Are you struggling to design aluminum die casting parts that balance quality, cost, and manufacturability? Crafting the perfect die-cast aluminum part can transform your project’s success, ensuring precision and durability.
As a leader in CNC and die casting services, HYCNC understands the challenges of creating optimized designs. With years of industry expertise, we’re sharing proven strategies to simplify your process.
In this aluminum die casting design guide, you’ll discover essential tips, from wall thickness optimization to draft angles, to create high-quality parts that perform. Ready to elevate your designs? Let’s dive in!
Understanding Aluminum Die Casting
What is Aluminum Die Casting
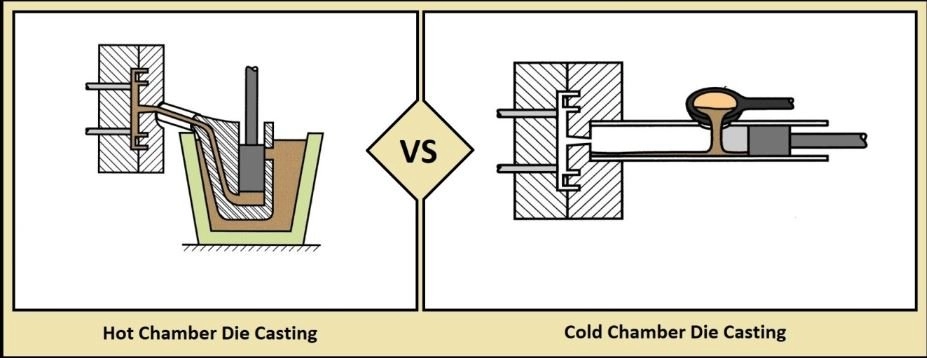
Wondering what aluminum die casting really means? It’s a manufacturing process where molten aluminum is injected under high pressure into a steel mold, or die. This method produces precise, complex parts with excellent surface finish and tight tolerances. The process is fast, repeatable, and ideal for high-volume production runs.
Benefits of Aluminum for Die Casting
Why choose aluminum for die casting? Aluminum stands out because it’s lightweight yet strong, making it perfect for durable parts that don’t weigh you down. It offers great corrosion resistance and excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. Plus, aluminum’s ability to flow smoothly during casting helps produce parts with intricate details. Using aluminum also supports sustainability goals since it’s highly recyclable.
Applications Across Industries
Where does aluminum die casting shine? You’ll find its use across many sectors:
- Automotive: Engine components, transmission parts, and housing units benefit from aluminum’s strength-to-weight advantage.
- Aerospace: Lightweight structural parts and brackets rely on aluminum’s durability.
- Electronics: Heat sinks and enclosures are often die cast from aluminum for better thermal management.
- Consumer Goods: Durable housings, appliance parts, and sporting equipment.
- Industrial: Machinery components and valve bodies take advantage of aluminum’s corrosion resistance.
Aluminum die casting offers a winning combination of precision, strength, and cost-effectiveness, making it a go-to choice for manufacturers across the board. For a deeper dive into die casting basics, check out our What is Die Casting article.
Key Design Considerations for Aluminum Die Casting
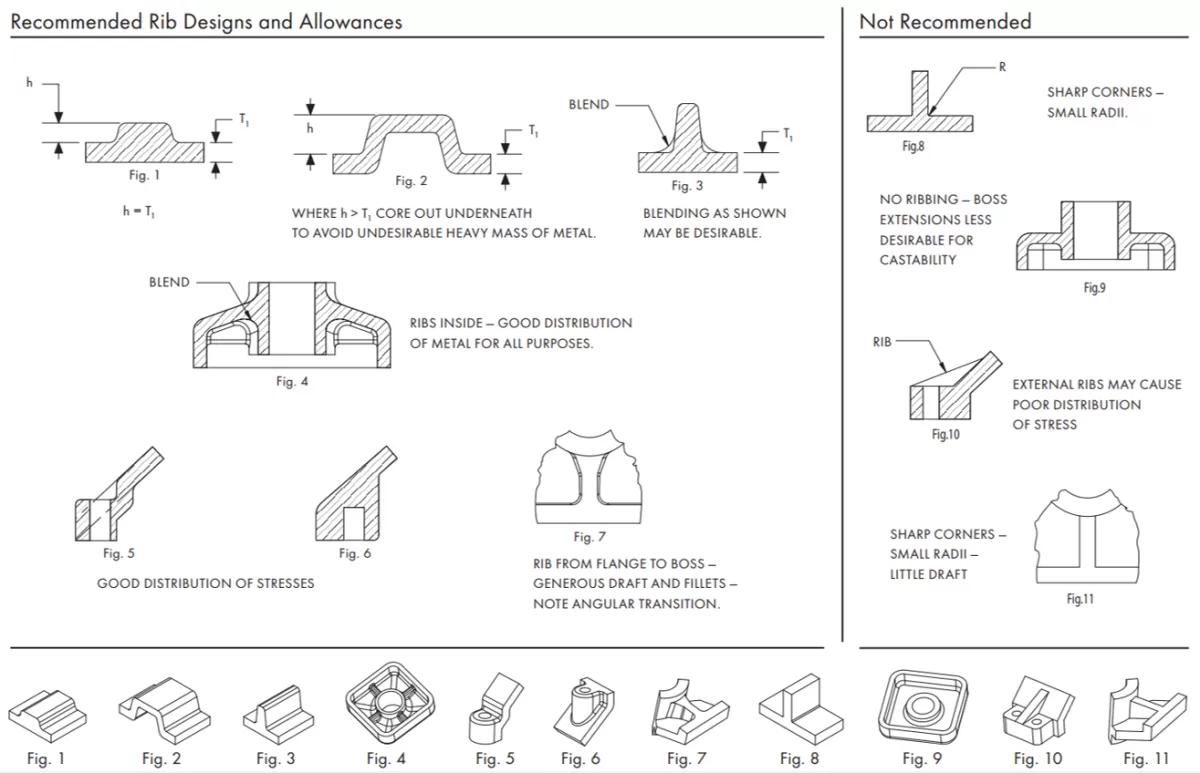
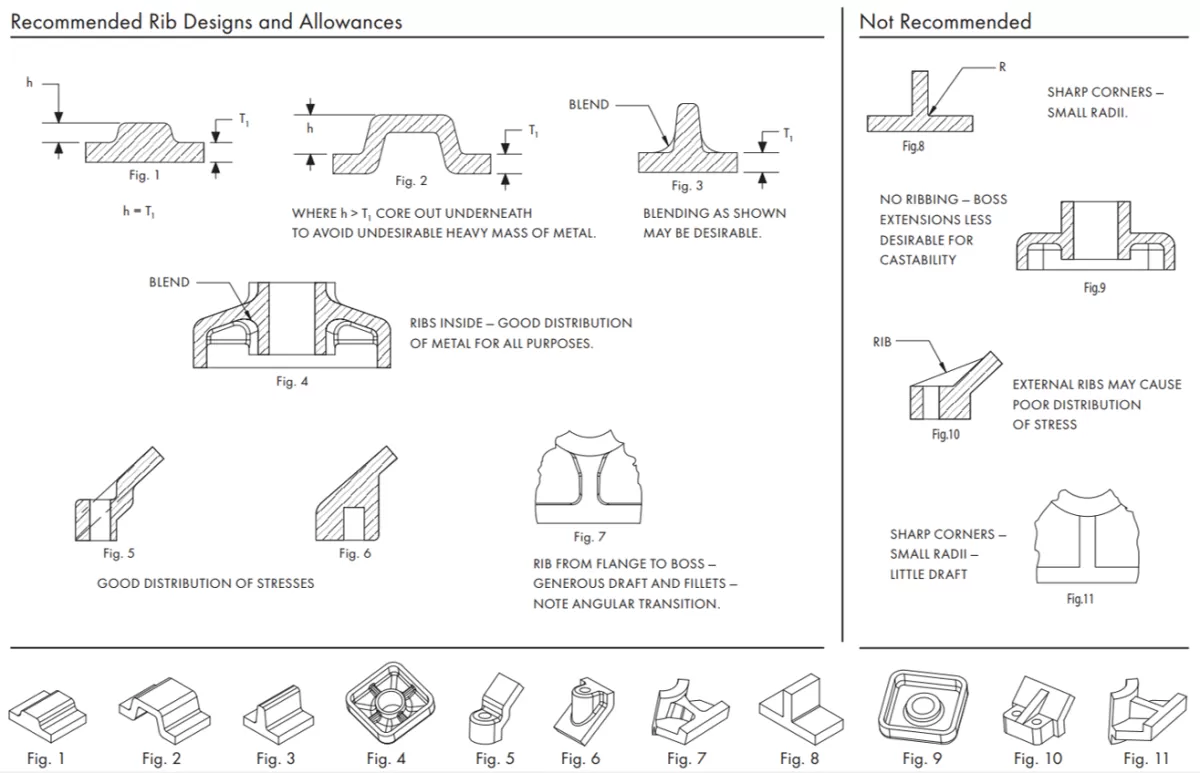
When designing for aluminum die casting, keeping key factors in mind can make your parts stronger, easier to produce, and more cost-effective. Here’s what matters most:
Wall Thickness Optimization
Consistent wall thickness is crucial. Aim for uniform walls to avoid shrinkage and warping during cooling. Typically, a thickness range of 0.04 to 0.12 inches works well, but thinner walls can save material if designed carefully. Avoid sudden thickness changes to reduce internal stresses and die wear.
Draft Angles for Easy Ejection
Include draft angles on vertical walls—usually around 1 to 3 degrees—to help parts release smoothly from the die. Without proper draft, parts can stick, causing damage or defects. The right draft angles also speed up production and reduce scrap rates.
Fillets and Radii for Strength and Flow
Sharp corners are weak spots and tough on molten aluminum flow. Adding fillets and radii smooths the flow inside the mold and strengthens the part by distributing stress more evenly. A radius of at least 0.5 times the wall thickness often works well.
Ribs and Coring for Structural Integrity
If you need extra strength without adding bulk, use ribs and coring. Ribs add stiffness and support while keeping weight down, and coring helps maintain wall thickness in complex shapes. Design ribs to be about 0.5 to 0.6 times the wall thickness with a proper draft.
Avoiding Undercuts
Undercuts increase tooling complexity and cost because they require side actions or more slides in the die. Whenever possible, design parts that can be ejected without undercuts to keep the process simpler and the price competitive. If needed, plan for them early with your manufacturer.
Alloy Selection
Choosing the right aluminum alloy affects performance and manufacturability. Common alloys like A380 and 535 aluminum offer a good balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and flow characteristics. Consider your application’s mechanical requirements and surface finish needs when picking an alloy.
For more detailed tips on aluminum die casting design and manufacturing, check out our guide on designing for die casting services.
Design for Manufacturing Best Practices
Importance of DFM in Die Casting
Design for manufacturing (DFM) is key when working with aluminum die casting. It means designing your parts so they’re easier, faster, and cheaper to produce without sacrificing quality. Keeping DFM in mind helps avoid common issues like defects, longer production times, and costly adjustments down the road. When you design with the die casting process in mind, you ensure the final part meets performance needs while staying cost-effective.
Minimizing Porosity and Defects
Porosity and defects are big concerns in aluminum die casting. Porosity happens when air or gas gets trapped inside the metal, weakening the part and affecting surface finish. To cut down on this:
- Use consistent wall thickness to promote smooth metal flow
- Include proper venting in the mold
- Choose the right aluminum alloy for your part’s needs
- Work with manufacturers who control casting parameters tightly
Addressing these during design helps reduce scrap rates and improves overall part reliability.
Surface Finishing Considerations
Surface finish can make or break your part’s look and performance. Aluminum parts from die casting often need extra finishing to meet aesthetic or functional requirements. Common surface finishing options include:
- Powder coating or painting for corrosion resistance
- Polishing or buffing for a smooth finish
- Anodizing to enhance durability and appearance
Design your part with finishing in mind, like adding draft angles and avoiding hard-to-reach spots, to make post-casting finishing easier and less costly.
Common Design Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When working on an aluminum die casting design, avoiding common mistakes can save time and cost while improving quality. Here are some key pitfalls and how to dodge them:
Uneven Wall Thickness
- Causes warping, shrinkage, and weak spots.
- Keep walls consistent to ensure smooth metal flow and solid parts.
Insufficient Draft Angles
- Makes ejection from the die tougher, increasing wear and defects.
- Use proper draft angles, typically 1 to 3 degrees, to help parts release easily.
Overlooking Alloy Properties
- Different aluminum alloys behave differently under heat and pressure.
- Choose the right alloy for your part’s strength, weight, and corrosion resistance needs.
Neglecting Post-Casting Machining
- Not planning for machining can lead to issues with tolerances and surface finishes.
- Design with machining steps in mind to avoid costly rework and delays.
Keeping these points in check smooths out the aluminum die casting process and leads to better, more reliable results.
Tools and Resources for Effective Design
CAD File Preparation
A good aluminum die casting design starts with clear, detailed CAD files. These files need to show precise dimensions, draft angles, and wall thicknesses to avoid confusion during the die casting process. Using standardized formats makes it easier for manufacturers to review and work with your design. Double-check your CAD model for any features that could cause casting defects or require complex machining later.
Collaboration with Manufacturers
Working closely with your die casting manufacturer is key to a successful project. Sharing your design early helps catch potential issues like undercuts or uneven walls that might cause defects. Manufacturers can suggest tweaks to improve manufacturability and reduce costs. Regular feedback loops ensure your part meets performance needs while staying efficient to produce.
Free Resources from HYCNC
HYCNC offers free resources to help you navigate aluminum die casting design. From design guides to tips on alloy selection and surface finishing, their materials are tailored to support US-based businesses looking for precision die casting and CNC machining services. Taking advantage of these tools can streamline your design process and help you avoid common pitfalls.
Using the right tools and maintaining open communication with your manufacturer can make all the difference in getting a strong, high-quality aluminum die cast part.
Case Study HYCNC’s Success in Aluminum Die Casting
At HYCNC, we’ve built a solid reputation for precision aluminum die casting and CNC machining services tailored to the U.S. market. Our focus on design for manufacturing (DFM) ensures parts are made right the first time, minimizing defects like porosity and uneven wall thickness.
Here’s how we deliver success:
-
Collaborative Design Process
We work closely with clients from the start, reviewing CAD files and offering practical advice on draft angles, fillets, and rib design to optimize the aluminum die casting process.
-
Optimized Alloy Selection
Our team guides you on choosing the best aluminum alloys for strength, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness, matching your product’s industry needs.
-
Minimized Defects and Faster Turnaround
By applying strict quality checks and using advanced CNC machining post-casting, we reduce defects and speed up production—helping you meet tight deadlines.
-
Surface Finishing Options
We provide expert surface finishing to enhance durability and appearance, critical for automotive, aerospace, and consumer product applications.
Our local customer base in the U.S. has benefited from this tailored approach, enjoying consistent quality and competitive lead times. Partnering with HYCNC means you get reliable, precision aluminum die casting solutions designed with your manufacturing goals in mind.