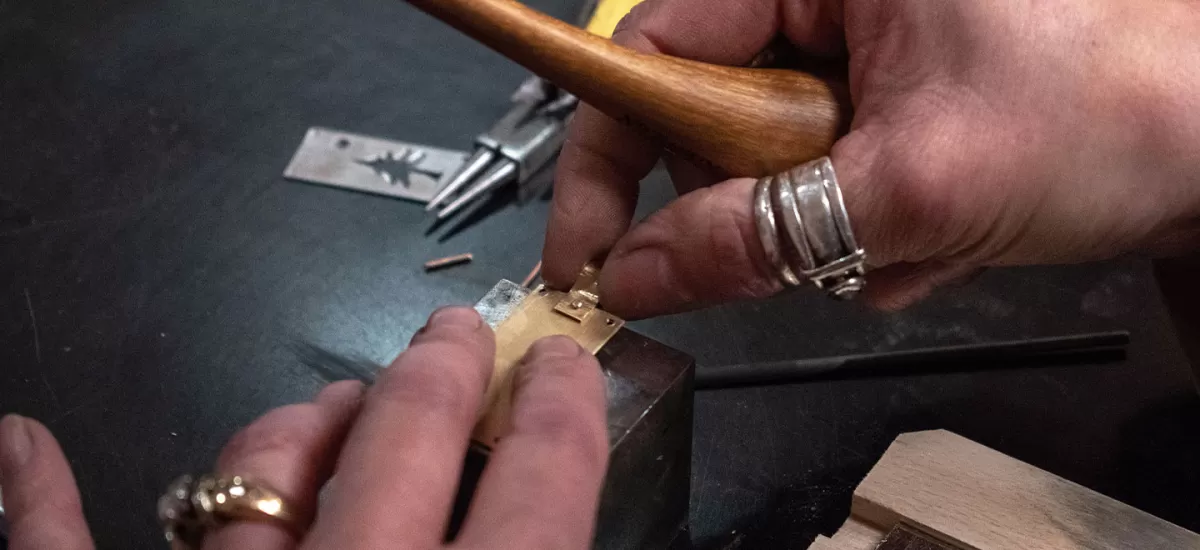
Cold Riveting: Your Guide to Precision Fastening Done Right
Struggling to find the best cold riveting solutions for your manufacturing needs? Choosing the right riveting technique can transform your production process, ensuring strength, efficiency, and durability. As experts in CNC machining, we at HYCNC understand the critical role cold riveting plays in industries like aerospace and automotive. In this guide, you’ll discover the essentials of cold riveting, from its core principles to advanced tools and real-world applications. Get ready to unlock practical insights and learn how HYCNC’s precision solutions can elevate your projects. Let’s dive in!
Understanding Cold Riveting The Basics
If you’ve ever wondered how materials get joined securely without heat, cold riveting is a key process to know. Cold riveting involves fastening materials by inserting and deforming a rivet at room temperature. Instead of heating the rivet like in hot riveting, cold riveting relies on plastic deformation, meaning the rivet’s metal is reshaped under pressure to hold parts together tightly.
Here’s what happens in cold riveting:
- A solid rivet is inserted into aligned holes of the materials.
- Force is applied, usually by a riveting tool, causing the rivet to deform and expand.
- This deformation locks the rivet in place, creating a strong joint without melting or heating the metals.
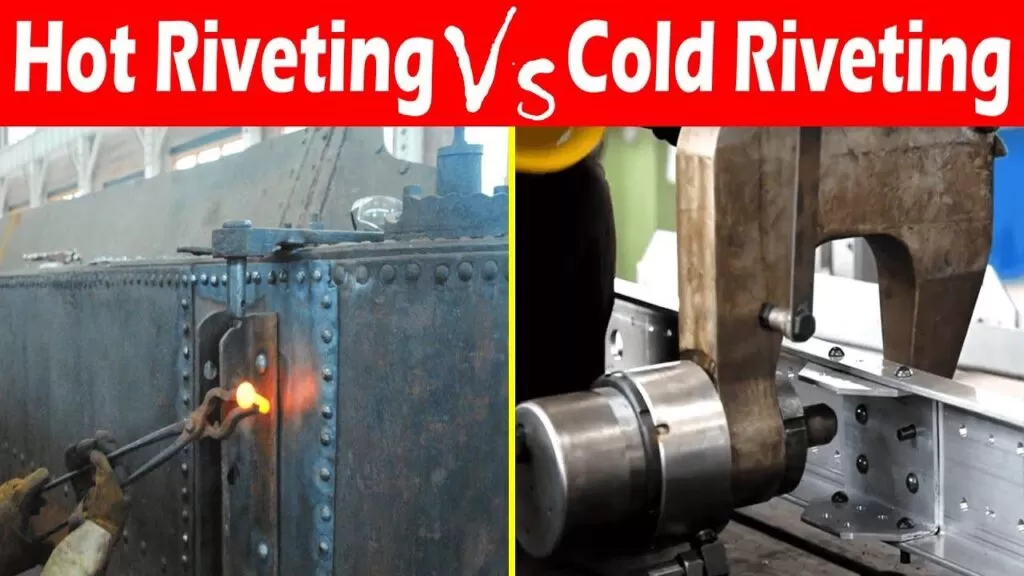
The difference between cold and hot riveting is mainly in how the rivet is formed. Hot riveting heats the rivet until it’s red-hot and malleable, allowing shaping before cooling to hold the joint. Cold riveting skips heating, relying on mechanical pressure alone, which preserves the material properties of the rivet and workpieces.
Some key differences include:
- Temperature: Cold riveting uses room temperature, hot riveting uses high heat.
- Material impact: Cold riveting avoids heat distortion or weakening; hot riveting can soften materials around the joint.
- Process speed: Cold riveting is typically faster and easier to automate.
- Applications: Cold riveting works best for precision joints and heat-sensitive materials.
Understanding these basics sets the foundation for knowing why cold riveting is widely used across industries where strength, precision, and material integrity matter.
Advantages of Cold Riveting
Cold riveting has some clear benefits that make it a top choice in many industries. First, it preserves the material’s original properties since it doesn’t involve heat. This means no heat distortion or weakening of metals, which keeps parts strong and reliable.
It’s also energy-efficient—using 60 to 80 percent less energy compared to hot riveting. This not only cuts costs but also supports greener manufacturing processes.
Cold riveting is versatile. It can easily join dissimilar materials like metals and composites, giving more flexibility in design and assembly without worrying about heat damage.
Finally, it’s cost-effective and well-suited for automation. This makes it perfect for high-volume production where speed and consistent quality are important. Using cold forming and CNC riveting tools helps maintain precision and efficiency across large runs.
Tools and Equipment for Cold Riveting
Cold riveting relies on the right tools to get the job done smoothly and accurately. At the basic level, essential tools include riveting guns, rivet sets, hole punches, and anvils. These help you place and secure rivets without any heat, ensuring the materials stay intact.
For more advanced work, pneumatic and hydraulic riveting guns give more power and control, making it easier to handle tougher materials or larger projects. Self-piercing rivet systems are also popular, especially when joining dissimilar materials like metals and composites, as they pierce and fasten in one step without pre-drilling.
HYCNC takes this further by using precision CNC machining for rivet and tool production. Their CNC service ensures that rivets and dies are made with exact specifications, improving fit and performance. This precision enhances consistency and durability, which is crucial in industries like aerospace and automotive where every rivet matters.
Applications of Cold Riveting Across Industries
Cold riveting is widely used across various industries in the United States because it offers strong, reliable joints without the risks of heat damage. Here’s how it plays out across key sectors:
-
Aerospace: Cold riveting is ideal for lightweight, high-strength joints in fuselages and wings. It helps keep aircraft structures safe and durable without compromising metal properties.
-
Automotive: From body panels to chassis parts and airbag components, cold riveting ensures strong connections while allowing manufacturers to avoid heat-related warping or weakening.
-
Electronics: Precision is crucial here. Cold riveting secures circuit boards and electrical connectors without exposing delicate components to heat, preserving functionality.
-
Construction: Metal roofing and structural assemblies benefit from cold riveting’s durable joints, which hold up well under stress and weather without the need for heating.
Overall, cold riveting is a go-to method when strength, precision, and material integrity matter, making it a versatile solution across these industries. For more on riveting types and their uses, check out our guide on blind riveting vs solid riveting.
Cold Riveting vs Hot Riveting A Comparative Analysis
When comparing cold riveting to hot riveting, the main difference lies in how the materials respond during the process. Cold riveting relies on work hardening—where the rivet material strengthens as it deforms without heat. This keeps the metal tough and durable. Hot riveting, on the other hand, uses annealing by heating the rivet first, which can soften the metal but allows easier shaping.
Energy use and cost also set them apart. Cold riveting is far more energy-efficient, using about 60-80% less energy since there’s no need to heat the rivets. This saves money and cuts down on processing time.
Material choice and thickness matter too. Cold riveting works best for thinner materials and heat-sensitive metals because it doesn’t cause heat distortion or weaken the parts. It’s also perfect when you need precise joints without risking thermal damage. Hot riveting shines with thicker, heavy-duty metals where heating helps form a stronger bond.
Overall, cold riveting is ideal for precision assemblies and materials sensitive to heat, making it a top pick in industries like aerospace and automotive. It offers strength, saves energy, and reduces the risk of damage compared to hot riveting.
For more on different riveting methods and material options, check out our guide on blind riveting vs solid riveting.
How HYCNC Enhances Cold Riveting with CNC Precision
At HYCNC, we take cold riveting to the next level by using CNC machining to create custom rivets and dies with pinpoint accuracy. This precision ensures every rivet fits perfectly, improving joint strength and reliability. We specialize in working with high-performance materials like tungsten carbide, which makes our tools and dies durable and long-lasting, even under tough production conditions.
Our equipment supports automation, allowing for high-speed and consistent riveting processes suitable for large-scale manufacturing. This means faster production times without sacrificing quality—a big win for industries like aerospace and automotive where precision and reliability matter most.
For example, in an aerospace project, HYCNC provided tailored CNC-machined rivets and dies that met tight tolerances for lightweight fuselage components. This helped our client achieve secure, high-strength joints with minimal weight impact. In the automotive sector, our CNC solutions enabled consistent riveting on chassis parts, improving both assembly speed and final product durability.
HYCNC’s combination of CNC precision, durable materials, and automation integration makes cold riveting more efficient and reliable, meeting the exact demands of U.S. manufacturers across various industries.
Tips for Successful Cold Riveting

Getting cold riveting right means paying attention to a few key details. Here’s how to make sure your joints are strong and consistent every time:
-
Choose the right rivet material and size
Match your rivet to the materials you’re joining. Aluminum rivets work well for light metals, while steel or stainless steel fit tougher jobs. The size should fit snugly without stressing the parts.
-
Ensure precise hole alignment and fit
Drill clean, correctly sized holes. Misalignment or oversized holes can cause weak joints or uneven stresses, leading to failure.
-
Optimize force application
Use the right amount of pressure when setting rivets. Too little won’t fully deform the rivet, while too much can damage material or tools. Consistency here is key.
-
Leverage HYCNC expertise for custom solutions
When you need precision rivet manufacturing or custom tools, HYCNC’s CNC machining services deliver accuracy and durable materials like tungsten carbide. They help tailor riveting solutions to your exact project needs.
Following these tips helps improve durability, speed up production, and reduce scrap—important for any U.S. manufacturer focusing on quality and efficiency.
Future Trends in Cold Riveting
Cold riveting is evolving fast, especially with new automation technologies that make the process faster and more precise. Micronized riveting, which uses tiny rivets, is becoming popular in electronics where space and accuracy matter a lot. This lets manufacturers secure delicate circuit boards and connectors without heat damage.
Another big trend is joining composite materials to metals. As industries like aerospace and automotive push for lighter, stronger parts, cold riveting is a go-to because it handles dissimilar materials without warping or weakening them.
At HYCNC, we’re focused on pushing these innovations further. Our CNC machining expertise lets us produce custom rivets and tools that meet the tightest tolerances needed for advanced projects. With automation integration, we help businesses improve consistency and throughput in cold riveting. This commitment keeps HYCNC at the forefront of next-gen cold riveting solutions, perfectly matching the demands of modern U.S. manufacturing.
FAQs About Cold Riveting
What materials can be joined with cold riveting
Cold riveting works great with a wide range of materials, including aluminum, steel, stainless steel, and even composites. It’s especially useful for joining dissimilar materials where welding or adhesives might fail.
How does cold riveting compare to welding
Unlike welding, cold riveting doesn’t require heat, so it avoids issues like warping, material weakening, or fire hazards. Cold riveting is faster, uses less energy, and can join heat-sensitive materials without damage. However, welding might offer higher strength in some heavy-duty applications.
Which industries benefit most from cold riveting
Cold riveting is widely used in aerospace, automotive, electronics, and construction industries. It’s ideal for applications needing lightweight, strong, and reliable joints without affecting material properties.
How can HYCNC help with cold riveting needs
At HYCNC, we provide precise CNC machining for custom rivets and tools tailored to your project specs. Our high-quality materials, like tungsten carbide dies, ensure durability and consistency. We also support automation integration—perfect for high-volume cold riveting. Whether aerospace or automotive, HYCNC delivers reliable, efficient solutions to make your cold riveting process smooth and accurate.