Are you curious about shell molding and how it can elevate your manufacturing projects? Choosing the right casting process can transform the quality and efficiency of your precision parts.
As experts in CNC machining, we at HYCNC understand the power of shell mold casting in delivering high-accuracy components for industries like automotive and aerospace. In this guide, we’ll break down what shell molding is, how it works, and why it’s a game-changer for creating durable, high-quality parts.
Get ready to explore the metal casting process that’s revolutionizing modern manufacturing. Let’s dive in!
Understanding Shell Molding Definition and Basics
Have you ever wondered how manufacturers create precise metal parts with smooth surfaces and tight tolerances? Shell molding, also known as shell mold casting, is a metal casting process designed to meet those exact needs. In simple terms, shell molding involves creating a thin, hard shell mold from resin-coated sand, which is then used to cast metal parts. This process combines aspects of traditional sand casting with resin technology to improve accuracy and surface quality.
What is Shell Molding
Shell molding is a precision casting technique where a heated metal pattern is coated with a mixture of sand and thermosetting resin. This forms a hardened shell that serves as the mold. Unlike conventional sand casting, where loose sand is packed into a flask, shell molding produces a rigid mold shell that can handle more intricate details and thinner walls.
A Brief History
The method was developed in the early 1940s as an improvement over traditional sand casting, responding to industries demanding better dimensional control and smoother finishes. Over time, shell molding gained popularity in automotive and aerospace industries due to its efficiency and accuracy.
Comparison to Sand Casting
Compared to standard sand casting, shell molding offers several key advantages:
- Better dimensional accuracy: The rigid shell mold maintains shape more precisely.
- Improved surface finish: Resin-coated sand reduces graininess in the final casting.
- Faster mold preparation: The process is less labor-intensive than building sand molds by hand.
- More intricate designs: Shell molds can capture fine details better than loose sand molds.
While sand casting remains widely used for large parts and low-cost applications, shell molding is favored when precision and surface quality are priorities in medium-sized batch production.
Understanding these basics sets the foundation to explore how shell molding works and why it’s a compelling choice for many manufacturing projects today.
How Shell Molding Works Step-by-Step Process
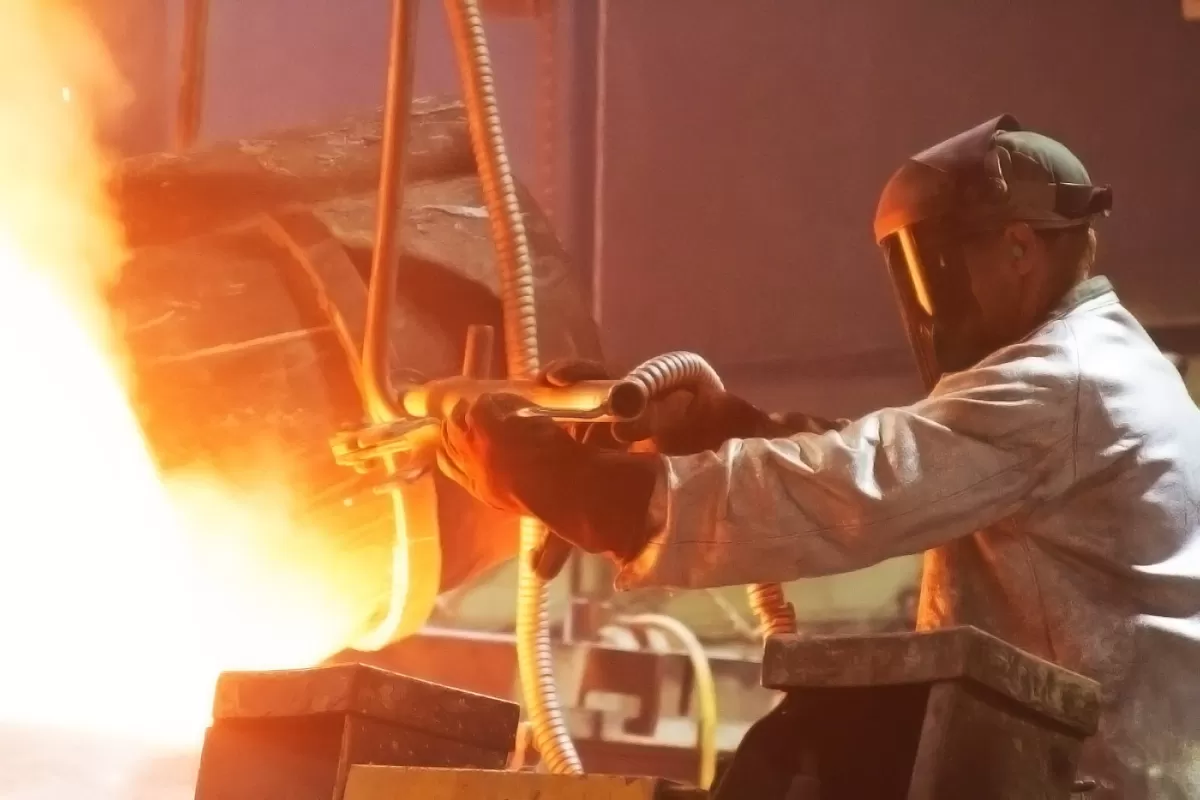

Shell molding is a precise metal casting process that uses resin-coated sand to form a hard shell mold. Here’s a simple breakdown of how it works:
Pattern Creation
The process begins with making a pattern, usually from metal or heated aluminum. This pattern is a replica of the final part you want to cast.
Heating the Pattern
Next, the pattern is heated to around 350°F to 500°F. The heat helps the resin-coated sand stick and form a shell.
Applying Resin-Coated Sand
Once the pattern is hot, resin-coated sand is applied evenly against its surface. The resin acts as a binder, holding the sand in place.
Curing the Shell
The coated sand stays on the heated pattern for a short time, allowing the resin to cure and harden, creating a thin, rigid shell mold.
Mold Assembly
After the shell hardens, it’s carefully removed from the pattern. Two shell halves are then joined together to form the complete mold.
Pouring Molten Metal and Cooling
Molten metal is poured into the assembled shell mold. The metal cools and solidifies inside, taking the shape of the mold.
Casting Removal and Cleaning
Once cooled, the shell mold is broken away, revealing the cast part. The casting then goes through cleaning processes to remove any remaining sand or residue.
This step-by-step method delivers detailed, accurate parts with a smooth surface right out of the mold—making shell mold casting a solid option for precision metalwork.
Materials Used in Shell Molding
When it comes to shell molding, choosing the right materials is crucial for a successful casting.
Common Metals Used
Shell mold casting works well with a variety of metals, including:
- Aluminum – Lightweight and great for automotive parts
- Cast iron – Popular for engine blocks and machinery
- Steel – Used when strength and durability are key
- Bronze and brass – Ideal for decorative and precision parts
These metals benefit from shell molding due to the process’s ability to handle detailed shapes and provide good surface finish.
Sand and Resin Types
The core of shell molding is the resin-coated sand. This special sand is coated with a thermosetting resin, which helps form a hard, thin shell when heated. Key materials include:
- High-quality silica sand – For heat resistance and strength
- Phenolic or thermosetting resin – Binds the sand and cures quickly on the heated pattern
The quality of sand and resin directly affects the mold’s strength, dimensional accuracy, and surface texture.
Importance of Material Selection
Picking the right combination of metal, sand, and resin impacts:
- Dimensional accuracy – Ensures the cast matches the design precisely
- Surface finish – Reduces the need for extra machining or polishing
- Durability of the mold – Supports consistent production runs
- Cost efficiency – Balances quality with material expenses
By focusing on material selection, shell molding offers a reliable way to produce precision castings with less cleanup and improved consistency compared to traditional sand casting.
For more on milling and finishing processes that often go hand-in-hand with shell molding, you might want to check out our guide on what is CNC machining.
Advantages of Shell Molding
Shell molding offers several key benefits that make it a popular choice for metal casting projects, especially in the U.S. market where precision and efficiency matter.
Dimensional Accuracy
This process provides excellent dimensional accuracy, which means the final cast parts come out very close to the design specifications. That reduces the need for extra machining and adjustments later on, saving time and money.
Surface Finish
Shell mold casting delivers a smooth surface finish right from the mold. This reduces the need for grinding or polishing, helping your parts look better and function well with less effort.
Reduced Post-Processing and Labor Costs
Because of the accuracy and surface finish, you spend less on post-processing steps. This cuts down labor costs and speeds up overall production time.
High Productivity
Shell molding is efficient for medium to large batch production. The molds are strong enough for repeated use but are faster to make than other precision molds, delivering higher output without sacrificing quality.
Automation Potential
This method fits well with foundry automation, which many U.S. manufacturers rely on today. Automated shell molding systems reduce manual handling and increase consistency, making it easier to scale up production with less human error.
Overall, shell molding offers a balance of precision, quality, and productivity, ideal for industries that demand reliable and cost-effective metal casting.
Disadvantages and Challenges
While shell molding offers many benefits, it comes with its downsides that are important to consider for your project.
-
Higher Resin-Coated Sand Cost
Shell mold casting relies on resin-coated sand, which is pricier than the regular sand used in traditional sand casting. This can increase overall material costs, especially for larger runs.
-
Expensive Tooling
The process needs high-quality metal patterns and precise tooling, which require a bigger upfront investment. This can make shell molding less attractive for small or one-off jobs where cost control is crucial.
-
Limited Suitability for Large or Small Batch Castings
Shell molding shines with medium to large production runs due to its repeatability and speed. However, for very small batches, the cost of tooling and material can outweigh the benefits. Similarly, very large castings might not be practical due to size limitations of the shell mold.
-
Porosity and Shrinkage Issues
Like other casting methods, shell molding can face challenges with casting porosity and shrinkage defects. Proper process control and design adjustments are needed to minimize these issues, especially when working with critical automotive or aerospace parts.
Understanding these challenges helps in deciding if shell molding fits your production needs and budget, especially when you want to balance quality with cost.
Applications of Shell Molding in Industry
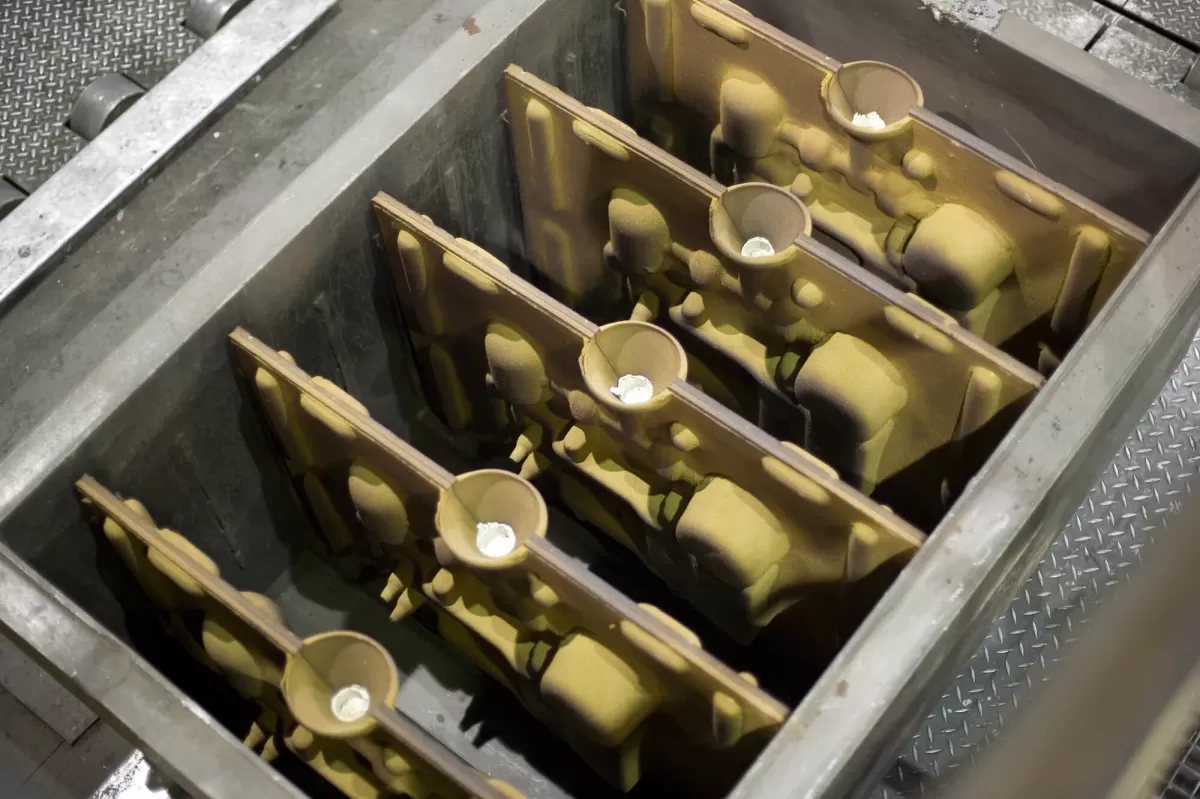

Shell molding is widely used across several industries thanks to its precision and efficiency. Here’s where it really shines:
Automotive Components
Shell mold casting is perfect for making parts like engine blocks, transmission housings, and suspension components. Its ability to deliver tight dimensional accuracy and a smooth surface finish means less machining after casting, which helps U.S. manufacturers speed up production and cut costs.
Aerospace Parts
In aerospace, where precision and lightweight designs matter, shell molding helps produce complex components with excellent strength and surface quality. This process supports the strict quality standards required for aircraft engines and structural parts.
Medical and Energy Sector Applications
Shell molding is great for medical device parts and energy sector components like turbine blades and pump housings. The fine detail and consistency the process offers are critical for reliability and performance in these fields.
Integration with CNC Machining
One big advantage for local U.S. shops is how well shell molding works with CNC machining. The cast parts come out closer to final shape, making CNC finishing faster and more precise. This integration supports custom solutions and small to mid-sized production runs, especially for industries needing both accuracy and quick turnaround.
Shell molding’s mix of precision, surface finish, and compatibility with automated machining makes it a versatile choice for U.S. manufacturers across automotive, aerospace, medical, and energy sectors.
Shell Molding vs Other Casting Methods
When choosing the right metal casting process, it helps to understand how shell molding stacks up against other popular methods.
Comparison with Sand Casting
Shell molding uses resin-coated sand and a heated pattern, which results in a thinner, stronger shell mold. This means better dimensional accuracy and a smoother surface finish compared to traditional sand casting. Sand casting tends to have rougher surfaces and less precision but can be cheaper for simple, low-volume parts. Shell molding reduces post-casting work, saving time in finishing and CNC machining.
Comparison with Investment Casting
Investment casting offers excellent precision and detail, often used for very complex parts. Shell molding is less expensive and faster for medium-complexity parts but doesn’t quite match the fine detail of investment casting. However, shell molding holds an edge in higher volume runs with quick turnaround.
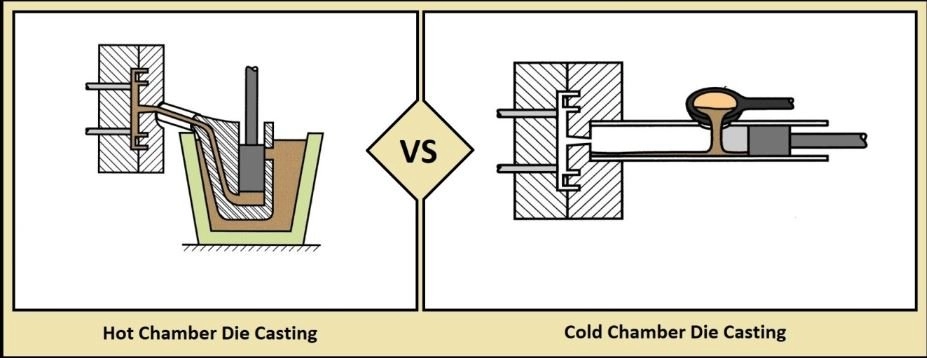
Comparison with Die Casting
Die casting uses metal molds and is great for very high-volume production with fast cycle times. Shell molding can handle metals that die casting can’t, like iron or steel, and provides more design flexibility without tooling costs as high as die casting. However, die casting often has better surface quality and thinner walls where high-volume and light metals are priorities.
In , shell molding strikes a balance between accuracy, surface quality, and cost. It’s a strong choice when you want better detail and less cleanup than sand casting but need a faster, more affordable option than investment or die casting—making it particularly useful for U.S. businesses aiming for efficient, precise metal parts production.
Why Choose Shell Molding for Your CNC Projects
Shell molding lines up well with CNC machining because it delivers parts with excellent dimensional accuracy and a smooth surface finish right out of the mold. This means less cleanup and fewer adjustments are needed before the CNC process, saving you time and effort.
Its precision makes shell mold casting ideal for producing complex shapes that fit perfectly into custom CNC workflows. You can easily integrate it into your CNC machining setup, speeding up production and ensuring parts meet tight tolerances.
From a cost perspective, shell molding reduces waste and post-processing labor. Faster mold turnaround and less finishing work help you stay on schedule and keep expenses down, especially when working on medium production runs.
If you want to learn more about how CNC and casting complement each other, check out this overview of what is CNC machining. It covers how precise casting methods like shell molding fit seamlessly into CNC projects designed for today’s manufacturing demands.