Understanding Cast Aluminum
What Is Cast Aluminum
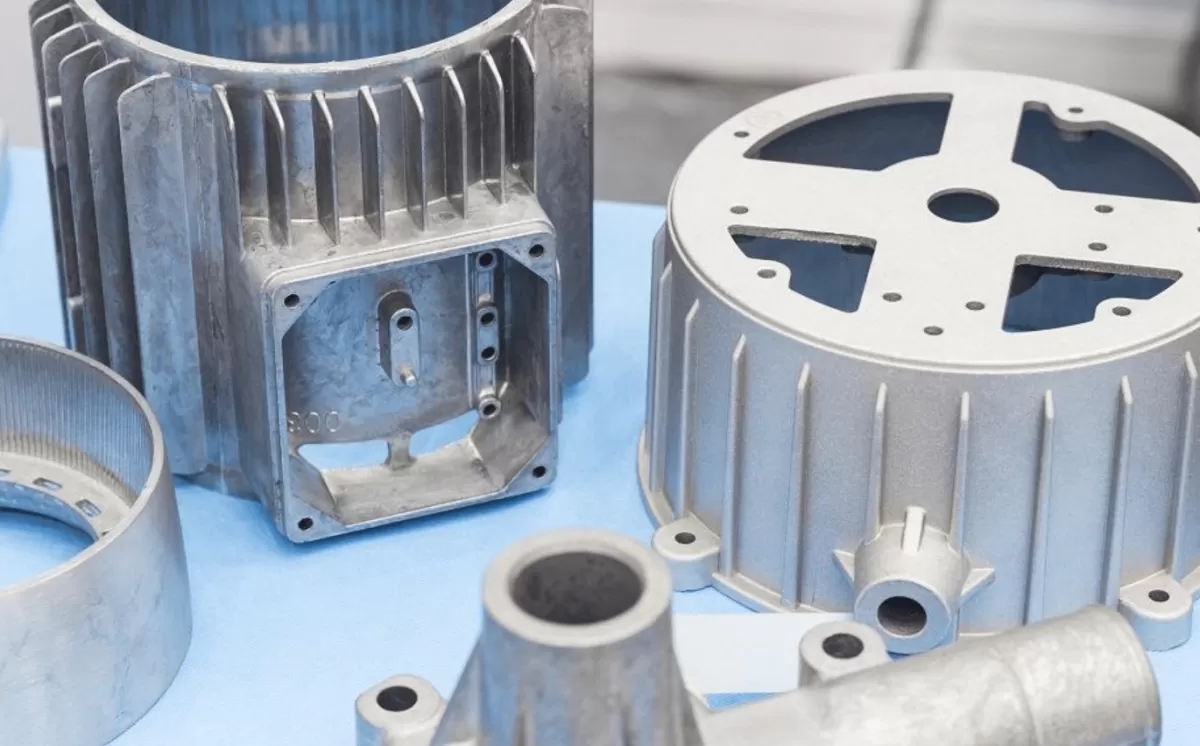
Cast aluminum is produced by pouring molten aluminum into a mold where it solidifies into the desired shape. This aluminum casting process allows for the creation of complex and intricate designs that might be difficult or costly to achieve with other manufacturing methods. Once cooled, the cast aluminum part is removed from the mold and can undergo further machining or finishing processes as needed.
Advantages of Cast Aluminum
- Cost-effective production: Casting is often more affordable for large volumes and complex shapes.
- Versatility in design: Allows for detailed features and complex geometries.
- Good corrosion resistance: Aluminum naturally resists oxidation, making cast parts durable in many environments.
- Lightweight properties: Compared to steel, cast aluminum provides strong components with reduced weight.
Disadvantages of Cast Aluminum
- Lower mechanical strength: Cast aluminum tends to have less tensile strength compared to forged aluminum.
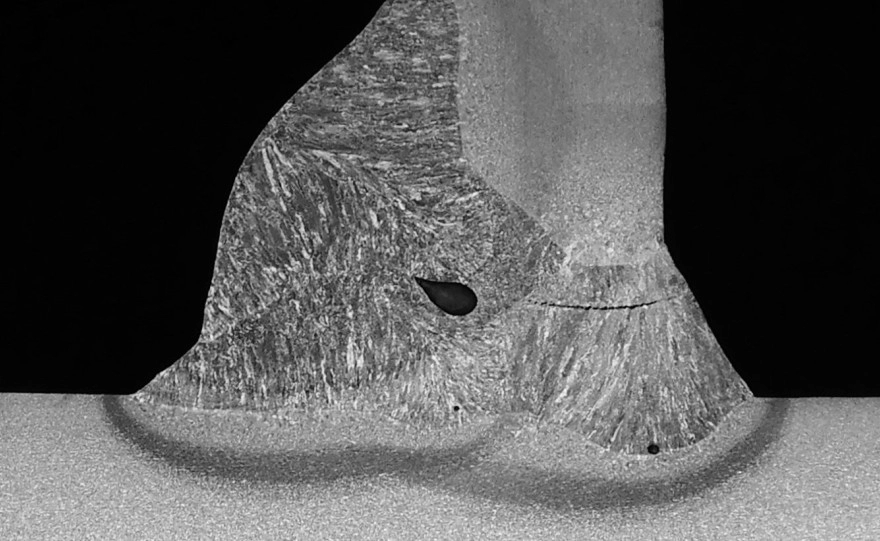
- Porosity issues: Casting defects like porosity can occur if not carefully controlled, affecting part integrity.
- Brittleness: Cast parts can be more brittle, making them less suitable for high-impact applications.
- Machining limitations: Sometimes cast aluminum requires additional machining to meet tight tolerances, increasing cost.
Applications of Cast Aluminum
Cast aluminum is widely used in automotive parts like engine blocks and housings due to its ability to form complex shapes. It’s also common in aerospace components, consumer electronics housings, and industrial machinery. Thanks to its cost-effective production and versatility, cast aluminum fits applications where moderate strength and detailed design are required.
For more on the aluminum casting process and how it compares to other methods, check out our detailed guide on metal casting.
Understanding Forged Aluminum

What Is Forged Aluminum
Forged aluminum is made by shaping a solid piece of aluminum under high pressure, often using a hammer or press. This process compresses the metal, aligning its grain structure and making it denser and stronger than other manufacturing methods. It’s a well-known aluminum manufacturing method favored when strength and durability are top priorities.
Advantages of Forged Aluminum
- High strength and durability: The forging process enhances the metal’s grain flow, making it tougher and more resistant to impact.
- Improved fatigue resistance: Ideal for parts that undergo stress or repeated loading, like automotive or aerospace components.
- Better structural integrity: Forged aluminum parts have fewer internal voids or defects, resulting in higher quality.
- Precision: The process allows for tighter tolerances and better mechanical properties, perfect for high-strength aluminum components.
Disadvantages of Forged Aluminum
- Higher cost: Forging requires more energy and tooling, so it tends to be more expensive than casting.
- Limited complexity: It’s harder to produce highly complex shapes compared to cast aluminum.
- Longer lead times: The forging process and tooling setup can take longer, impacting delivery schedules.
Applications of Forged Aluminum
Forged aluminum is commonly used where strength and reliability are crucial, including:
- Automotive parts like crankshafts, connecting rods, and wheels
- Aerospace components requiring lightweight strength
- High-performance bike frames and sporting goods
- Industrial machinery parts that demand toughness and durability
If you want to explore more about aluminum manufacturing methods, check out our insights on metal casting and how CNC machining plays a role in working with both cast and forged aluminum.
Key Differences Between Cast Aluminum and Forged Aluminum
Understanding the difference between cast aluminum vs forged aluminum helps you pick the right material for your project. Both have unique manufacturing methods, strengths, and weaknesses. Here’s a clear comparison and detailed analysis.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Cast Aluminum | Forged Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Aluminum is melted and poured into molds | Aluminum billet is shaped under high pressure |
| Strength | Good, but can have internal porosity or weak spots | Very high strength and durability due to grain alignment |
| Weight | Slightly heavier due to porosity | Lighter and denser |
| Cost | More cost-effective for complex shapes | Generally more expensive due to processing time |
| Surface Finish | May require extra machining for smoothness | Better surface finish with less machining |
| Durability | Suitable for moderate stress applications | Ideal for high-stress parts needing toughness |
| Typical Applications | Engine blocks, housings, decorative parts | Aircraft components, bike frames, high-performance parts |
Detailed Analysis
-
Manufacturing: Cast aluminum uses the aluminum casting process where molten metal is poured into molds, making it easier to produce complex shapes and large parts cost-effectively. Forged aluminum is created by compressing solid aluminum billets, aligning the grain structure for greater strength.
-
Strength and Durability: Forged aluminum offers better mechanical properties thanks to fine, aligned grain structures which improve strength and fatigue resistance. Cast aluminum parts can have tiny air pockets (porosity) that make them weaker under high stress.
-
Weight and Machining: Forged parts are denser and often lighter, which benefits performance-focused projects. Cast parts might need extra precision CNC machining aluminum services to refine surface finish and remove casting marks.
-
Cost and Applications: Cast aluminum is generally cheaper, favored for items where detailed shapes and moderate strength are enough. Forged aluminum is pricier but preferred when parts must handle heavy loads, such as in aerospace or automotive components.
Knowing these key differences ensures you pick the right aluminum manufacturing method for durability, cost, and strength—essential for local U.S. projects where reliability and cost-efficiency matter.
How to Choose Between Cast and Forged Aluminum for Your Project
Picking between cast aluminum and forged aluminum depends on what your project really needs. Here are some key factors to think about:
Factors to Consider
-
Strength and Durability
Forged aluminum offers higher strength and better fatigue resistance. If your project requires tough, high-strength parts that won’t bend or crack easily, forged is usually the way to go. Cast aluminum works fine for less demanding uses but can be more brittle.
-
Complexity of Shape
Cast aluminum shines when you need detailed shapes or complex designs since the aluminum is poured into molds. Forging is better for simpler, solid components where strength is the priority.
-
Production Volume and Cost
For larger production runs, casting is often more cost-effective because molds can be reused and the process is faster. Forging can be more expensive upfront but may save money in the long run if strength and durability reduce replacement costs.
-
Machining and Finishing
Forged aluminum typically machines better, giving a cleaner finish and tighter tolerances in CNC machining. Cast aluminum may require more polishing and finishing work.
-
Weight Considerations
Both methods produce lightweight parts, but forged aluminum often has a better strength-to-weight ratio, ideal for applications like automotive or aerospace components.
Case Studies
-
Automotive Industry
Forged aluminum is commonly used for critical components like wheels, connecting rods, and chassis parts that need to withstand heavy stress. Cast aluminum is preferred for engine blocks and housings due to its shape flexibility and cost benefits.
-
Consumer Electronics
Cast aluminum is popular in enclosures and housings where complex shapes and aesthetic finishes matter more than ultra-high strength.
Decision-Making Tips
- Assess the part’s load requirements and operating environment.
- Consider your budget and production volume.
- Think about how complex the design is.
- Don’t forget post-production processes like machining and finishing.
- When in doubt, consult with a trusted CNC shop like HYCNC to guide you through the best aluminum manufacturing methods tailored to your project.
Choosing the right aluminum method upfront saves time, money, and headaches down the road. For more details on how casting compares to CNC machining aluminum, check out our post on CNC vs Cast.
Why Choose HYCNC for Your Aluminum CNC Machining Needs
When it comes to aluminum CNC machining, whether you need cast aluminum or forged aluminum parts, HYCNC has you covered. Our team knows the ins and outs of both aluminum manufacturing methods, so we deliver parts that meet your exact specs and quality standards.
Expertise in Both Cast and Forged Aluminum
We understand the unique properties of cast aluminum and forged aluminum. This knowledge allows us to optimize the aluminum casting process and forging techniques for your project. From high-strength aluminum components to cost-effective aluminum production, we tailor our approach to get the best results for your specific application.
Custom Solutions
Every project is different, and at HYCNC, we offer precision CNC machining aluminum services customized to your needs. Whether you need complex shapes from forged aluminum or intricate designs from cast aluminum, our CNC service team works closely with you to create parts that fit your goals perfectly.
Quality Assurance
Quality matters, especially in industries like automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing where durability is key. We have strict quality control measures in place to ensure each aluminum part meets the highest standards for strength and consistency. You can trust HYCNC for reliable, long-lasting aluminum alloy applications.
Get Started Today
Ready to get the right aluminum parts for your project? Contact HYCNC and let’s discuss how our custom CNC machining and aluminum manufacturing methods can work for you. We’re here to provide expert advice and top-quality results for your next aluminum component.
FAQs
What is the main difference between cast aluminum and forged aluminum?
Cast aluminum is made by pouring molten aluminum into molds, while forged aluminum is shaped under high pressure to create a denser, stronger material.
Which is stronger, cast aluminum or forged aluminum?
Forged aluminum is generally stronger and more durable due to its tighter grain structure and fewer internal defects.
Is cast aluminum good for CNC machining?
Yes, cast aluminum works well with CNC machining and is often used for complex shapes and cost-effective production.
Can I use forged aluminum for high-strength components?
Absolutely. Forged aluminum is preferred for parts that need high strength and toughness, like automotive and aerospace components.
Which aluminum material is more cost-effective?
Cast aluminum typically costs less because its manufacturing process is simpler and allows for mass production.
Are there applications where cast aluminum is better than forged aluminum?
Yes, cast aluminum suits parts with intricate designs and where weight isn’t the main factor. It’s common in housings and heat exchangers.
How does CNC machining differ for cast vs forged aluminum?
Cast aluminum is easier to machine due to its lower density, while forged aluminum might require tougher cutting tools because of its strength.
Can HYCNC machine both cast and forged aluminum parts?
Yes. We specialize in precision CNC machining for both cast and forged aluminum, offering customized solutions to fit your needs.
How do I decide which aluminum type to use for my project?
Consider strength needs, design complexity, budget, and production volume. We’re here to help with expert advice whenever you need it.