Are you struggling to decide between shearing and laser cutting for your sheet metal cutting needs? Choosing the right method can transform your project’s efficiency, quality, and cost. As experts in CNC processing, we at HYCNC understand the stakes of picking the perfect cutting technique. In this guide, we’ll break down the key differences between shearing and laser cutting, offering clear, practical insights based on real-world applications. Whether you’re crafting automotive parts or intricate aerospace components, you’ll discover which method suits your goals. Let’s dive into the sheet metal cutting contrast and find the best solution for you!
Overview of Sheet Metal Cutting
Sheet metal cutting is a fundamental process in metal fabrication where flat metal sheets are shaped or sized by removing or separating sections. It’s essential in creating parts for industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and construction. The goal is to prepare metal sheets for further manufacturing or assembly with precision and efficiency.
Common methods for cutting sheet metal include shearing, laser cutting, plasma cutting, and waterjet cutting. Each offers distinct advantages depending on the material, thickness, and desired outcome. Shearing uses mechanical force to slice metal sheets, while laser cutting employs focused light to achieve fine, intricate cuts.
In today’s manufacturing environment, CNC cutting plays a crucial role. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines automate the cutting process, enhancing accuracy, repeatability, and speed. Whether it’s CNC machining for complex shapes or CNC laser cutting for precision edges, these technologies streamline production and reduce material waste, making them indispensable in modern sheet metal fabrication.
Shearing Process Features and Applications

What is Shearing
Shearing is a straightforward sheet metal cutting technique where a straight blade slices through metal by applying force. Think of it like using giant scissors to cut metal sheets into desired sizes. It’s one of the oldest and most common methods in sheet metal fabrication, often done using a shearing machine or hydraulic shearing equipment.
How Shearing Works
In shearing, the metal sheet is placed flat on a platform, and a blade moves down vertically or at an angle to cut through the material. The process relies on a mechanical or hydraulic press that pushes the blade with enough force to shear the metal along a straight line. It doesn’t remove any metal; it just separates the piece into parts.
Advantages of Shearing
- Fast and efficient for straight cuts on sheet metal.
- Low cost compared to more complex cutting methods.
- Minimal setup time, making it great for high-volume projects.
- Requires less maintenance and simpler equipment.
- Suitable for various metal types, including steel, aluminum, and stainless steel.
Limitations of Shearing
- Only cuts in straight lines, no curves or intricate shapes.
- Edge finish can be rough, sometimes needing additional processing.
- Limited thickness capability—too thick metals are hard to shear.
- Less precise compared to CNC-controlled methods, which affects design complexity.
Applications
Shearing is ideal when you need a quick, clean straight cut without much fuss. It is commonly used in:
- Cutting large sheets into smaller sections.
- Preparing stock for further processing like bending or welding.
- Fabricating parts that don’t require detailed shapes, such as brackets, panels, and covers.
For more details on sheet metal cutting methods and costs, check out our Sheet Metal Cutting Cost guide.
Laser Cutting Process Features and Applications
What is Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a precise metal cutting technique that uses a focused laser beam to slice through sheet metal. It’s widely used in sheet metal fabrication, especially where detailed and complex shapes are required. This method fits perfectly with CNC machining systems, offering high accuracy and clean edges.
How Laser Cutting Works
A laser cutting machine directs a high-powered laser beam onto the metal surface. The laser heats, melts, or vaporizes the material in a controlled way, guided by CNC cutting software to follow exact designs. Fiber laser cutting, a modern type of laser cutting, offers faster speeds and works well with various metals, including stainless steel and aluminum.
Advantages of Laser Cutting
- High precision and clean cuts with smooth edges
- Great for complex shapes and detailed designs
- Fast processing with less material distortion
- Can cut a wide range of metal types and thicknesses
- Minimal need for secondary finishing after cutting
- Compatible with CNC cutting for automation and repeatability
Limitations of Laser Cutting
- Higher upfront cost compared to traditional cutting methods like shearing
- Can be slower on very thick metal sheets
- Requires skilled operators and proper maintenance
- Some materials may reflect the laser, affecting cutting efficiency
Applications of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is ideal for detailed metal fabrication projects like custom enclosures, automotive parts, aerospace components, and decorative panels. It’s a top choice for businesses needing fast, precise metal cutting services for both prototypes and high-volume runs.
Head to Head Comparison Shearing vs Laser Cutting
Precision and Quality
Laser cutting leads when it comes to precision and finish. It can cut intricate shapes with clean, smooth edges and minimal burring. Shearing is more basic—it’s great for straight cuts but won’t offer the same level of detail or edge quality. If you need tight tolerances or complex designs, laser cutting is the clear winner.
Speed and Efficiency
Shearing works fast for simple, straight cuts, especially in thin to medium thickness sheet metal. Laser cutting takes a bit longer due to the precise beam control but can handle complex patterns in a single pass without tool changes. For high volume, repetitive straight cuts, shearing saves time, but for custom or complex cuts, laser cutting is more efficient.
Cost Considerations
Shearing machines generally cost less to operate and maintain. They’re simpler and don’t need expensive consumables. Laser cutting has higher upfront and operating costs due to equipment and energy needs. However, for projects requiring precision or complex shapes, laser cutting reduces labor and finishing costs, balancing out expenses.
Material Versatility
Laser cutting works well on a wider range of materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, and even some plastics. Shearing is mostly limited to thinner metals, and very thick or hard metals can be tricky. If your project demands different materials or thicknesses, laser cutting offers more flexibility.
Design Flexibility
Shearing is best for straight, simple cuts—it’s not designed for curves or patterns. Laser cutting excels here, handling curves, holes, and intricate designs with ease, making it ideal for custom or detailed parts.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Shearing produces no fumes or dust, making it a cleaner process, but it involves moving heavy metal parts that can pose safety risks without proper precautions. Laser cutting emits fumes and requires ventilation, plus safety safeguards to protect operators from the laser beam. Both methods need proper safety measures, but shearing’s mechanical nature generally means fewer airborne hazards.
Summing it up: For straightforward, fast, and cost-effective cuts on common sheet metals, shearing is solid. For precision, complex designs, and material variety, laser cutting is the go-to choice in modern sheet metal fabrication and CNC cutting environments.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Project
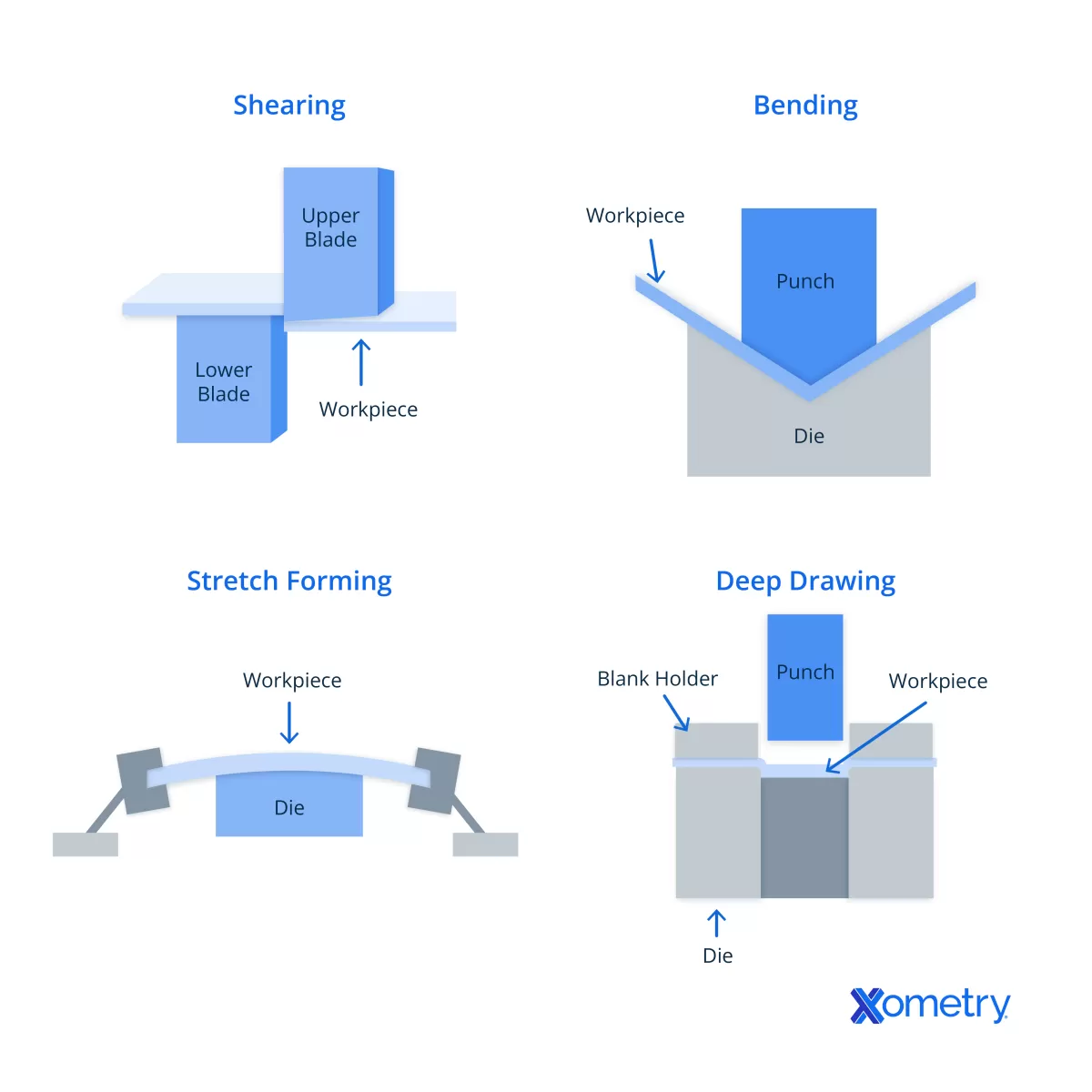
Picking the right sheet metal cutting method depends on your project’s needs, budget, and the kind of metal you’re working with. Here’s a quick guide to help you decide between shearing and laser cutting.
Factors to Consider
- Material Type and Thickness: Thick sheets work better with shearing, while laser cutting handles thin to medium metals with high precision.
- Precision and Detail: If your design requires tight tolerances or complex shapes, laser cutting is the way to go.
- Quantity and Speed: For large volumes and straight cuts, shearing is faster and more cost-effective.
- Budget: Shearing usually costs less upfront, but laser cutting offers lower waste and less finishing work.
- Design Complexity: Laser cutting supports intricate patterns and small details; shearing works best for simple, straight cuts.
When to Choose Shearing
- You need quick, straight cuts on thicker sheet metals.
- The project is straightforward without detailed or intricate shapes.
- Budget constraints call for a cost-effective cutting option.
- You’re producing large batches where speed matters.
When to Choose Laser Cutting
- The project requires high precision and detailed cuts.
- You’re working with thin to medium-thickness metals.
- Complex shapes, holes, and fine features are needed.
- Minimizing post-cutting finishing is a priority.
- You want flexibility for various metal types.
HYCNC’s Solutions
At HYCNC, we offer both hydraulic shearing and fiber laser cutting services, tailored to your project’s specific needs. Our CNC cutting expertise means you get precision metal cutting no matter the scale or complexity. Whether you need fast, cost-effective shearing or high-end laser cutting for detailed work, we deliver reliable, top-quality results here in the U.S. We help businesses choose the right metal fabrication process to save time and control costs while getting the job done right.
FAQs
What is the main difference between shearing and laser cutting?
Shearing is a straight-edge cutting process that uses a blade to slice through sheet metal, ideal for simple cuts and straight lines. Laser cutting uses a focused laser beam to cut complex shapes with high precision and smooth edges.
Which method is better for precision metal cutting?
Laser cutting offers higher precision and cleaner edges, making it perfect for detailed designs. Shearing is faster for straight cuts but doesn’t provide the same level of detail.
Can shearing handle thick metals?
Shearing works best on thinner sheets up to certain thicknesses. For thicker or harder metals, laser cutting or other cutting methods might be more effective.
Is laser cutting more expensive than shearing?
Laser cutting usually has a higher upfront cost due to machine investment and energy use. Shearing is generally more affordable for basic cuts and large volumes.
How important is CNC in these cutting methods?
Both shearing and laser cutting benefit from CNC technology. CNC machining improves accuracy, repeatability, and speed, especially for complex cuts in laser cutting.
Which method is more environmentally friendly?
Shearing produces minimal waste and uses less energy. Laser cutting can consume more power but reduces material waste by allowing precise cuts and nesting.
When should I choose shearing over laser cutting?
Pick shearing when you need fast, straight cuts on large sheets and a more budget-friendly option. It’s great for simple parts and large batch runs.
When is laser cutting the better option?
Choose laser cutting for complex shapes, fine details, and when a smooth finish is essential. It’s ideal for prototypes, intricate designs, and a variety of metal types.
Can HYCNC help with both shearing and laser cutting needs?
Yes, HYCNC offers professional CNC sheet metal fabrication including hydraulic shearing and fiber laser cutting services tailored to your project requirements. We’ll help you choose the best method for your needs.