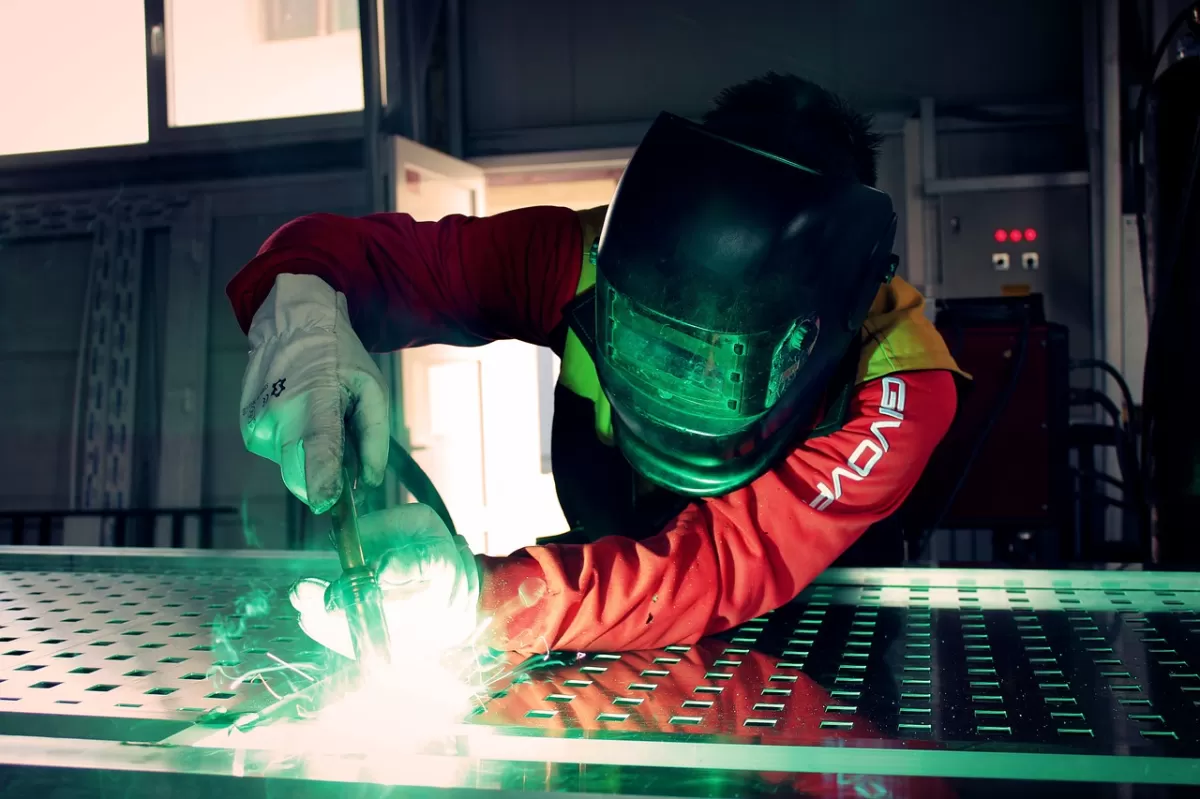
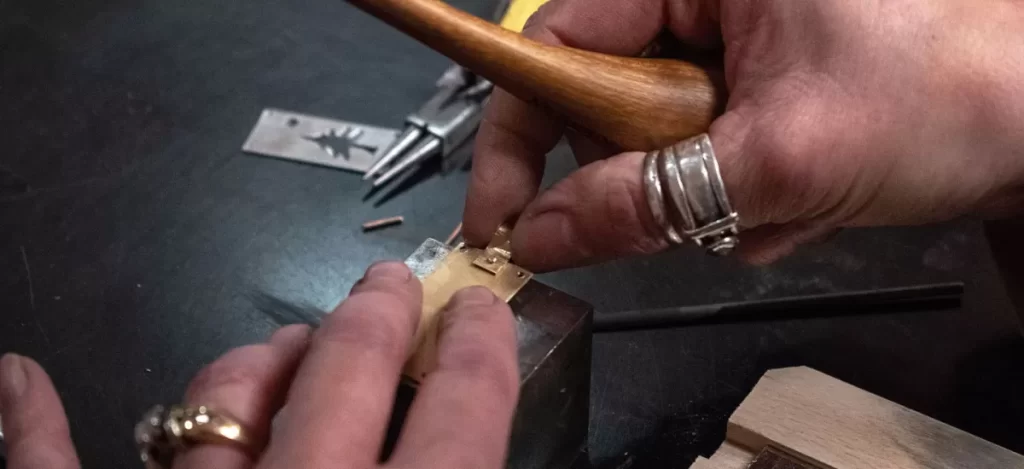
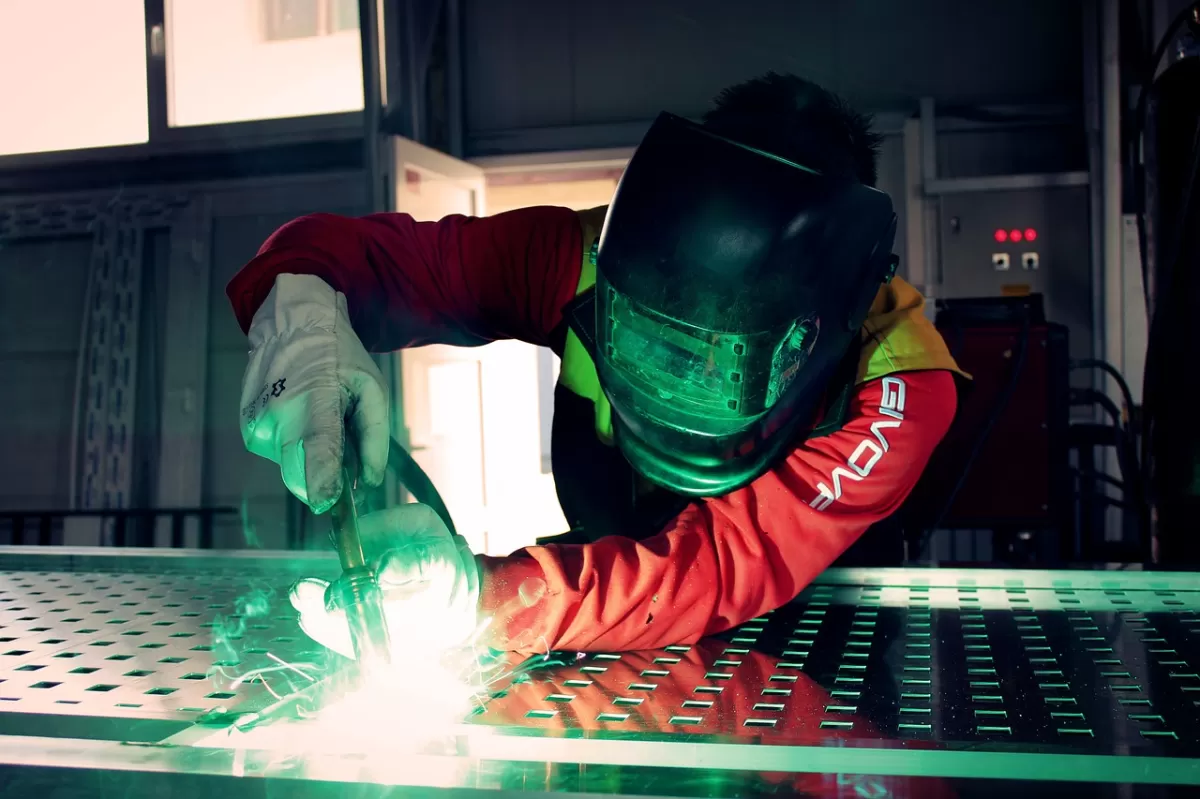
Are you torn between welding and riveting for your next CNC project? Choosing the right metal joining technique can make or break your budget and project quality.
As a CNC machining expert, I’ve seen how the cost of welding vs. riveting impacts decisions in manufacturing. With HYCNC’s real-world experience, I’m sharing a clear, no-fluff comparison to help you save money and get results.
In this guide, you’ll uncover the true costs of welding and riveting, their pros and cons, and which method suits your project best.
Ready to make a smart choice? Let’s dive in!
Understanding Welding and Riveting
What is Welding
Welding is a metal joining technique that uses heat or pressure to fuse materials together, creating a strong, permanent bond. It involves melting the base metals and sometimes adding filler material to form a solid joint. Common welding methods include MIG, TIG, and arc welding, each suited for different metals and applications.
What is Riveting
Riveting is a mechanical fastening process where metal pins (rivets) are inserted through pre-drilled holes in two or more pieces of material. These rivets are then deformed or hammered at the ends to hold the pieces together securely. It’s widely used for assembling sheets or structural components without heat, making it ideal for joining dissimilar materials or heat-sensitive parts.
Why Compare Costs
Both welding and riveting play crucial roles in metal fabrication and CNC machining, but they come with different costs and benefits. Comparing welding vs riveting cost helps manufacturers choose the most cost-effective, durable, and efficient method for their specific project needs. Understanding these differences can save money, improve production speed, and ensure long-lasting quality in metal assembly.
Cost Breakdown Welding vs Riveting

When comparing welding vs riveting cost, it’s important to break down the major expenses involved. Knowing where your money goes helps make a smarter choice for your project.
Initial Setup Costs
Welding usually requires more upfront investment in equipment. You need welding machines, protective gear, and sometimes gas supplies. Riveting tools are often simpler and cheaper to get started with, especially for small jobs.
Labor Costs
Welding typically needs skilled labor, which means higher hourly rates. A certified welder’s time adds up fast. Riveting is often quicker and can be done with less specialized training, so labor costs tend to be lower.
Material Costs
Welding materials include filler metals, shielding gas, and electrodes, which add to the overall cost. Riveting mainly involves purchasing rivets, which are generally inexpensive but the type and size of rivets can impact material expenses.
Maintenance and Long Term Costs
Welded joints usually require less maintenance over time if done right, making them cost-effective for long-term durability. Riveted joints may need regular checks and tightening, especially in high-vibration environments, which can increase maintenance costs.
Understanding these cost factors gives a clearer picture when deciding between welding and riveting for manufacturing or CNC machining fabrication.
Key Factors Influencing Costs

When figuring out whether welding or riveting is more expensive, several key factors come into play:
Project Scale and Complexity
- Large, complex projects usually drive up costs regardless of method. Welding often requires more preparation and precision for big jobs, which can increase labor time. Riveting might be faster on simpler assemblies but gets tricky as complexity grows.
Material Type
- The kind of metal matters. Some metals weld easily and cheaply, while others need special equipment or filler metals, raising costs. Riveting works well with thinner sheets or softer metals but might need stronger, more expensive rivets for heavier materials.
Industry Requirements
- Different industries have different standards. Aerospace, automotive, and construction often require strict inspections, quality controls, and certifications that affect both welding and riveting costs. Welding might need extra testing for strength; riveting could require specialized rivet types or torque tools.
Production Speed
- If speed is a priority, riveting can often be faster because it doesn’t need cooling or finish welding steps. However, automated welding systems in CNC machining and fabrication can speed things up and bring down long-term costs.
Knowing these factors helps decide which method fits your budget and project needs better.
Pros and Cons of Welding and Riveting
Welding Pros and Cons
Pros
- Creates strong, permanent joints often stronger than the base metal
- Good for complex shapes and tight spaces
- Minimal added weight since no extra fasteners are needed
- Offers a smooth finish, which can be important for aesthetics or aerodynamics
Cons
- Requires skilled labor and safety precautions
- Initial welding equipment and setup can be costly
- Not always easy to disassemble or repair without cutting
- Heat can cause distortion or weaken some metals
Riveting Pros and Cons
Pros
- Faster assembly on some types of projects, which can save labor costs
- Easier to inspect and maintain since rivets are visible
- Good for joining dissimilar metals without heat damage
- Riveted joints can be replaced or repaired more easily than welded ones
Cons
- Adds extra weight due to fasteners
- Rivet holes can weaken the metal over time
- Usually less strong and less airtight than welds
- May require more material overlap, increasing costs
When deciding between welding vs riveting cost and benefits, it really comes down to your project’s needs for strength, flexibility, and budget. For CNC machining fabrication or sheet metal fabrication in the US, weighing these pros and cons helps you pick the most cost-effective metal assembly method.
Real World Applications and Case Studies
When it comes to CNC machining fabrication, both welding and riveting have their place depending on the project. Welding is often preferred for heavy-duty metal joining, especially in automotive, aerospace, and construction industries where strength and durability are crucial. For example, car frames and aircraft parts typically rely on welded joints because they offer long-term stability under stress.
On the other hand, riveting shines in applications where disassembly or vibration resistance matters. Industries like shipbuilding and electronics use rivets to join sheet metal since riveting allows quick assembly and easier repairs. Rivet types for CNC projects are widely used in sheet metal fabrication where tight tolerances and consistent fastener placement matter.
From a cost perspective, companies that leverage CNC machining with welding equipment often face higher initial setup costs but benefit from stronger, more permanent joints. Meanwhile, riveting can reduce labor time, cutting down on overall manufacturing costs for simpler structures.
Cost Saving Tips:
- Choose riveting for lighter assemblies where access for welding is limited.
- Use robotic welding in CNC fabrication to speed up production and reduce labor costs.
- Consider hybrid approaches—welding critical joints while riveting less stressed parts.
- Regular maintenance of welding equipment reduces downtime and unexpected expenses.
These real-world examples show the balance between material requirements, industry standards, and budget constraints. Understanding the specific needs of your CNC machining project is key to choosing the most cost effective metal assembly method.
Which is More Expensive The Verdict

When comparing welding vs riveting cost, welding usually comes out as more expensive upfront. Welding equipment costs, skilled labor, and setup often push the price higher than riveting, especially for smaller or simpler projects. Riveting tends to have lower initial setup and material costs, making it budget-friendly for certain applications.
However, the overall expense depends on your project size, material type, and long-term needs. Welding offers stronger, more durable joints that can reduce maintenance and replacement costs over time. Riveting might be cheaper initially but could require more frequent checks or repairs in some cases.
At HYCNC, we evaluate every job carefully to recommend the most cost-effective metal assembly method tailored to your needs. Whether you need precise CNC machining fabrication with welded joints or efficient riveting for quicker turnaround, we help balance quality and cost.
- Welding generally more expensive upfront but offers long-term durability
- Riveting cheaper initially, better for simpler assemblies
- The best choice varies by project scope and industry requirements
- HYCNC provides expert guidance for cost-effective fabrication
Choosing the right metal joining technique with us ensures your manufacturing cost stays in check without compromising quality.
FAQs
Is welding stronger than riveting
Welding generally creates stronger joints because it fuses metals together, making a continuous bond. Riveting relies on mechanical fastening, which can be strong but usually isn’t as durable under heavy stress or dynamic loads.
Can riveting be used in CNC machining
Yes, riveting is commonly used in CNC machining, especially in sheet metal fabrication where precise, repeatable mechanical fastening is needed. It’s ideal for joining dissimilar metals and avoiding heat distortion.
How can I reduce welding costs
Use automated welding equipment to speed up production
Choose simpler weld types suited to your project
Optimize material selection to reduce filler metal needs
Prevent defects by following best welding practices (check out our welding tips)
Proper design can reduce rework and material waste
What industries prefer riveting over welding
Riveting remains popular in aerospace, automotive, and shipbuilding industries where vibration resistance, disassembly, and heat sensitivity are factors. It’s also preferred when working with thin metals or coated surfaces that might get damaged by welding heat.
How does HYCNC ensure cost effective fabrication
At HYCNC, we combine advanced CNC machining with precise fabrication methods, selecting the right joining technique for your project needs. We focus on minimizing waste, reducing labor time, and preventing defects in both welding and riveting. This approach helps deliver high-quality results while keeping costs in check.