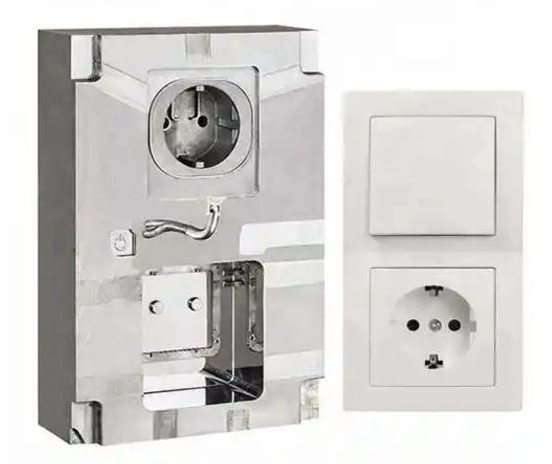
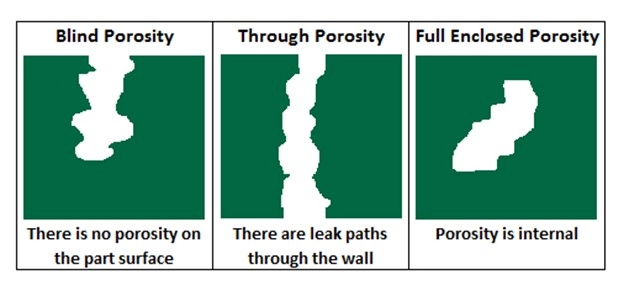
Types of Porosity in Die Casting
Porosity is a common defect in die casting that affects the quality and performance of parts. Understanding the different types of porosity helps in diagnosing issues and improving production. The three main types are gas porosity, shrinkage porosity, and micro porosity.
Gas Porosity
This occurs when gas becomes trapped in the molten metal during the die casting process. Common gases like air or hydrogen dissolve in the liquid metal and form bubbles as it solidifies. Gas porosity appears as small, round voids inside the casting, often leading to weak spots that can compromise the part’s strength.
Shrinkage Porosity
Shrinkage porosity happens due to metal solidifying unevenly. As molten metal cools and contracts, it sometimes leaves behind cavities where material has pulled away. These voids are larger and irregular in shape, usually found in thicker sections of the casting, and can cause brittleness or cracks over time.
Micro Porosity
Micro porosity is a combination of tiny, closely spaced pores distributed throughout the casting. This form is often harder to detect but can affect surface finish and mechanical properties. It typically results from a mix of gas entrapment and shrinkage during rapid cooling.
Identifying the type of porosity is essential for applying the right solutions and ensuring aluminum die casting and other alloys meet high-quality standards.
Causes of Porosity in Die Casting Process Related Factors Material Related Factors Design Related Factors

Porosity in die casting can pop up for a few main reasons tied to the process, the materials, and the design of the part.
Process Related Factors
- Improper Mold Temperature: Too hot or too cold molds can cause gas to get trapped, leading to gas porosity.
- High Injection Speed: If the molten metal flows too fast, air gets trapped inside, which causes bubbles.
- Inconsistent Pressure: Poor pressure control during solidification can create shrinkage porosity where the metal pulls away.
- Inadequate Venting: Without proper air escape routes, gases build up and form porosity defects.
Material Related Factors
- Alloy Cleanliness: Dirty or contaminated alloys carry gases and impurities that cause porosity issues.
- Moisture in Metal or Mold: Water turns to steam and causes gas porosity. It’s important to keep everything dry.
- Incorrect Alloy Composition: Some alloys are more prone to shrinkage or gas porosity if not mixed properly.
Design Related Factors
- Complex Geometries: Thin walls and sharp corners can trap air and cause uneven cooling, leading to porosity.
- Poor Gate Location: Where the metal enters affects flow and solidification—bad placement often increases gas or shrinkage porosity.
- Inadequate Runners and Vents: If the mold doesn’t allow air to escape efficiently, porosity is more likely to happen.
Understanding these causes helps us tackle porosity from every angle, improving the quality and reliability of die cast parts.
Effects of Porosity on Die Cast Parts
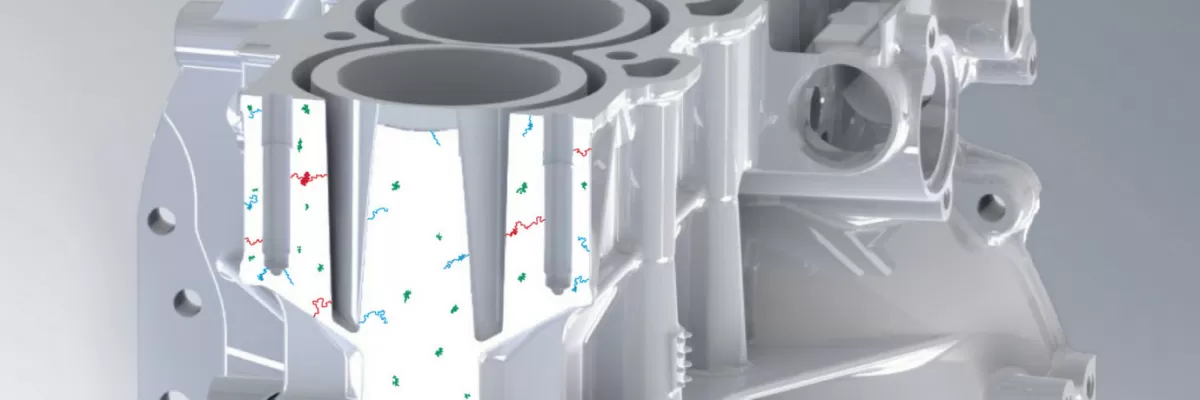
Porosity can cause several problems in die cast parts, impacting their quality and performance.
Structural Integrity
Porosity weakens the metal’s strength. Gas pockets or shrinkage voids create weak spots that can lead to cracks or failure under stress. This is a big concern, especially in critical parts where durability matters, like automotive or aerospace components.
Functional Issues
Porosity affects how parts fit and perform. Internal voids may cause leaks in fluid-containing parts or affect heat transfer in cooling systems. It can also lead to dimensional inaccuracies, causing problems in assembly or operation.
Aesthetic and Finishing Problems
Surface porosity can ruin the look and feel of a part. Visible holes or rough areas make it harder to apply finishes like paint or plating uniformly. This can increase rejection rates or require expensive rework to meet quality standards.
Managing porosity is vital to ensure your die cast parts are reliable, functional, and visually appealing. For more on how porosity links to common die casting defects, check out our guide on types of casting defects.
How to Prevent Porosity in Die Casting
Preventing porosity in die casting starts with smart planning and control. Here are key strategies to minimize die casting defects like gas porosity and shrinkage porosity.
Optimizing Mold Design
- Use proper mold design optimization to improve metal flow and cooling rates.
- Add well-placed vents and overflow areas to allow trapped gases to escape.
- Design gating and runner systems that reduce turbulence and prevent air entrapment.
- Ensure uniform wall thickness to avoid shrinkage porosity.
Check out our Aluminum Die Casting Design Guide for detailed tips on mold design.
Process Control Techniques
- Maintain consistent melting and pouring temperatures to reduce gas absorption.
- Control injection speed and pressure to avoid air pockets in the molten metal.
- Use quality dies and regularly maintain them to prevent defects from wear and damage.
- Properly dry molds and control humidity to reduce moisture-related gas porosity.
Simulation and Analysis Tools
- Use casting simulation software to predict areas prone to porosity before production starts.
- Analyze metal flow, solidification, and cooling patterns to find weak spots in design or process.
- Make adjustments based on simulation results to optimize the entire casting process.
Partnering with Experts Like HYCNC
Working with an experienced partner like HYCNC ensures better control over porosity issues. We combine our deep knowledge of die casting defect prevention with advanced CNC machining services to deliver high-quality parts with minimal porosity. Our team also uses the latest process control and simulation tools to help you get the best results from your die casting projects.
For more on die casting fundamentals, visit our guide on What is Die Casting.
Detecting and Measuring Porosity
Identifying porosity in die casting is crucial to ensure the quality and durability of the finished parts. Here are the main methods we use to detect and measure porosity:
Visual Inspection
This is the simplest way to spot porosity. You look for surface defects like tiny holes, pits, or rough patches on aluminum die casting parts. While it won’t catch internal pores, it’s quick and effective for spotting obvious issues early.
Non Destructive Testing
These methods let you check inside the casting without cutting it open. Techniques like X-ray inspection or ultrasonic testing reveal gas porosity and shrinkage porosity hidden beneath the surface. Non destructive testing is key for maintaining high standards, especially for critical parts where internal flaws can cause failure.
Destructive Testing
Sometimes, you need to break open a part to really see what’s going on inside. Destructive testing involves cutting and examining cross sections to measure micro porosity and assess alloy cleanliness directly. It’s used mostly for quality audits or when non destructive methods show something suspicious.
By combining these detection methods, you get a clear picture of porosity issues, which helps in process control and improving mold design optimization. This way, manufacturers can reduce die casting defects and deliver better, stronger parts.
Case Study HYCNCs Success in Reducing Porosity
At HYCNC, we’ve helped many clients tackle porosity in their die casting projects, improving both quality and performance. One recent example involved an aluminum die casting manufacturer struggling with high levels of gas and shrinkage porosity that affected part strength and surface finish.
We started by analyzing their mold design and casting process, identifying areas where trapped gas and uneven cooling were the main causes. By optimizing their mold design and adjusting process controls like shot speed and temperature, we significantly reduced the formation of gas pockets and shrinkage cavities.
Next, we incorporated vacuum impregnation and precision CNC machining services to address any remaining micro porosity and surface defects. This combination not only improved structural integrity but also enhanced the final appearance and dimensional accuracy.
The result? A notable drop in rejection rates and improved overall durability for the client’s die cast parts. Our approach shows how expert process control and post-casting solutions can effectively minimize porosity issues, ensuring more consistent, high-quality outcomes.
To learn more about controlling casting defects like porosity, visit our metal casting services page.
Post Casting Solutions for Porosity

Even with the best process control, some porosity can slip through. That’s where post casting solutions come in handy to improve your die cast parts.
Vacuum Impregnation
This is a go-to fix for tiny pores that cause leaks or weaken parts. Vacuum impregnation fills those tiny voids with a sealant, usually under vacuum pressure, making your parts airtight and stronger. It’s especially useful for aluminum die casting where gas porosity or shrinkage porosity can create weak spots.
Surface Treatments
Surface treatments can mask minor porosity and boost your parts’ durability:
- Coatings like anodizing or powder coating add a barrier.
- Painting improves appearance and protects against corrosion.
These treatments don’t fix the porosity itself but help with finishing and part life.
CNC Machining for Precision
Sometimes you need to remove porosity-affected areas to guarantee performance. CNC machining services can precisely cut or reshape die cast parts, ensuring critical surfaces are smooth, porosity-free, and ready for tight tolerances. This post-processing step is vital in applications where quality can’t be compromised.
Using these post casting techniques in combination can save parts from rejection and extend their usefulness. At HYCNC, we offer expert CNC machining services and support to help control porosity issues after casting, ensuring the best quality components for the U.S. market.
Best Practices for Manufacturers

To reduce porosity in die casting and improve part quality, manufacturers should focus on these best practices:
-
Optimize mold design
Make sure the mold allows smooth metal flow and proper venting to avoid gas pockets and shrinkage.
-
Maintain material cleanliness
Use high-quality alloys free from contaminants to minimize gas porosity and defects.
-
Implement strict process control
Keep injection speed, temperature, and pressure within ideal ranges for consistent results.
-
Use simulation tools
Run casting simulations early to find and fix porosity risks before production starts.
-
Perform regular non destructive testing
Catch porosity issues early with X-rays or ultrasound to prevent faulty parts reaching customers.
-
Apply vacuum impregnation post casting
Seal micro porosity and improve part durability without extensive rework.
-
Partner with experienced CNC and casting experts
Work with professionals, like HYCNC, who understand die casting porosity and offer tailored CNC machining services for precision finishing.
Following these steps helps manufacturers deliver stronger, better-looking die cast parts that meet US market standards and customer expectations.
FAQs about Porosity in Die Casting
What is porosity in die casting?
Porosity refers to tiny holes or voids in a die cast part. These can weaken the part and cause problems with strength, appearance, or function.
What causes porosity in die cast parts?
Porosity usually comes from trapped gas (gas porosity), metal shrinkage during cooling (shrinkage porosity), or tiny pores from rapid solidification (micro porosity). Factors like mold design, casting process control, and clean alloys all play a role.
How can I detect porosity in die cast parts?
Common methods include visual inspection, non destructive testing (NDT) like X-ray or ultrasonic tests, and sometimes destructive testing if necessary.
Can porosity be prevented?
Yes. Optimizing mold design, maintaining proper process controls, using simulation tools, and making sure the alloy is clean helps reduce porosity. Partnering with experienced die casting services such as HYCNC ensures quality parts.
Does porosity affect the strength of die cast parts?
Yes, porosity weakens the structural integrity, reduces fatigue resistance, and can cause leaks or cracks.
What post casting processes fix porosity?
Vacuum impregnation seals pores, surface treatments improve finish, and CNC machining can remove defective areas to restore part quality.
Is porosity common in aluminum die casting?
Yes, aluminum die casting often faces porosity issues due to alloy characteristics and cooling rates, but proper controls minimize its impact.
Where can I learn more about die casting defects and solutions?
Visit HYCNC’s blog for detailed guides on die casting and related defects to help improve your casting outcomes.
If you have more questions about porosity or die casting in general, feel free to reach out. We’re here to help you get the best quality parts possible.