- Automotive parts requiring corrosion protection and wear resistance
- CNC machined parts where both protection and visual appeal matter
Anodizing offers a strong finish that works well across many industries, making it a preferred choice when you want a tough, attractive, and corrosion-resistant coating.
Alodine vs Anodize Key Differences

When comparing Alodine coating and anodizing, several key differences stand out in how they protect and finish aluminum surfaces.
Process Comparison
- Alodine is a chemical treatment that creates a thin chromate conversion coating on aluminum, enhancing corrosion resistance and paint adhesion without adding much thickness.
- Anodizing is an electrochemical process that thickens the natural aluminum oxide layer, making the surface harder and more durable.
Coating Thickness and Durability
- Alodine coatings are very thin, usually just a few microns, so they offer moderate protection but can wear off faster under heavy use.
- Anodized layers are much thicker, often 5 to 25 microns, providing a tougher, longer-lasting finish that resists scratches and abrasion better.
Corrosion Resistance
- Both finishes improve corrosion resistance, but anodizing offers superior protection, especially in harsh environments, due to its thick oxide layer.
- Alodine offers good resistance for indoor or mild outdoor conditions but may need additional coatings for heavy-duty protection.
Electrical Conductivity
- Alodine coatings retain electrical conductivity, which makes them useful in electronics or applications requiring grounding.
- Anodizing is an insulator, so it doesn’t conduct electricity, which can be a factor when choosing a finish for electrical parts.
Aesthetic Options
- Alodine usually produces a clear to light gold or bronze finish. It’s subtle and not highly decorative.
- Anodizing offers more color options, from clear to black, blue, or red, and can create a more visually appealing and customizable surface.
Cost and Complexity
- Alodine is generally less expensive and faster since it’s a simple chemical dip process.
- Anodizing tends to cost more due to equipment, time, and energy needed for the electrochemical process, but it adds more value through durability and appearance.
In , Alodine is great for lightweight corrosion protection and maintaining conductivity, while anodizing provides a harder, more durable finish with more color choices and better corrosion resistance. Your project’s specific needs will guide which finish fits best.
Pros and Cons of Each Finish
Alodine Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Quick and cost-effective application
- Provides good corrosion resistance for aluminum
- Enhances paint adhesion without adding much thickness
- Maintains electrical conductivity, useful for electronic parts
- Environmentally friendlier than older chromate coatings
Cons:
- Less durable than anodizing—can wear off or fade over time
- Limited color options, mostly yellowish or clear finishes
- Not as strong against heavy abrasion or extreme environments
- Contains some chemicals that require careful handling
Anodizing Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Creates a thick, hard aluminum oxide layer that lasts long
- Excellent corrosion and wear resistance
- Wide range of colors and finishes available
- Non-conductive surface, which can be a benefit or drawback depending on use
- Suitable for heavier-duty applications and outdoor use
Cons:
- More expensive and time-consuming than Alodine
- The surface can be more brittle, prone to chipping if mishandled
- Reduces electrical conductivity, limiting some applications
- Requires specialized equipment and skilled application
Choosing between Alodine and anodizing really depends on your project’s needs—whether you want quick protection and conductivity or a long-lasting, tough surface.
Applications in CNC Machining
When it comes to CNC machining, choosing the right surface finish is crucial for both performance and appearance. At HYCNC, we work with both Alodine and anodizing finishes depending on the project needs.
Alodine Use Cases
- Great for parts that need quick corrosion resistance without adding much thickness
- Ideal for aluminum components that will be painted or glued later because Alodine improves paint adhesion
- Common in aerospace and automotive parts where lightweight metal treatment is important
- Useful when electrical conductivity is needed, like in electrical housings or connectors
Anodizing Use Cases
- Perfect for parts that require a tough, durable surface that resists scratches and wear
- Commonly used for consumer electronics, architectural components, and outdoor equipment
- Popular when an attractive, colored finish is desired since anodizing allows dyeing
- Best for parts exposed to harsh environments needing excellent corrosion protection
HYCNC Expertise
At HYCNC, we know how to tailor surface finishes to your specific CNC project. Whether you need a thin, functional Alodine layer or a thick, durable anodized coating, we ensure high-quality results. Our experienced team guides you through selecting the right finish for your aluminum parts to maximize durability, appearance, and overall performance in your application.
How to Choose the Right Finish for Your Project
Picking between Alodine and anodize isn’t always straightforward. Here’s how to make the best choice for your CNC machining project.
Factors to Consider
- Material type: Some finishes work better on specific aluminum alloys.
- Corrosion resistance needed: If your part faces harsh environments, anodizing usually offers stronger protection.
- Electrical conductivity: Alodine keeps conductivity, anodizing doesn’t, so know if that matters.
- Appearance preferences: Anodizing gives more color options and a thicker finish, while Alodine offers a slimmer, clear coating.
- Cost constraints: Alodine is typically cheaper upfront, but anodizing may save money long term with better durability.
- Paint adhesion: Need to paint over the part? Alodine usually provides a better base for paint.
- Production volume and timing: Some finishes are faster to apply in large batches.
- Environmental and safety standards: Alodine involves chemicals that need careful handling, anodizing is often cleaner.
Decision Framework
- Define what matters most – durability, appearance, or cost.
- Match your project’s environment and use case with finish benefits.
- Factor in delivery time and volume.
- Consider future maintenance and lifespan.
HYCNC Consultation Services
At HYCNC, we help you navigate these choices based on your project’s specific needs, budget, and timeline. Our experts can recommend the most effective finish—whether Alodine chromate conversion coating or anodizing—to ensure your parts perform well and look great. Reach out to us for a detailed consultation tailored to your machining project.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
When it comes to environmental impact and safety, Alodine and anodizing differ quite a bit.
Alodine Environmental Concerns
Alodine uses chromate conversion coating, which involves chemicals that can be harmful to both workers and the environment if not handled properly. The process releases hexavalent chromium, a toxic substance regulated under strict safety standards in the U.S. Facilities using Alodine must have controls in place to manage waste and exposure risks. While effective for corrosion resistance, the environmental footprint is higher compared to some alternatives.
Anodizing Eco Friendly Processes
Anodizing is generally considered more environmentally friendly. It’s an electrochemical process that uses less harmful substances and produces a stable aluminum oxide layer without toxic byproducts. Many anodizing operations now follow greener practices, recycling water and minimizing waste. This makes anodizing a safer choice for the workplace and the environment.
HYCNC Commitment
At HYCNC, we prioritize sustainable CNC machining finishes. We ensure all treatments meet or exceed EPA guidelines and focus on options that reduce environmental impact without compromising quality. Our team advises clients on the safest, most eco-friendly finish that fits their project needs, balancing performance, safety, and environmental responsibility.
Cost Comparison and Long Term Value
When deciding between Alodine and anodize coatings for your CNC machining project, cost plays a big role.
Initial Costs
Alodine typically comes with a lower upfront price since it’s a simpler chemical treatment that doesn’t require expensive equipment. This makes it a go-to for projects where budget is tight and quick turnaround is needed. Anodizing, on the other hand, tends to cost more initially. Its electrochemical process is more involved and requires specialized tanks and power supplies, so the price reflects that.
Long Term Value
While anodizing might demand a higher start-up cost, it often pays off in the long run. Anodize coatings create a thicker, harder aluminum oxide layer that resists wear and corrosion better over time. Alodine provides decent corrosion resistance but isn’t as durable, especially in harsh environments or heavy-use parts.
At HYCNC, we balance cost and quality to fit your project’s specific needs. Our competitive pricing ensures you get the best value whether you choose Alodine for quick and cost-effective protection or anodizing for long-lasting finish and enhanced surface durability. We help you decide what works best for your budget and application, making sure you don’t pay more than you need to for your CNC machining finishes.