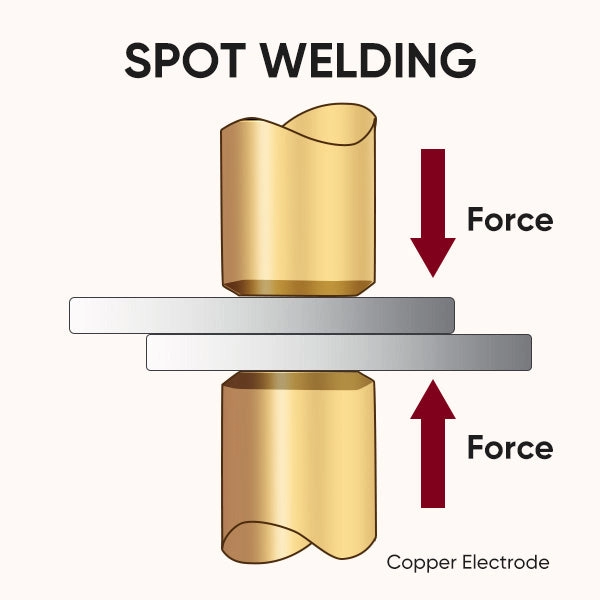
What is Spot Welding
Have you ever wondered how two pieces of metal are joined quickly and securely without adding extra materials? That’s spot welding. It’s a type of resistance welding where electrical current and pressure come together to create a strong bond between metal sheets.
Spot welding works by passing a high electric current through two copper electrodes that clamp the metal pieces. The resistance between the metals generates heat, which melts the contact area just enough to fuse them together. Once the current stops, the metals cool and solidify as a welded joint, often called a weld nugget.
This process is popular because it’s simple, fast, and cost-effective. You don’t need filler metals or flux, and the equipment is straightforward. Spot welding is ideal for joining thin sheets of metal and is widely used in industries like automotive manufacturing and electronics where speed and precision matter.
How Does Spot Welding Work
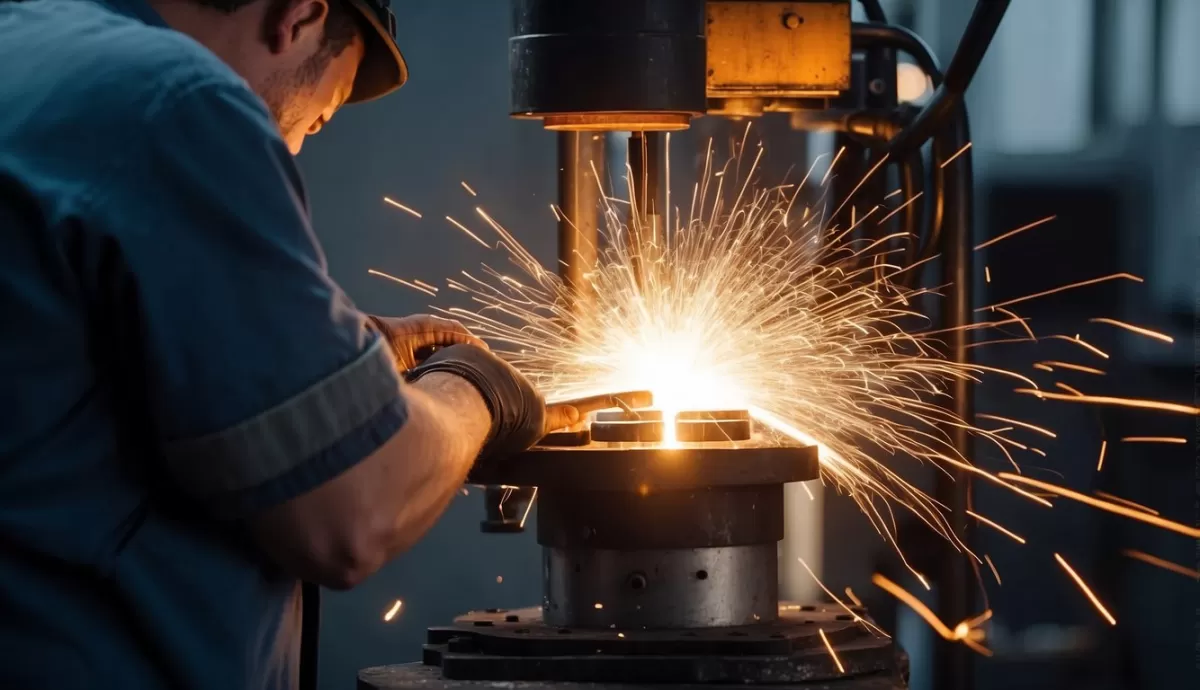

Spot welding starts with proper preparation. Cleaning the metal surfaces is essential to ensure good electrical conductivity and a strong weld. Any dirt, rust, or oil can interfere with the process, so cleaning is a must.
Next is alignment. The metal sheets are carefully positioned between two copper alloy electrodes. These electrodes conduct electricity and apply pressure right where the weld will form.
When the electrodes are in place, a high electric current passes through the metals at the contact point. The resistance to the current generates intense heat, causing the metal to melt just enough to fuse together. This spot is often called the weld nugget.
Pressure is applied by the electrodes during the current flow to hold the metals tightly together. After the current stops, cooling solidifies the weld, making a strong bond between the sheets.
The weld quality depends on several key parameters, including:
- Current intensity and duration
- Electrode pressure and alignment
- Metal thickness and type
- Surface cleanliness
Controlling these factors carefully ensures consistent, high-quality spot welds. For more on avoiding spot welding defects, check out common solutions here.
Types of Spot Welding
Spot welding comes in several types, each suited for different materials and applications. The most common is Resistance Spot Welding, widely used in the automotive industry and sheet metal fabrication. This method uses copper electrodes to apply pressure and pass electrical current through metal sheets, creating strong weld nuggets quickly and efficiently.
For materials with high conductivity like aluminum, Capacitor Discharge Spot Welding is a great option. It delivers a short, high-energy current burst, making it easier to weld metals that are harder to join using traditional resistance spot welding.
When working with plastics or lightweight metals, Ultrasonic Spot Welding is preferred. This technique uses high-frequency vibrations to generate heat at the joint, providing a clean weld without melting the entire material.
All these spot welding methods can be seamlessly integrated into CNC workflows. Combining spot welding with CNC machining and automation ensures precise, repeatable welds at a high speed, ideal for high-volume production runs and complex assemblies. This integration enhances efficiency and quality control in metal fabrication and other industries.
Applications of Spot Welding
Spot welding is widely used across several industries thanks to its speed and reliability. In the automotive industry, it’s the go-to method for joining car body panels, ensuring strong, seamless connections that hold up under stress. The aerospace sector relies on spot welding for assembling lightweight aircraft parts where precision and strength are critical.
In electronics, spot welding is key for manufacturing circuit boards and battery packs, providing precise, clean welds without damaging sensitive components. The construction and appliance industries also use spot welding to join structural metal parts and build durable furniture.
Many of these applications benefit from specialized CNC metal fabrication services, which integrate spot welding into automated workflows for consistent quality and efficiency. This helps businesses in the U.S. keep production running smoothly while maintaining high standards.
Advantages of Spot Welding

Spot welding is favored for its incredible speed, often completing welds in just 0.01 to 0.63 seconds. This quick process boosts productivity, especially for high-volume jobs like automotive manufacturing.
It’s also cost-effective since it doesn’t require extra materials like filler metals or flux, cutting down on expenses and cleanup time.
With automation compatibility, spot welding fits seamlessly into robotic systems and CNC workflows, making it a go-to for modern metal fabrication shops aiming for precision and efficiency.
Lastly, spot welding uses localized heat, which means only the weld area gets hot. This helps minimize distortion and damage to the surrounding metal, ensuring a cleaner, more precise weld every time.
Limitations of Spot Welding

Spot welding works best with conductive metals like steel and some aluminum alloys, which means it’s not suitable for non-conductive materials or very thick metals. If the metal is too thick, the weld might not penetrate fully, leading to weak joints.
Another downside is the appearance—spot welds often leave visible marks that need extra finishing or grinding to look clean. This can add time and cost, especially in applications where aesthetics matter.
Also, spot welding demands careful control of parameters like current, pressure, and timing. Without skilled operators or precise CNC programming, weld quality can suffer, resulting in weak or inconsistent joints.
That’s where CNC expertise makes a difference. With advanced CNC machining and welding automation, it’s easier to set precise controls, monitor weld quality, and reduce human error—helping overcome many of these limitations efficiently.
Spot Welding vs Other Welding Methods

When comparing spot welding to MIG and TIG welding, each method has its strengths. MIG and TIG offer more versatility because they can handle different materials and thicknesses, often creating stronger, more flexible joints. But spot welding wins on speed and cost. It’s much quicker—usually less than a second per weld—and doesn’t require extra materials like filler or flux, which keeps things simple and affordable.
Clinching is another alternative that joins metals without heat. It’s great for avoiding heat damage, but it’s only good for thinner sheets and can’t handle thicker metals like spot welding can.
Spot welding’s speed, low cost, and easy automation make it a favorite for CNC applications. It fits right into automated workflows and works perfectly for the sheet metal parts often made with CNC machining. That’s why spot welding is often the go-to choice in industries focused on efficiency and precision fabrication.
Spot Welding Equipment and Technology
Spot welding uses different types of equipment depending on the job size and volume. For small or on-site tasks, portable spot welders are popular because they’re easy to carry and quick to set up. In workshops, bench spot welders are common—they offer steady power and control for sheet metal welding projects. For large-scale manufacturing, like automotive or aerospace, robotic spot welders handle high-volume production with speed and consistent quality.
Advanced spot welding technology also improves precision and efficiency. Modern machines come with better control systems to monitor weld quality and adjust parameters in real-time. This means less material waste and stronger weld nuggets. Whether you need a simple handheld tool or a fully automated system, the right spot welding equipment makes all the difference for reliable and cost-effective metal fabrication.
Safety Tips for Spot Welding

Spot welding involves high heat and pressure, so safety is a must. Here are some key tips to keep in mind:
- Watch out for pinch points between the copper electrodes. Your fingers or hands can get caught if you’re not paying attention.
- Always wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from sparks or metal splatter.
- Make sure your workspace is well-ventilated to avoid inhaling any fumes produced during welding.
- Use shrouds or guards on foot switches to stop accidental machine activation.
Following these safety steps helps prevent injuries and keeps your spot welding projects smooth and trouble-free.
Why Choose HYCNC for Spot Welding and CNC Services
At HYCNC, we combine expert spot welding with advanced CNC machining services to deliver precise, reliable results every time. Our integration of spot welding into CNC workflows means you get consistent weld quality with automated efficiency—perfect for industries that demand speed and accuracy.
Choosing HYCNC means benefiting from:
- Precision welding tailored to your specific metal fabrication needs
- Automation-ready processes for faster turnaround and reduced costs
- Industry-focused solutions spanning automotive, aerospace, electronics, and more
- Expert handling of complex materials with strict weld quality control
If you’re looking for top-notch spot welding paired with professional CNC services, reach out to HYCNC. We provide customized solutions designed to meet your project goals efficiently. Contact us today to learn how we can support your fabrication needs.