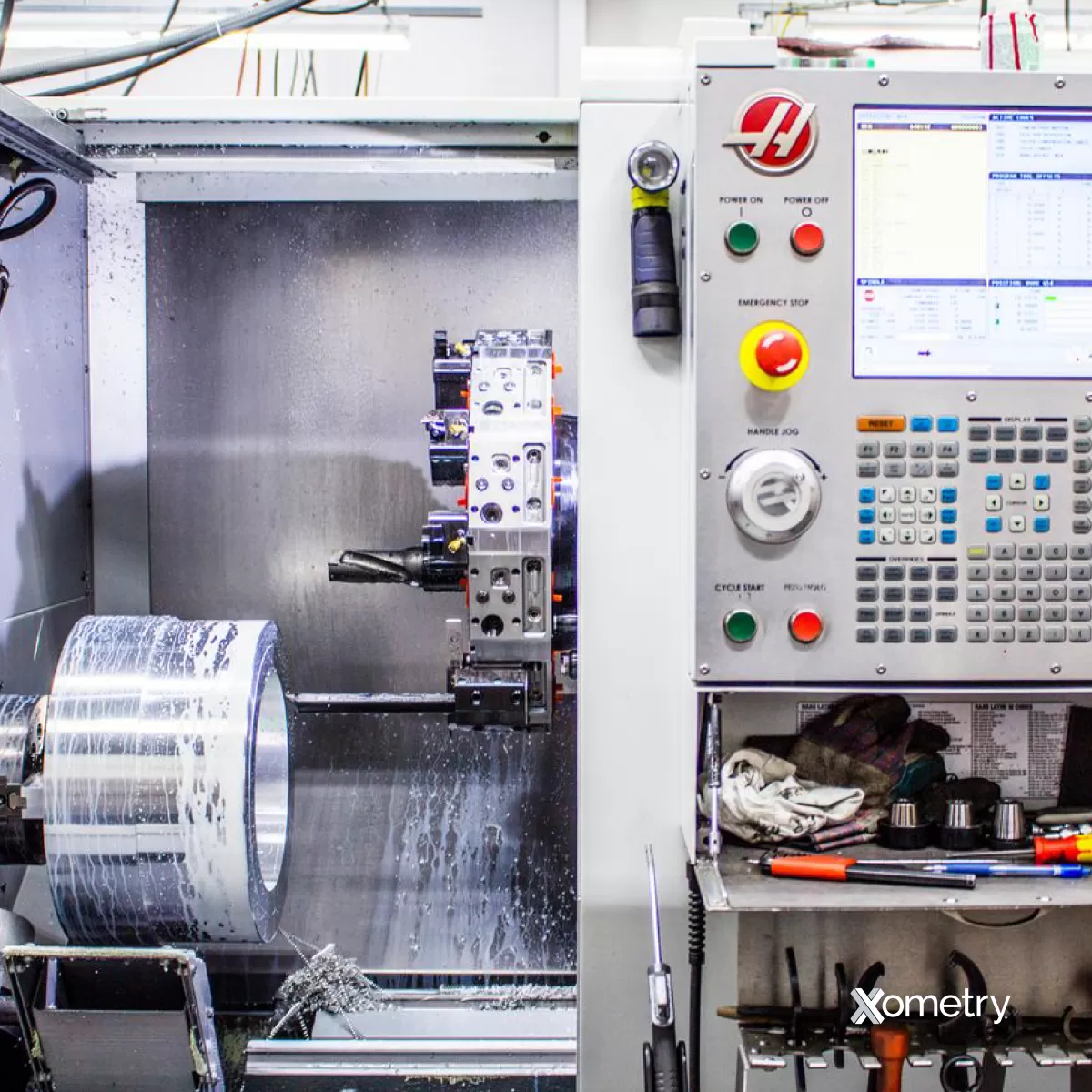
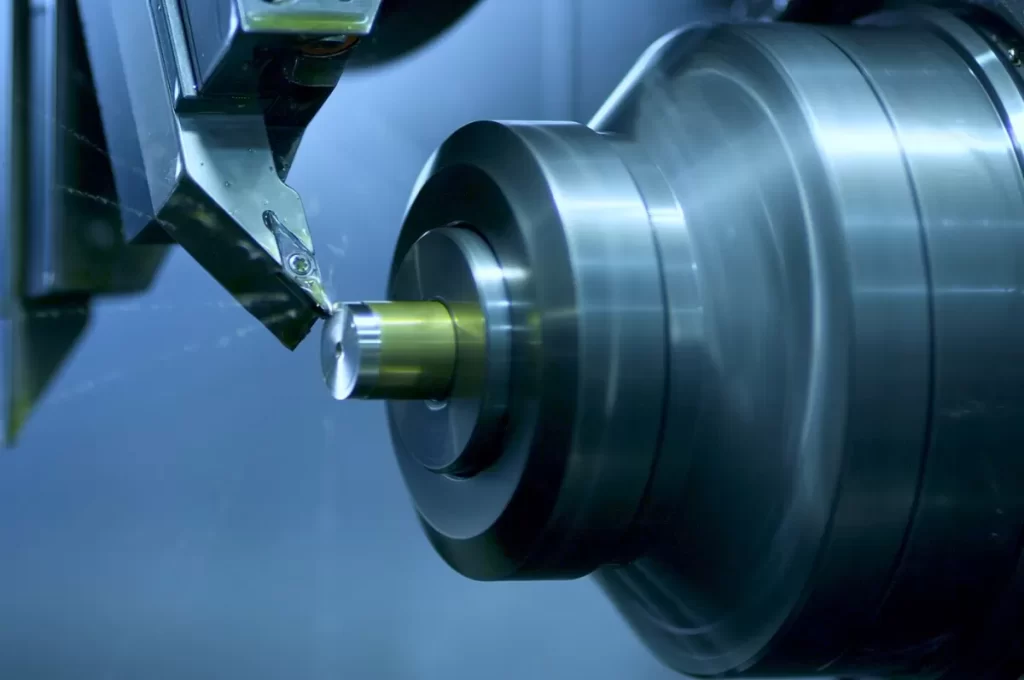
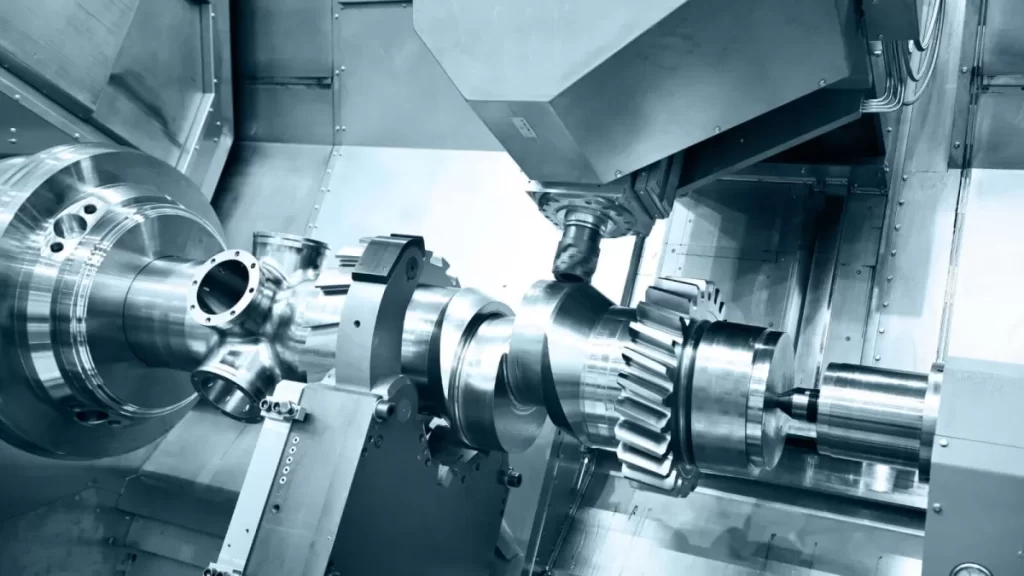
Are you torn between CNC prototyping and 3D printing for your next project? Choosing the right manufacturing method can make or break your timeline, budget, and product quality. As prototyping experts at HYCNC, we’ve guided countless designers and engineers through this decision with real-world solutions. Whether you need precision parts or complex designs fast, this guide breaks down the differences, benefits, and costs of CNC versus 3D printing to help you pick the perfect approach. Ready to make an informed choice? Let’s dive in!
Introduction to CNC Prototyping and 3D Printing
Are you wondering whether CNC prototyping or 3D printing is right for your project? Both methods have transformed how products move from concept to reality, but they work very differently.
What Is CNC Prototyping
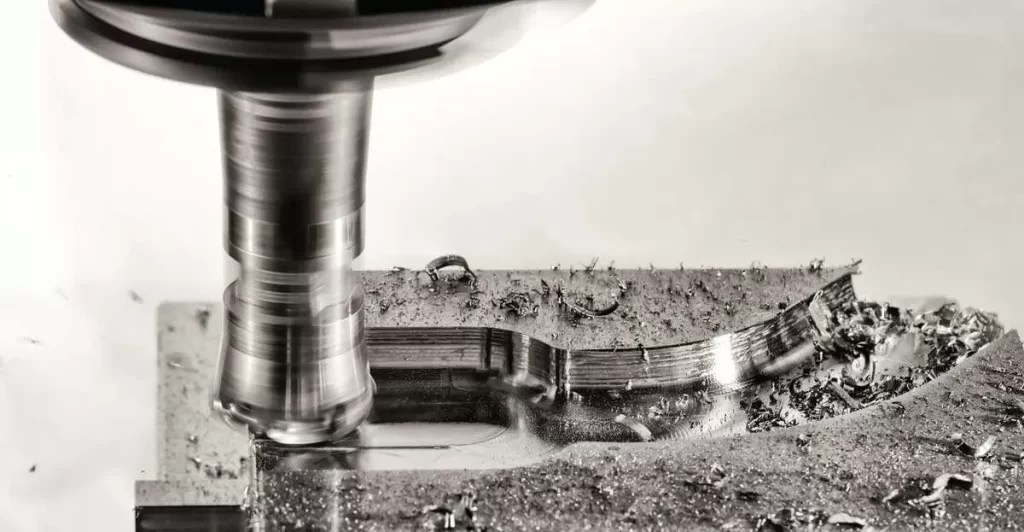
CNC prototyping uses computer-controlled machines to cut material away from a solid block, shaping parts with high precision. This process, known as subtractive manufacturing, has been around since the 1940s when early CNC machines revolutionized manufacturing by automating drilling and milling tasks. Today, CNC machining is widely used across industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices for creating functional prototypes and low-volume production parts with tight tolerances.
What Is 3D Printing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, builds parts layer by layer from materials like plastics, resins, or metals. Invented in the 1980s, it initially served rapid prototyping but quickly expanded into making complex geometries and custom components. Industries such as healthcare for custom implants, consumer products, and even construction use 3D printing for fast prototyping and unique designs that would be hard to make with traditional methods.
Why Compare CNC and 3D Printing
Choosing between CNC machining vs 3D printing depends on factors like material, part complexity, cost, and speed. Understanding their strengths helps you pick the right prototyping method—whether you need sharp precision, quick turnaround, or intricate shapes. This guide breaks down the key differences and when to use each for your best results.
Key Differences Between CNC Prototyping and 3D Printing
When comparing CNC prototyping vs 3D printing, understanding their main differences helps decide which fits your project best.
Manufacturing Process
- CNC Prototyping uses subtractive manufacturing. It starts with a solid block of material, and machines cut away what’s not needed.
- 3D Printing is additive. It builds parts layer by layer, usually from melted plastic or metal powders.
Precision and Tolerances
- CNC machines deliver high precision, often within thousandths of an inch, making them ideal for tight tolerances.
- 3D printing can produce detailed shapes but usually has less precision and looser tolerances, depending on the technology used.
Material Options
- CNC prototyping works with metals, plastics, and hardwoods, offering a broad range of real-world materials.
- 3D printing materials include various plastics, resins, and some metals, but options are often more limited compared to CNC machining.
Speed and Turnaround Time
- 3D printing is typically faster for quick, low-volume prototypes or complex parts because it doesn’t require tooling.
- CNC prototyping can take longer due to setup and machining time, especially for complex parts or tougher materials.
Cost Considerations
- 3D printing usually has lower upfront cost, making it cost-effective for low-volume or one-off parts.
- CNC is more cost-efficient for medium-to-high volume runs, but initial setup and tooling can add to expenses.
Geometric Complexity
- 3D printing excels at making intricate, complex shapes that would be hard or impossible to machine.
- CNC prototyping works best for simpler geometries but struggles with internal cavities and highly complex designs.
Understanding these differences makes it easier to pick the right prototyping method for your needs, whether you want speed, precision, material choice, or cost efficiency.
Pros and Cons of CNC Prototyping
Advantages
- High precision and accuracy: CNC machining offers tight tolerances, making it ideal for parts that need exact measurements.
- Wide material options: From metals like aluminum and steel to plastics, CNC prototyping supports a broad range of materials.
- Strong and durable parts: Since it’s a subtractive process, parts are solid and sturdy, often matching production-level quality.
- Surface finish: CNC can provide smooth finishes that usually require little to no post-processing.
- Repeatability: Great for producing multiple prototypes with consistent quality and dimensions.
Limitations
- Complex geometries are challenging: CNC struggles with very intricate shapes or internal cavities that can be made easily with 3D printing.
- Higher setup time and cost: Initial programming and tooling take longer and add cost, especially for small runs.
- Material waste: Since it cuts away from a block, it produces more scrap compared to additive processes like 3D printing.
- Limited to rigid materials: Soft or flexible prototypes are harder to achieve with CNC machining.
Understanding these pros and cons helps you decide if CNC prototyping fits your project needs, especially when precision and material strength are priorities.
Pros and Cons of 3D Printing Advantages Limitations

3D printing offers some clear benefits that make it popular for many prototyping projects:
- Fast turnaround: You can go from design to part quickly, especially for complex shapes.
- Complex geometries: It handles intricate designs and internal features that CNC machining can’t easily make.
- Low waste: As an additive process, it uses only the material needed, reducing scrap.
- Customization: Ideal for one-off parts or small batches with unique features.
- Wide range of materials: Including plastics, resins, and some metals, suited for prototypes and functional parts.
However, there are some limitations to keep in mind:
- Surface finish and strength: 3D printed parts often need extra finishing and might not match CNC parts in durability.
- Precision and tolerances: Generally, 3D printing has lower accuracy compared to CNC machining.
- Material restrictions: While growing, the choice of materials is still narrower than CNC’s options.
- Speed on larger runs: For bigger production runs, 3D printing can be slower and more costly.
- Post-processing needs: Parts usually require cleaning, curing, or support removal, adding time and effort.
Understanding these pros and cons helps you decide when 3D printing fits your project best. For some projects, it’s unbeatable, while others call for the precision and material flexibility of CNC prototyping.
When to Choose CNC Prototyping
CNC prototyping is your go-to when you need high precision and strong, durable parts. It works best if your prototype must closely match the final product in material and finish. Think metal components, tight tolerances, or parts that have to withstand real-world stress.
Choose CNC prototyping when:
- You require excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy
- The design uses standard materials like aluminum, steel, or plastics that CNC machines can handle
- You need quick turnaround time for low- to medium-volume runs
- Complex machining or detailed cuts are necessary but don’t involve overly complex internal geometries
- Your prototype will undergo functional testing, like mechanical or thermal performance
In short, CNC machining is ideal if your project demands precise, strong parts made from traditional industrial materials. It’s also well-suited for those who value tight tolerances and a professional-grade look without relying on 3D printed layers.
When to Choose 3D Printing
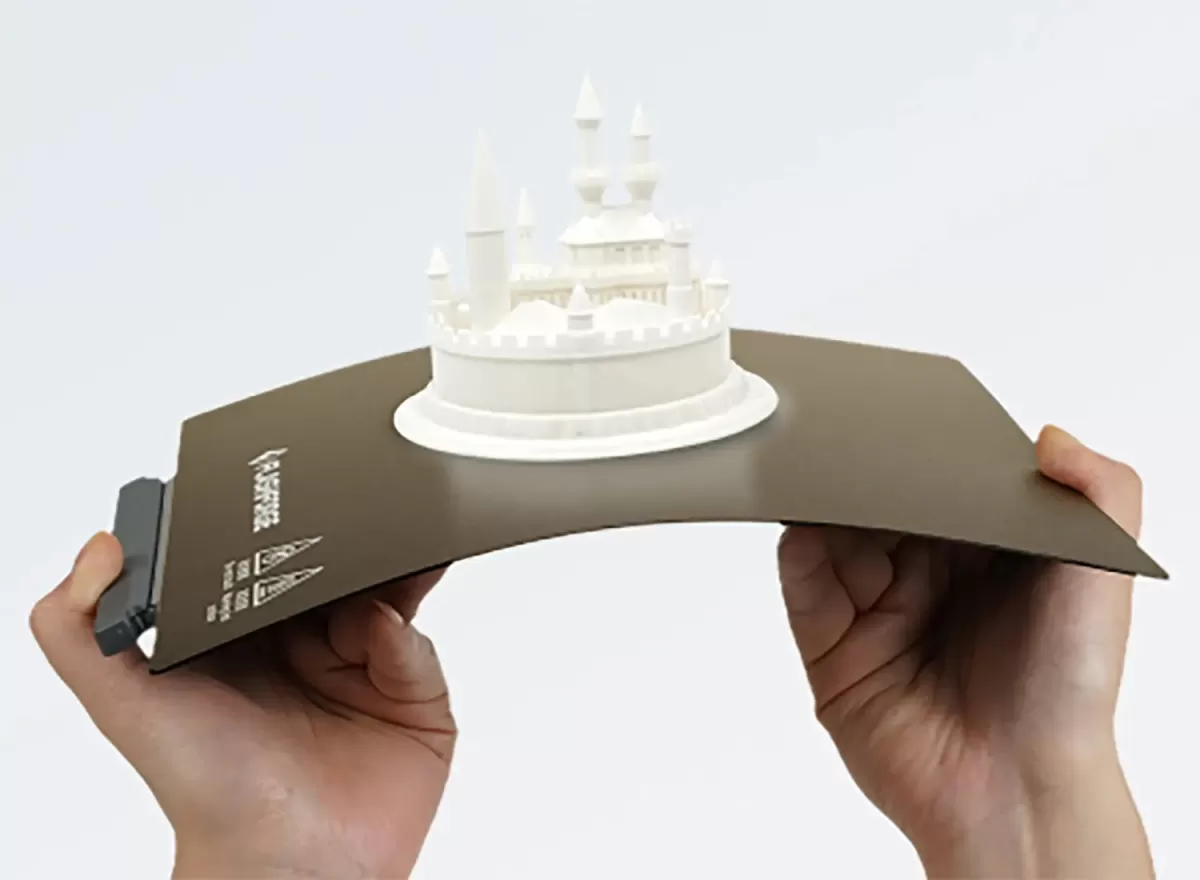

3D printing is your go-to when you need quick, cost-effective prototypes, especially for complex shapes that are tough to make with CNC machining. It’s great for:
- Testing unique or intricate designs that involve internal features or complex geometries
- Rapid iterations to tweak your model without extra setup costs
- Low-volume production or one-off custom parts
- Using lightweight or specialized materials like certain plastics and resins
- Projects where speed matters more than tight tolerances
- Creating parts with less waste, since it’s an additive process building layer by layer
If your prototype needs fast turnaround, a flexible design, or involves shapes that subtractive manufacturing can’t handle easily, 3D printing often saves you time and money. It’s also the smarter choice for startups and small businesses in the US market aiming for affordable prototyping without compromising design freedom.
Cost Comparison CNC vs 3D Printing
Low-Volume Production
When it comes to low-volume production, 3D printing usually has the edge. Since it’s an additive process, there’s minimal setup involved, which means you can go straight from design to part quickly and affordably. For small batches or custom parts, 3D printing keeps costs down because you don’t need expensive tooling or extensive programming like with CNC machining. This makes 3D printing a popular choice for prototypes, one-offs, or limited runs.
Medium-to-High Volume Production
For medium to high volumes, CNC prototyping becomes more cost-effective. Although CNC requires some upfront costs for tooling and machine setup, the per-part cost drops significantly as you produce more parts. CNC machining is faster for producing large quantities of parts with consistent precision and durable materials. So, if your project demands hundreds or thousands of parts, CNC machining usually wins on cost and speed.
Material and Post-Processing Costs
Material choice affects cost in both methods. CNC offers a wide range of metals and plastics, often at competitive prices, but waste material increases costs due to its subtractive process. On the other hand, 3D printing materials tend to be more expensive per pound, especially for advanced polymers and resins. Post-processing is another factor—CNC parts often require less finishing, while 3D printed parts may need cleaning, curing, or smoothing to reach the desired look and strength. These extra steps can add time and cost to 3D printed prototypes, depending on your needs.
In , 3D printing saves money on low-volume, complex designs, while CNC machining is more economical for larger quantities and offers a broader choice of materials with tighter tolerances. Your project size, production speed, and material needs will guide which method costs less overall.
Combining CNC and 3D Printing for Optimal Results

Sometimes the best way to get the perfect prototype is by using both CNC prototyping and 3D printing together. This combo lets you take advantage of the strengths of each method while covering their weaknesses.
Here’s how combining CNC machining and 3D printing works in your favor:
-
Start with 3D Printing for Complex Shapes: 3D printing handles intricate, detailed designs and complex geometries that would be tough or time-consuming for CNC. It’s great for quick, low-volume runs or custom parts with lots of curves and internal features.
-
Use CNC Machining for Precision and Finish: After 3D printing, CNC machining can clean up the part, improve surface finish, and achieve tighter tolerances. This is especially useful when functional parts need strength or exact fits, which 3D printing alone might not provide.
-
Save Time and Costs: By 3D printing initial prototypes or detailed areas, then switching to CNC for finishing, you cut overall production time and material waste. This hybrid approach often beats relying on just one method.
-
Expand Material Options: Combining both lets you work with a wider range of materials. Use plastic or resin 3D prints for form prototypes and CNC machine metals or harder plastics for functional testing.
For businesses in the US looking to balance speed, quality, and costs, blending CNC and 3D printing is a smart move. It maximizes the benefits of subtractive and additive manufacturing, giving you tailored prototypes that check all the boxes.
How HYCNC Can Help You Choose
At HYCNC, we understand that deciding between CNC prototyping and 3D printing can be tricky. That’s why we offer expert guidance tailored to your project’s specific needs. Whether you’re working on a low-volume run, need tight CNC machining tolerances, or want to explore complex 3D printing designs, we help you pick the best rapid prototyping method.
Our team evaluates factors like:
- Material options for prototyping
- Desired precision and finish
- Turnaround time and budget
- Geometric complexity of your design
By combining both subtractive and additive manufacturing insights, we deliver solutions that save you time and money. Plus, if your project benefits from blending CNC machining and 3D printing, we’ll help you optimize that hybrid workflow.
Visit our rapid prototyping services page to learn how HYCNC can streamline your prototyping process and get your product to market faster.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Choosing between CNC prototyping and 3D printing comes down to what your project really needs. If you want tight tolerances, strong materials, and clean finishes, CNC machining is often the way to go. It’s perfect for parts that need durability or when you’re working with metals and harder materials.
On the other hand, 3D printing shines when you need quick turnaround times, complex shapes, or low-volume custom parts. It’s cost-effective for rapid prototyping and can handle designs that CNC can’t easily produce due to its subtractive nature.
Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer here. Think about factors like:
- Material needs
- Production volume
- Design complexity
- Cost limits
- Speed of delivery
For many U.S.-based businesses, combining both CNC and 3D printing can bring out the best in each method. Start with 3D printing for fast prototypes, then move to CNC for precision and strength in final parts.
If you’re unsure about the best fit for your project, HYCNC can help you navigate these choices based on your specific requirements. Getting the right prototyping method helps speed up your product development while controlling costs.
In the end, understanding the differences between CNC machining vs 3D printing is key to making smart decisions that save time, reduce waste, and deliver quality results.