What Is Machining
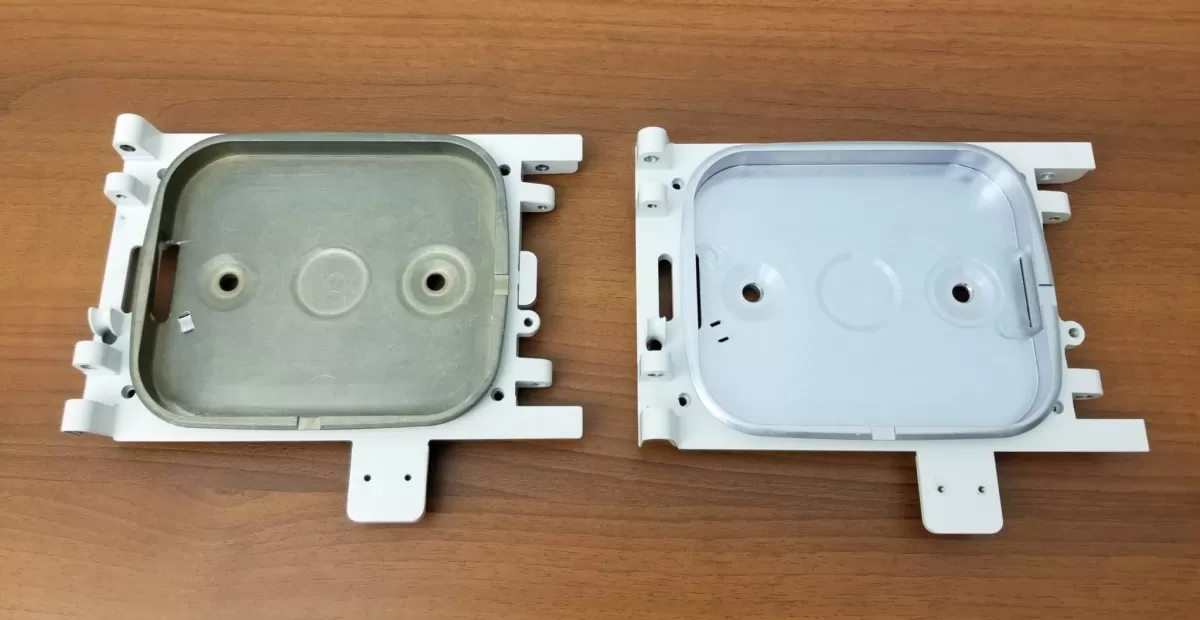
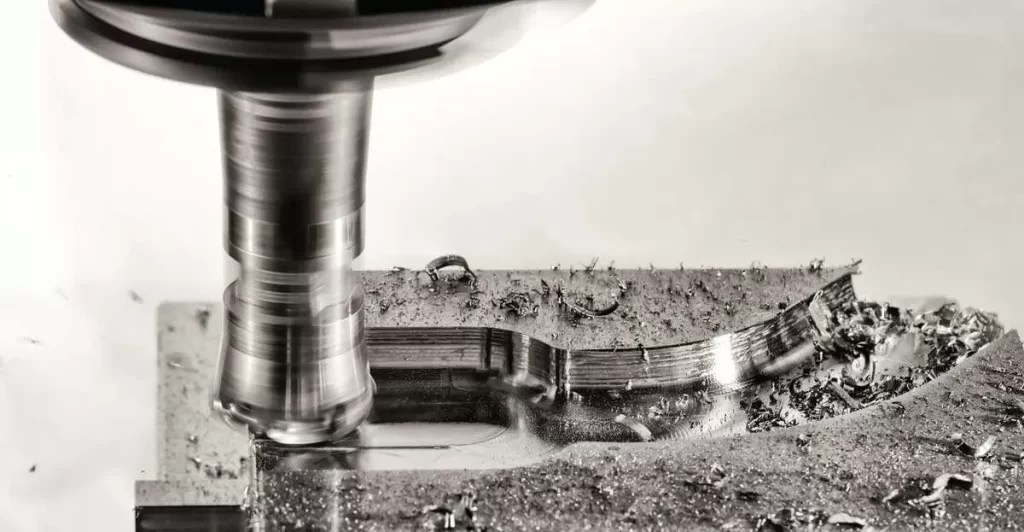
Machining is a subtractive manufacturing process where material is removed from a solid workpiece using CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines. This method precisely shapes the part by cutting away unwanted material to achieve the desired form and dimensions.
Common machining techniques include CNC milling, turning, drilling, and grinding. These processes enable manufacturers to work with a wide range of materials—from metals to plastics and composites—delivering tight tolerances and high precision.
Machining is ideal for prototyping, low volume production, and creating complex geometries that require accuracy. For example, HYCNC specializes in CNC machining custom aluminum parts, providing tailored solutions that meet demanding specifications with fast turnaround times.
What Is Casting
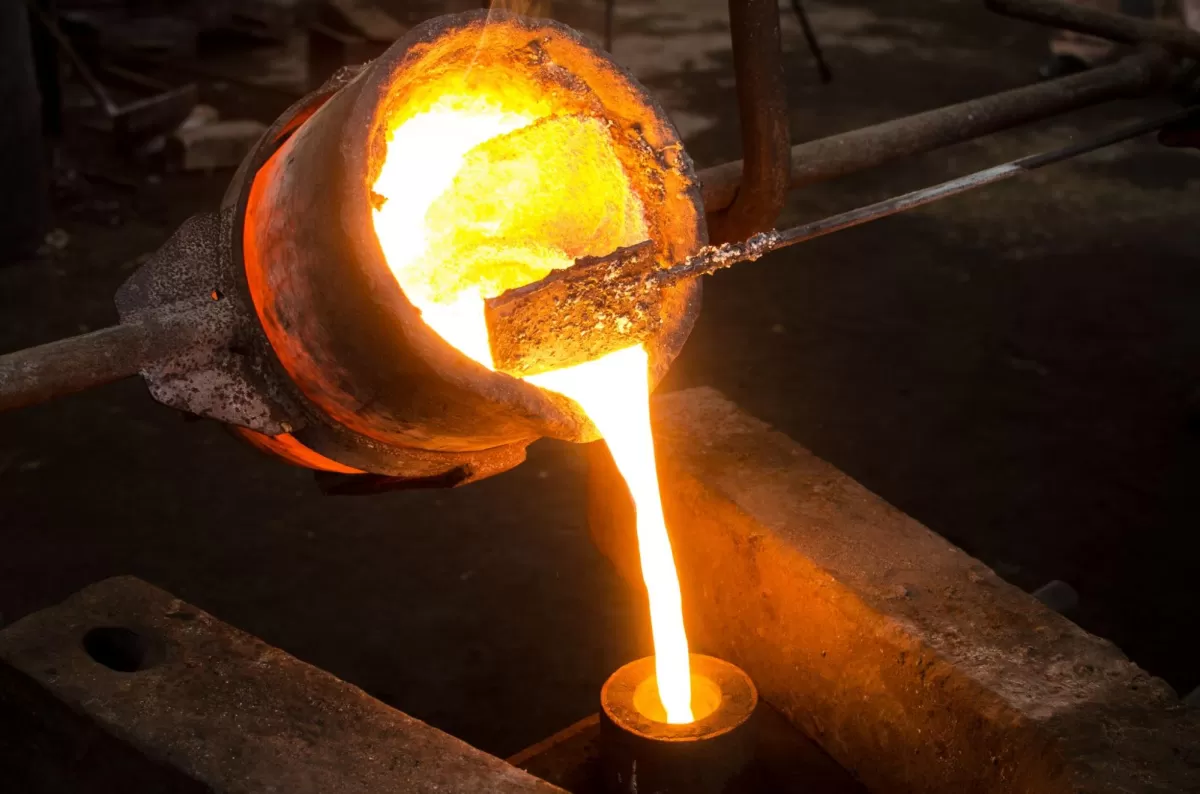

Casting is a formative manufacturing process where molten metal is poured into a mold and allowed to solidify. This method shapes parts by filling the mold’s cavity, creating complex designs that might be hard to make with other techniques.
There are several common types of casting:
- Die Casting – Uses high-pressure to force molten metal into steel molds, perfect for detailed parts and high volume.
- Sand Casting – Uses sand molds that are easy to create and modify, ideal for larger components and lower volume runs.
- Investment Casting – Also called lost-wax casting, great for intricate shapes requiring high accuracy.
Casting stands out for its ability to produce complicated shapes efficiently and cost-effectively, especially when you need large quantities. It works well for items like engine blocks, turbine blades, and other intricate industrial components.
At HYCNC, we provide support for machined castings, combining casting’s affordability with machining’s precision to deliver high-quality parts tailored for your needs.
Key Differences Between Machining and Casting

The main difference between machining and casting lies in the process. Machining is a subtractive method where material is cut away from a solid block using CNC machines. Casting, on the other hand, is formative—molten metal is poured into molds to create shapes as it solidifies.
When it comes to precision and tolerances, machining offers tighter control, making it ideal for parts needing exact measurements. Casting can produce complex shapes but often requires secondary machining to achieve precise dimensions.
Machining is more versatile with materials, handling metals, plastics, and composites. Casting mainly focuses on metals like aluminum, steel, and iron.
Production volume is another big difference. Machining suits low to medium volumes, perfect for prototypes or custom jobs. Casting excels at high-volume production where consistent parts are needed in large batches.
Cost-wise, machining has a higher per-unit price since it’s more labor- and time-intensive. Casting requires higher upfront tooling costs for mold creation but lowers the cost per part when producing large quantities.
Lead time varies too. Machining setups are faster, great for quick prototypes and short runs. Casting needs more time initially to create molds but can churn out parts quickly once production starts.
For more insight on different casting types and costs, check out our metal casting services and what is die casting.
Pros and Cons of Machining
Advantages
- High precision and tight tolerances: Machining with CNC machines delivers exact dimensions you can count on.
- Quick setup for prototypes and small batches: It’s fast to get started, making it great for testing and limited runs.
- Works with many materials: Metals, plastics, and composites — machining handles them all smoothly.
- Excellent surface finish and repeatability: You get smooth, consistent parts every time.
Disadvantages
- Higher material waste: Since machining cuts away material, there’s more scrap compared to other methods.
- More expensive for large-scale production: Costs add up when you’re making thousands of parts.
- Limited ability for complex internal shapes: If your design has tricky internal cavities, machining alone might not work well.
Pros and Cons of Casting
Advantages
- Cost effective for high volume production – Casting is great when you need lots of the same part, helping lower costs per unit.
- Ideal for complex shapes and internal cavities – It can create detailed designs and hollow sections that are tough to machine.
- Minimal material waste – Because you pour metal into molds, there’s less leftover scrap compared to machining.
- Scalable for mass production – Once molds are made, casting can quickly ramp up to large quantities.
Disadvantages
- Higher initial tooling costs – Making molds and dies takes time and money upfront.
- Potential defects like porosity and shrinkage – Cast parts can have small voids or misshapes due to the metal cooling process.
- May require secondary machining for precision – To hit tight tolerances or detailed finishes, some cast parts need extra machining.
When to Choose Machining vs Casting
Choose Machining
- You need high precision and tight tolerances
- Working on prototyping or low to medium production volumes
- Parts have complex external features or custom designs
- For example, HYCNC’s CNC milling delivers precise aerospace components
Choose Casting
- You’re aiming for high volume production with consistent quality
- Parts require complex internal geometries or are large components
- Designs are cost-sensitive and stable over time
Hybrid Approach
- Combine casting for near net shapes to save material and time
- Use machining for precision finishing and critical details
- Example: HYCNC machined casting services optimize production for best value and quality
Cost and Efficiency Considerations
When comparing machining vs casting, cost and efficiency are key factors to keep in mind.
Cost
- Casting requires higher initial tooling costs because molds need to be made upfront. This makes casting a smart choice for large production runs where the cost per part goes down as volume increases.
- Machining has lower setup costs but higher per-unit costs, especially for large batches. It’s ideal for prototypes or low to medium volume runs.
Lead Time
- Machining setups are quicker, allowing faster turnaround on prototypes and small batches.
- Casting takes longer upfront due to mold creation, but once molds are ready, production speeds up for mass quantities.
Material Waste and Sustainability
- Casting is more material-efficient, with minimal scrap since molten metal fills molds, reducing waste.
- Machining is subtractive, so it generates more scrap material, but recycling options exist.
At HYCNC, we help optimize your costs by combining casting and CNC machining efficiently. Our integrated solutions balance tooling investment, lead times, and material use to fit your project’s scale and budget.
Real World Applications and Case Studies
In the automotive industry, casting is often used for engine blocks thanks to its ability to shape complex parts efficiently, while machining handles precision gears that require tight tolerances. For aerospace, casting produces intricate turbine blades, and machining is key for structural components where accuracy and surface finish are critical. Industrial equipment frequently benefits from a hybrid approach—starting with casting for near net shapes, then machining to fine-tune large, complex parts.
At HYCNC, we helped a client cut costs by 30% using this combined method. By casting the basic form and applying precise CNC machining for finishing, we optimized both production speed and quality. This hybrid process is a great example of how machining and casting can work together for better results.
How to Decide Key Factors to Consider
Choosing between machining and casting depends on several key factors:
-
Design complexity
If your part has intricate shapes or internal cavities, casting is often the better choice. For parts needing precise external features or tight tolerances, machining works best.
-
Production volume
Low to medium volumes usually favor machining because of faster setup and less tooling cost. For high volume runs, casting becomes more cost-effective.
-
Material requirements
Machining handles a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. Casting is mostly limited to metals and alloys.
-
Budget and timeline
Machining has lower upfront costs and quicker lead times, perfect for prototypes or quick turnarounds. Casting requires upfront investment in molds but offers savings over large production runs.
-
Quality needs
Consider surface finish, tolerance tightness, and mechanical properties. Machining delivers higher precision and better finishes, while casting may need secondary machining to meet those needs.
Why Choose HYCNC for Machining and Casting Needs
At HYCNC, we specialize in both CNC machining and machined casting services, delivering precise and reliable manufacturing solutions. Our state-of-the-art equipment combined with skilled engineers means your projects get the attention and accuracy they deserve.
We offer customized solutions whether you need prototyping, low volume runs, or high volume production. No matter the size or complexity, HYCNC is committed to quality, precision, and fast turnaround times to keep your production on schedule.
Ready to get started? Contact HYCNC today for a free quote or consultation and see how we can support your machining and casting needs.