Struggling to create 3D printed threads that are precise and durable? Whether you’re a hobbyist crafting custom screws or an engineer prototyping for production, mastering 3D printing threads can transform your projects. As a leader in CNC and 3D printing services, HYCNC has empowered countless designers to produce flawless threaded parts with ease. In this guide, you’ll uncover expert tips, proven techniques, and how HYCNC’s precision solutions can elevate your work. Let’s dive into the art and science of 3D printing threads!
Understanding 3D Printing Threads
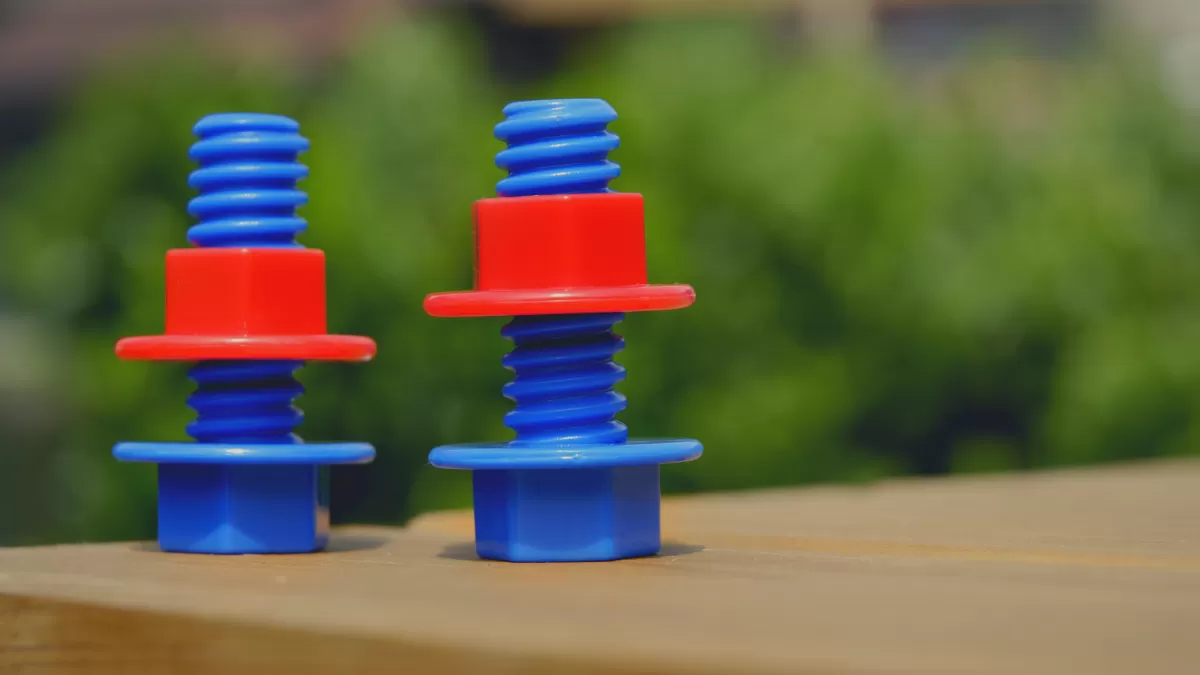
If you’ve ever wondered how screws and bolts work when made with 3D printing, you’re not alone. 3D printed threads are spiral grooves on parts, just like traditional threads, but created layer by layer using 3D printing technology. These can be internal threads (like the inside of a nut) or external threads (like the outside of a screw). Getting these threads right is crucial if you want your parts to fit and function properly.
What Are 3D Printed Threads
In simple terms, 3D printed threads are designed features that allow parts to screw into each other just like standard fasteners. Unlike machining, where threads are cut out, 3D printing builds them as part of the layering process. This means you can create functional 3D printed threads including complex shapes hard to machine traditionally.
Benefits of 3D Printing Threads
- Customization: Easily design custom thread types or pitches that standard screws don’t offer.
- Rapid Prototyping: Quickly test thread designs without tooling.
- Cost Efficiency: Avoid expensive machining for low-volume or one-off parts.
- Complex Geometry: Produce threads in hard-to-reach places or on unusual shapes.
This versatility opens new doors in threaded part manufacturing and prototyping.
Common Thread Standards
When designing 3D printed threads, sticking to recognized standards ensures compatibility:
| Thread Type | Description | Common Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Unified Thread (UNC/UNF) | Standard inch threads | General fasteners in the U.S. |
| Metric Threads (M) | Metric measurements | International and engineering |
| Acme Threads | Trapezoidal shape for power transmission | Lead screws, motion control |
Choosing the right thread pitch and standard helps make sure your 3D printed threads match with off-the-shelf nuts, bolts, or inserts.
If you want to learn more about how 3D printing fits with traditional machining, check out our guide on CNC prototyping vs 3D printing for a deeper understanding.
Understanding these basics sets you up to design and print reliable, functional threads that work for your project’s needs.
Designing 3D Printed Threads Best Practices

When designing 3D printed threads, getting the basics right is key to making parts that fit and function smoothly. Here are some important points to keep in mind.
Key Design Parameters
- Thread pitch and profile: Use standard thread pitches, like UNC or ISO, to ensure compatibility and strength. Avoid making the thread pitch too fine, as 3D printers can struggle with small details.
- Thread tolerance: Increase tolerances compared to CNC machining because 3D printing is less precise. Leave extra clearance, especially for internal threads.
- Thread direction: Specify right-hand or left-hand threads clearly to match your assembly needs.
- Wall thickness and layer height: Design thicker threads for durability. Finer layer heights can improve thread detail but take longer to print.
CAD Software for Thread Design
Good CAD software can simplify thread design for 3D printing. Popular options include:
- Fusion 360: Great for creating custom threads with adjustable parameters.
- SolidWorks: Offers built-in thread tools and templates for quick design.
- TinkerCAD: Simple and user-friendly, best for basic thread designs and beginners.
These tools let you model both internal and external threads, making sure your 3D printed screws and threaded parts fit perfectly.
Avoiding Common Design Mistakes
- Don’t make threads too thin: Thin threads can easily break or strip after printing.
- Avoid sharp corners: Rounded thread roots reduce stress concentrations and improve strength.
- Account for printer limitations: Know your printer’s minimum feature sizes to avoid details that won’t print cleanly.
- Test fit prototypes: Before full production, print prototypes to check fit and function.
Following these design best practices will help you create strong, functional 3D printed threads that work reliably.
Printing Techniques for High Quality Threads
Creating strong, precise 3D printing threads starts with picking the right technology. For functional 3D printed threads, FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) works well for prototypes and basic parts. However, if you need higher detail and accuracy, SLA (Stereolithography) or SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) are better choices since they produce smoother and more precise threads.
Choosing the Right 3D Printing Technology
- FDM: Affordable, widely available, good for rough or larger threads
- SLA: Excellent for fine, detailed internal/external threads
- SLS: Durable, great for complex shapes and strong mechanical threads
Optimizing Print Settings
Proper settings are key to avoid rough or inaccurate threads:
- Use a smaller layer height for smoother thread surfaces
- Increase infill density to boost thread strength
- Slow down print speed near threads to improve precision
- Ensure adequate shell thickness for stronger external threads
Material Selection for Durability
Material choice impacts thread strength and lifespan:
- Nylon and polycarbonate offer excellent durability and flexibility for functional threads
- PETG balances ease of printing with decent strength
- Avoid brittle materials like PLA for load-bearing or moving threaded parts
By combining the right printing tech, fine-tuned settings, and durable materials, you can produce high-quality 3D printed screws and threaded parts that perform reliably in real-world applications.
Post Processing and Enhancing Thread Performance

Once your 3D printed threads are done, post processing is key to boost their function and durability. Here’s what helps get the best results:
Post Processing Techniques
- Sanding and smoothing: Clean up rough edges on both internal and external threads to ensure smooth fits.
- Thread tapping: Running a tap tool through printed holes can sharpen internal threads for better screw engagement.
- Heat treatment: Certain materials improve strength with controlled heating, reducing brittleness on threads.
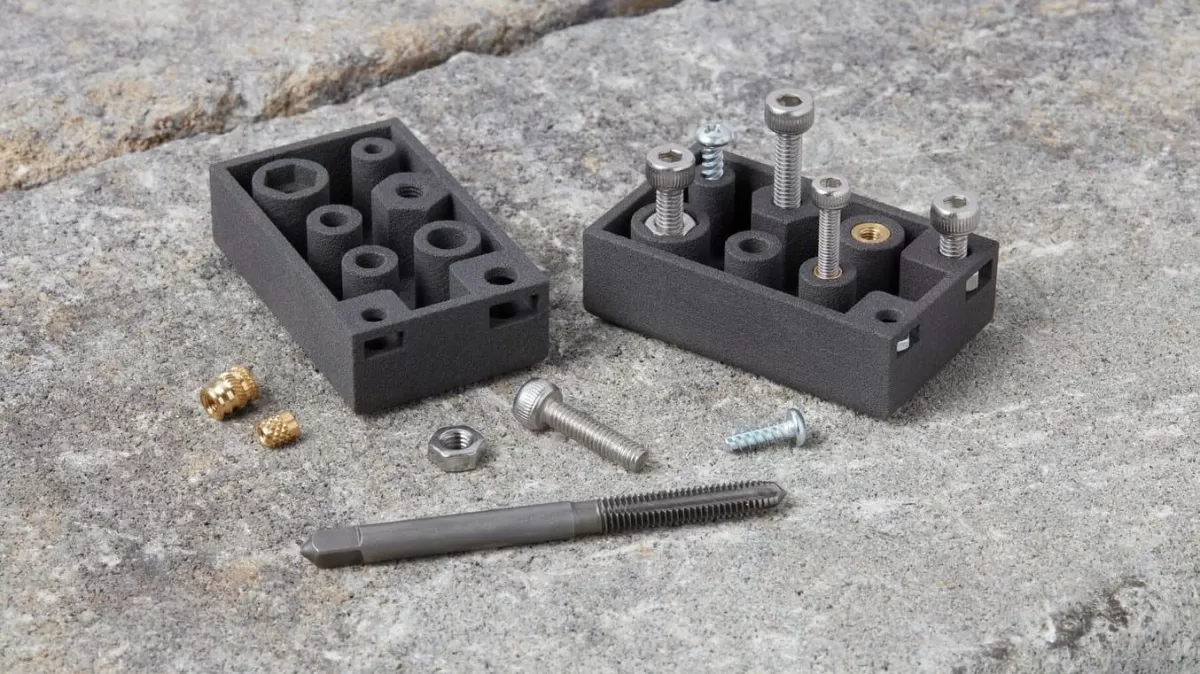
Using Threaded Inserts
Adding threaded inserts is a smart move when you need strong, durable threads that can handle repeated screwing and unscrewing. This combines 3D printing with tried-and-true metal threads for reliability in functional parts.
Testing and Quality Assurance
Make sure your threads fit well and hold tight by:
- Checking screw fit with gauges or actual screws.
- Performing pull tests to measure thread strength.
- Inspecting for alignment and uniformity to avoid stripped or weak threads.
Post processing and quality checks ensure your functional 3D printed threads perform well in real-world applications, especially for critical parts in the US market where reliability matters.
Applications of 3D Printed Threads
Industry Use Cases
3D printed threads are widely used across various industries where custom or low-volume threaded parts are needed fast and cost-effectively. These include aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and consumer products. For example, aerospace companies rely on functional 3D printed threads to create lightweight, durable parts for prototypes and small runs. In automotive, 3D printing threaded inserts help create reliable fastening solutions without the long lead times of traditional manufacturing. Medical device makers benefit from customizable internal and external threads for tailored instruments and equipment.
Using 3D printed screws and threaded parts in prototyping speeds up design validation, helping companies get to market faster with less waste. Additionally, 3D printing supports on-demand production, which is perfect for businesses needing quick turnaround or custom thread designs without huge tooling costs.
HYCNC’s Role in Threaded Part Production
At HYCNC, we blend expert CNC machining with advanced 3D printing services to deliver precise threaded parts tailored to your needs. Whether you require strong 3D printing thread strength for functional end-use components or rapid prototyping threads for testing, we have the right technology and know-how. Our focus is on quality, accuracy, and fast delivery, making us a trusted partner in threaded part manufacturing in the US market.
If you’re interested in combining CNC and 3D printing for ideal thread results, check out our detailed insights on CNC prototyping vs 3D printing. This helps you choose the best method for your project.
At HYCNC, we’re ready to help you bring your 3D printed threaded parts from concept to reality—efficiently and reliably.
Troubleshooting Common Thread Printing Issues
Even with the best designs and printers, 3D printing threads can sometimes run into problems. Here are some common issues and how to fix them.
Rough or Inaccurate Threads
- Cause: Poor layer adhesion, low print resolution, or wrong print settings.
- Fix: Increase printer resolution, slow down print speed, and check your layer height. Using finer nozzles can help too. Also, make sure your CAD thread design matches your printer’s capabilities.
Weak or Stripped Threads
- Cause: Under-extrusion, incorrect thread dimensions, or printing with brittle materials.
- Fix: Use stronger, more flexible materials designed for thread strength. Double-check your thread pitch and size in the CAD software. Increasing wall thickness around the thread area can add strength. Consider using threaded inserts if you need extra durability.
Misalignment or Poor Fit
- Cause: Warping during printing or inaccurate calibration can cause threads not to match up.
- Fix: Calibrate your 3D printer regularly. Print threads with a slight tolerance to avoid too-tight fits. Cooling the part slowly can reduce warping. Test print small sections before the full part to ensure fit.
By understanding these issues and how to address them, you’ll improve your success rate in producing strong, functional 3D printed threads every time.
Why Choose HYCNC for 3D Printed Threads
When it comes to 3D printing threads, HYCNC stands out because of our strong expertise in both CNC machining and advanced 3D printing technologies. This combination means we fully understand the precision and durability required for functional 3D printed threads, whether internal or external.
We specialize in rapid prototyping and on-demand production, so whether you need a quick proof of concept or small batch manufacturing, we can deliver fast without sacrificing quality. Our team works closely with you to optimize thread design and printing parameters, ensuring the best thread strength and fit for your application.
Ready to get started? Contact us today to get a quote and see how HYCNC can help bring your threaded parts to life with precision and reliability. For more on how 3D printing compares with CNC processes, check out our guide on CNC prototyping vs 3D printing.
FAQs
What are 3D printing threads?
3D printing threads are screw-like features created directly on printed parts, allowing for functional fastening without needing extra hardware. These can be internal (female) or external (male) threads designed and printed right into your model.
Can I print strong and functional threads with 3D printing?
Yes, but it depends on your design, material, and printing method. Using the right thread pitch, layer height, and materials like nylon or reinforced filaments improves thread strength.
What’s the difference between internal and external 3D printed threads?
Internal threads are inside holes, like nuts, and external threads are on the outside, like bolts. Each requires slightly different design and print settings for the best results.
Which CAD software is best for 3D printing thread design?
Popular CAD programs like SolidWorks, Fusion 360, and AutoCAD have built-in tools for creating standard threads optimized for 3D printing.
Can I use threaded inserts with 3D printed parts?
Absolutely. Threaded inserts provide extra durability, especially in softer materials like PLA. They’re great for parts that need repeated assembly and disassembly.
How do I fix rough or inaccurate threads on my 3D prints?
Try adjusting your print layer height, increasing print resolution, or using post-processing like sanding or tapping. Correcting design parameters may also help.
Is CNC machining better than 3D printing for threaded parts?
Both have their place. CNC offers precision and strength, but 3D printing is faster and great for prototyping, custom parts, or low-volume runs. Combining both, like printed parts with CNC-threaded inserts, is common.
How does HYCNC support 3D printed thread production?
We offer expert 3D printing combined with CNC machining for high-quality threads, rapid prototyping, and on-demand production tailored for US customers’ needs.
Where can I get a quote for 3D printed threaded parts?
Contact HYCNC directly for fast, reliable quotes tailored to your project specifications and timeline.




