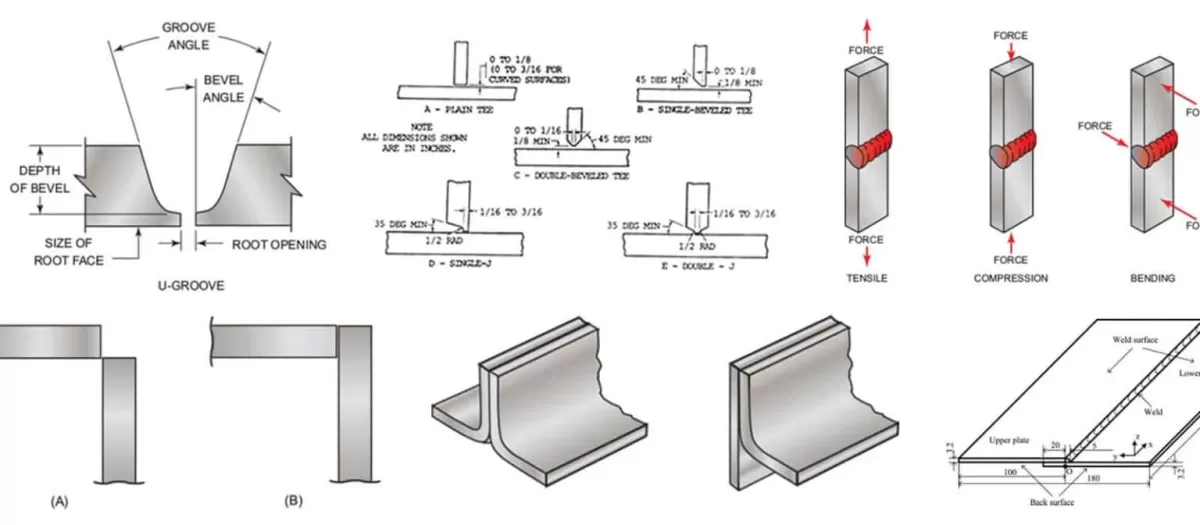
What Are Welding Joints
Welding joints are the specific ways two or more pieces of metal are joined together through welding. Simply put, they define how the surfaces meet and fuse during the welding process. The type of welding joint you choose influences the strength, durability, and overall quality of the finished product.
Understanding welding joints is crucial because they affect everything from structural integrity to ease of fabrication. The right joint can prevent weak spots and reduce the chance of weld defects, which saves time and money in production.
When it comes to CNC machining and fabrication, welding joints play a key role. CNC machines prepare parts with precision, ensuring tight fits and correct angles for each joint type. This accuracy is essential for consistent weld quality, especially in industries that demand high-performance metal. Proper joint design paired with CNC machining improves efficiency and results stronger, more reliable welded structures.
The 5 Basic Types of Welding Joints

Welding joints come in different styles, each suited to specific tasks and materials. Understanding the 5 basic types of welding joints helps you pick the right one for your project, especially when combining welding with CNC machining for precision results. Here’s a quick breakdown of each type, including what they are, where you can use them, their pros and cons, and how HYCNC brings value to the process.
1. Butt Joint
Description
Two pieces of metal are placed edge edge in the same plane and welded along the seam.
Variations**
Single butt, double butt, and beveled edges for deeper penetration.
Applications
Common in pipelines, sheet metal fabrication, and structural parts.
Pros
Strong weld with good penetration
Simple setup and easy to inspect
Cons
Requires precise alignment
May need edge preparation
HYCNC Insight
With our CNC machining services, we ensure exact edge preparations, making your butt joint welds clean and strong every time.
2. Tee Joint
Description
One piece of metal is positioned perpendicular to another, forming a “T” shape and welded at the intersection.
Variations
Fillet welds on one or both sides.
Applications
Used in frames, supports, and cross-sections of structures.
Pros
Offers good strength with less prep
Easy access for welding
Cons
Can be prone to stress at the junction
May require multiple welds for strength
HYCNC Insight
Our precise CNC cutting allows for tight fits in tee joints, reducing stress points and improving overall weld quality.
3. Corner Joint
Description
Two metal pieces meet at a right angle, typically forming a corner, and welded on the outside edge.
Variations
Closed or open corners, with single or double fillet welds.
Applications
Commonly found in box frames, cabinets, and metal enclosures.
Pros
Good for joining perpendicular parts
Relatively easy to weld
Cons
Not ideal for high-stress applications
Can be weak on the inside corner if not welded properly
HYCNC Insight
Using CNC for accurate cuts helps our customers avoid gaps that weaken corner joints, ensuring tighter, stronger weld connections.
4. Lap Joint
Description
One piece of metal overlaps another and is welded along the edge of the overlap.
Variations
Partial or full overlap depending on thickness and load requirements.
Applications
Widely used in sheet metal fabrication and repair work.
Pros
Strong joint for uneven thicknesses
Requires less precision in alignment
Cons
Added thickness can increase weight
Potential corrosion issues if not sealed properly
HYCNC Insight
Our CNC precision ensures perfectly trimmed parts for lap joints, minimizing material waste and optimizing fit.
5. Edge Joint
Description
Edges of two or more pieces are placed side by side and welded along the edge.
Variations
Used mostly on sheets or thin parts where edges can be joined.
Applications
Ideal for sheet metal fabrication, panels, and flanges.
Pros
Suitable for joining thin material
Easy to prepare for welding
Cons
Not very strong under heavy loads
Limited to thinner materials
HYCNC Insight
With our CNC service, edge joints get precise edge finishing, which reduces weld defects and improves quality on delicate thin materials.
Choosing the right welding joint depends on your project needs. At HYCNC, we combine expert CNC machining with welding know-how so your joints come out perfect — strong, clean, and fit for purpose every time.
How to Choose the Right Welding Joint
Factors to Consider
Picking the right welding joint depends on a few key factors:
-
Material Type and Thickness: Different joints work better with specific metals and thicknesses. Thin sheets usually need joints like butt or lap joints, while thicker materials might require corner or tee joints.
-
Strength Requirements: Think about how much load or stress the joint will face. Butt and tee joints often offer strong, reliable bonds for structural uses.
-
Accessibility and Welding Position: Sometimes the joint location limits the welding angle or tools you can use. Choose joints that match your workspace and welding setup.
-
Cost and Efficiency: Some joints are faster and cheaper to prepare and weld, which impacts your project timeline and budget.
-
Final Application: Consider the part’s design and function. For example, lap joints are great for overlapping metal in sheet fabrication, while edge joints suit sealing or joining edges.
HYCNC’s Role
At HYCNC, we help you figure this out by combining our CNC machining precision with welding know-how. We assess your product’s needs, material specs, and application to recommend the most effective weld joint type. This ensures strong, efficient fabrication without overspending on excess materials or complex welding.
Our expertise in CNC machining for welding prep means every piece fits perfectly, simplifying joint preparation. We’re here to make your welding process smoother—from design to final assembly—help choose and execute the best weld joint for your project.
Welding Techniques for Each Joint Type
Overview
Different welding joints call for different welding techniques to ensure strong, lasting connections. Your choice of welding method depends on the joint type, material, and project requirements. Common methods include MIG, TIG, and Stick welding. Each technique offers its own balance of speed, precision, and heat control.
Joint-Specific Tips
- Butt Joint: Usually done with MIG or TIG welding for clean, deep welds. Proper edge preparation is key to avoid weak spots.
- Tee Joint: TIG welding works well here since it offers control to weld the perpendicular surfaces smoothly.
- Corner Joint: MIG welding is popular for corners because it’s fast and handles thin materials well. Pre-fit parts to reduce gaps.
- Lap Joint: Stick or MIG welding often fits lap joints better because they help fill gaps and provide strong overlap.
- Edge Joint: TIG welding shines in edge joints due to precise heat input, which prevents warping on thin edges.
HYCNC Advantage
At HYCNC, we combine quality CNC machining with precise welding joint preparation, ensuring the right fit for each joint type. Our CNC expertise optimizes part accuracy, reducing rework and weld defects. We guide you in matching the best welding technique to your materials and joint design, improving durability and performance in your projects.
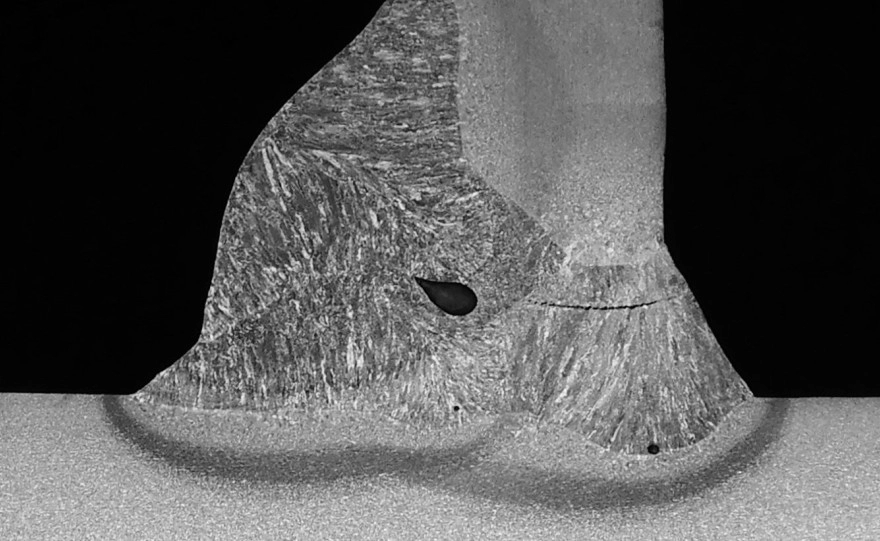
Common Weld Imperfections and How to Avoid Them
Even the best welders face challenges with weld imperfections. These flaws can weaken joints and cause failures if not detected and fixed early. Here are some common issues and how to avoid them:
Common Weld Issues:
Porosity: Small gas pockets trapped in the weld metal- Cracks: Breaks that form during or after welding.
- Undercut: Grooves melted into the base metal near the weld edge.
- Incomplete Fusion: Poor bonding between the weld and base metal.
- Slag Inclusion: Non-metallic material caught in the weld.
- Distortion: Warping caused by uneven heat distribution.
How to Prevent Weld Defects:
- Clean the metal surface thoroughly before welding.
- Choose the right welding technique and parameters for the joint type.
- Control heat input to minimize distortion and cracking.
- Use proper filler materials matched to the base metals.
- Maintain consistent welding speed and angle.
- Inspect welds regularly during fabrication.
At HYCNC, we combine precise CNC machining with skilled welding services to minimize imperfections. Our experience with CNC service ensures that parts fit perfectly before welding, reducing stress points and enhancing joint quality. Plus, our thorough quality checks catch defects early, so you get strong, reliable welds every time.
To learn more about avoiding welding defects, check out our detailed guide on welding defects.
Real-World Applications of Welding Joints

Welding joints are everywhere in industries across the United States. They play a vital role in building strong, durable products and structures that stand the test of time. Whether it’s constructing buildings, fabricating automotive parts, or assembling heavy machinery, the choice of welding joint impacts performance, safety, and longevity.
Industries Using Welding Joints
- Construction – Structural steel frameworks rely heavily on butt and tee joints for strong connections.
- Automotive – Lap and corner joints are common in car bodies and chassis for lightweight yet sturdy builds.
- Aerospace – Precision edge joints and joints ensure tight seams and reliability under stress.
- Manufact and Fabrication – All five joint types are used depending on the part and materials.
- Shipbuilding – Heavy-duty lap and tee joints help withstand harsh marine environments.
Examples of Welding Joints in Use
- Steel bridges mostly use butt and tee joints for solid support.
- HVAC ductwork often relies on lap joints for better sealing.
- Aluminum panels in aircraft assembly typically join with edge and butt welds for smooth finishes and strength.
- Agricultural equipment frames use corner and lap joints to resist vibrations and heavy loads.
HYCNC Case Study
At HYCNC, we’ve seen firsthand how picking the right welding joint boosts quality and efficiency. One U.S.-based machinery manufacturer came to us needing precision weld joint preparation combined with CNC machining. We helped by precisely cutting components that matched corner and lap joint designs. This not only reduced assembly time but improved weld strength by ensuring exact fits.
Our CNC services work seamlessly with welding needs, making it easier to produce parts ready for specific joint types. This saves time, cuts rework, and delivers consistent, reliable results every time.
If you’re looking to improve your welding process or need custom joint prep for your projects, HYCNC is ready to assist—combining smart design, CNC machining, and welding expertise tailored for American industry demands.
FAQs
What is the strongest welding joint
The strongest welding joint often depends on the application, but generally, the butt joint is considered one of the strongest. It allows full penetration welds, creating a solid bond between two pieces, especially in structural applications.
Which joint is best for thin sheet metal
For thin sheet metal, the lap joint is usually the best choice. It provides good strength and reduces the risk of burn-through during welding, making it ideal for delicate or lightweight metals.
How does material thickness affect joint choice
Material thickness plays a big role in deciding the weld joint type:
- Thin materials often use or edge joints to avoid warping or burn-through.
-Thicker materials** can handle butt or tee joints, which allow deeper weld penetration for stronger bonds.
Can HYCNC assist with custom weld joint preparation
Yes, HYCNC offers expert CNC machining and sheet metal fabrication services that help prepare parts precisely for custom welding joints. This ensures better fit, alignment, and weld quality for your specific project needs.
What welding techniques work best for each joint type
Different joint types pair well with specific welding methods:
- Butt joints work great with MIG or TIG welding for strong, clean welds.
- Tee joints often use stick welding or MIG depending on material and position.
- Corner joints benefit from TIG or MIG due to better control.
- Lap joints usually go well with MIG or spot welding for quicker work.
- Edge joints can use TIG or gas welding but are less common in heavy-duty applications.
At HYCNC, we match the right welding technique with your joint type to ensure optimal results every time.